An IDE (Integrated Development Environment) simplifies coding by combining editing, debugging, and build automation tools in a single platform, boosting your productivity. Build automation tools streamline repetitive tasks like compiling code, packaging, and testing, ensuring consistent and error-free software delivery. Explore the rest of this article to discover how integrating these tools can transform your development workflow.
Table of Comparison
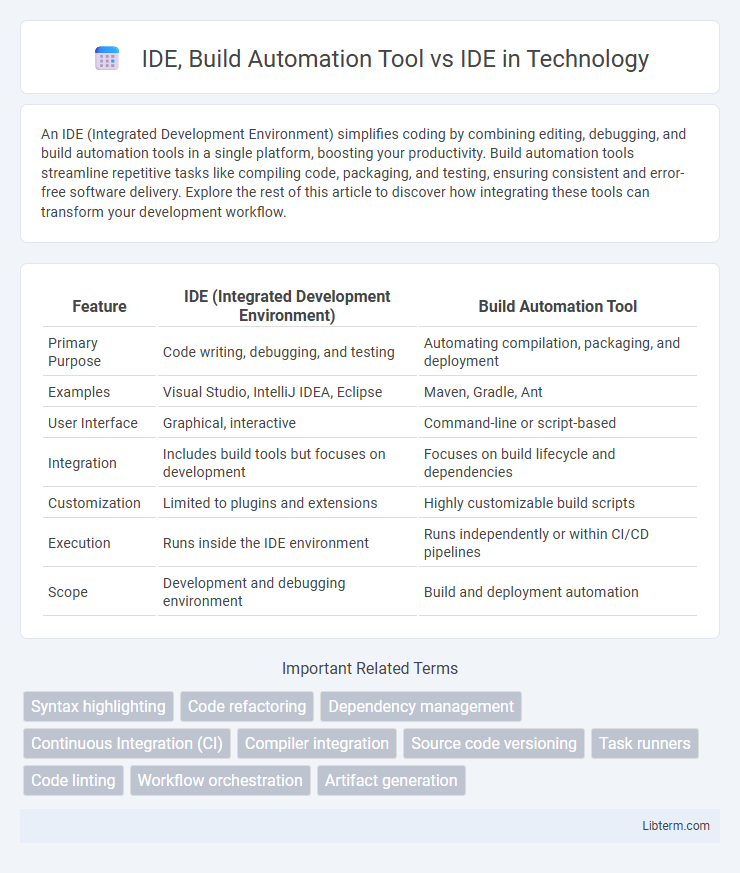
| Feature | IDE (Integrated Development Environment) | Build Automation Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Code writing, debugging, and testing | Automating compilation, packaging, and deployment |
| Examples | Visual Studio, IntelliJ IDEA, Eclipse | Maven, Gradle, Ant |
| User Interface | Graphical, interactive | Command-line or script-based |
| Integration | Includes build tools but focuses on development | Focuses on build lifecycle and dependencies |
| Customization | Limited to plugins and extensions | Highly customizable build scripts |
| Execution | Runs inside the IDE environment | Runs independently or within CI/CD pipelines |
| Scope | Development and debugging environment | Build and deployment automation |
Introduction to IDEs and Build Automation Tools
IDEs (Integrated Development Environments) streamline software development by combining code editing, debugging, and testing into a single interface, enhancing developer productivity. Build automation tools automate repetitive tasks such as compiling source code, packaging binaries, and running tests, enabling consistent and efficient build processes. While IDEs offer comprehensive environments for writing and managing code, build automation tools focus specifically on simplifying and accelerating the process of compiling and deploying software projects.
What is an Integrated Development Environment (IDE)?
An Integrated Development Environment (IDE) is a software application providing comprehensive facilities for software development, including a source code editor, debugger, and build automation tools within a single interface. IDEs enhance developer productivity by integrating essential programming tools such as syntax highlighting, code completion, and version control support. Unlike standalone build automation tools that focus solely on compiling and managing builds, IDEs offer a complete environment to write, test, and debug code efficiently.
Key Features of Modern IDEs
Modern IDEs integrate comprehensive code editing, debugging, and intelligent code completion to streamline software development. Build automation tools focus on compiling, testing, and deploying code automatically, enhancing efficiency in the build process. Key features of modern IDEs include real-time error detection, version control integration, and support for multiple programming languages, enabling seamless development workflows.
What is a Build Automation Tool?
A Build Automation Tool automates the process of compiling source code into executable programs, managing dependencies, running tests, and deploying applications, significantly enhancing development efficiency. Unlike an Integrated Development Environment (IDE), which provides a comprehensive interface for coding, debugging, and project management, build automation tools focus specifically on automating repetitive tasks within the software build lifecycle. Popular build automation tools like Maven, Gradle, and Ant streamline continuous integration and delivery workflows by ensuring consistent, error-free builds.
Core Functions of Build Automation Tools
Build automation tools specialize in compiling source code, managing dependencies, and deploying applications efficiently, reducing manual tasks and error rates during software development. Unlike integrated development environments (IDEs), which focus on code writing, debugging, and project navigation, build tools execute repetitive processes such as testing, packaging, and version control integration through automated scripts. Core functions of build automation tools include continuous integration support, task orchestration, and environment configuration, streamlining the development lifecycle and enhancing productivity.
IDE vs Build Automation Tool: Fundamental Differences
An Integrated Development Environment (IDE) provides a comprehensive interface for coding, debugging, and testing software, integrating tools like code editors, compilers, and debuggers in one application. A build automation tool, such as Maven or Gradle, specializes in automating the process of compiling, linking, and packaging code, managing dependencies and build scripts without a graphical user interface. The fundamental difference lies in functionality: IDEs support interactive development workflows, whereas build automation tools focus on streamlining and automating the build lifecycle often within continuous integration pipelines.
When to Use an IDE Over a Build Automation Tool
Choose an IDE when you need an integrated environment for writing, debugging, and testing code with real-time feedback and visual tools. IDEs excel in managing project files, code completion, syntax highlighting, and quick error detection, making them ideal for individual developers or small teams during active development phases. Build automation tools are better suited for automating repetitive tasks like compiling, testing, and deployment, but they lack the interactive coding features central to an IDE experience.
Advantages and Limitations of Build Automation Tools
Build automation tools streamline the software development process by automating tasks such as compiling code, running tests, and packaging applications, which enhances consistency and efficiency across projects. These tools integrate seamlessly with various IDEs, supporting continuous integration and deployment workflows, but they can introduce complexity requiring developers to learn specific scripting languages or configuration formats. Despite their advantages in reducing manual errors and speeding up builds, limitations include potential difficulties in customization and slower build times for large-scale projects if not properly optimized.
Combining IDEs with Build Automation Tools for Efficient Development
Combining IDEs like Visual Studio Code or IntelliJ IDEA with build automation tools such as Maven, Gradle, or Jenkins enhances development efficiency by streamlining code compilation, testing, and deployment processes. This integration enables real-time error detection, automated dependency management, and continuous integration workflows directly within the coding environment, reducing manual intervention. Developers benefit from cohesive toolchains that improve productivity, ensure build consistency, and accelerate project delivery timelines.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Development Workflow
Build automation tools streamline compiling, testing, and deployment processes, enhancing efficiency by automating repetitive tasks within development workflows. Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) offer comprehensive code editing, debugging, and version control features, centralizing development activities in a single application. Selecting the right tool depends on project complexity, team collaboration needs, and the balance between automation and integrated development features to optimize productivity and maintainability.
IDE, Build Automation Tool Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com