Dynamic environments require adaptability and continuous innovation to thrive in ever-changing markets. By embracing flexibility and proactive strategies, your business can respond swiftly to new opportunities and challenges. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective approaches for maintaining a dynamic edge.
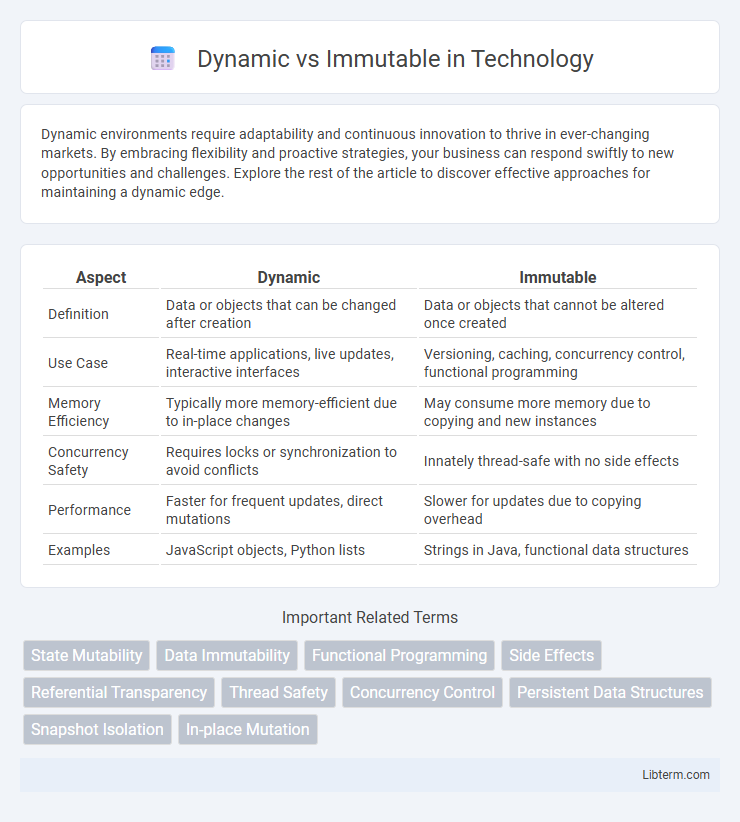
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Dynamic | Immutable |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data or objects that can be changed after creation | Data or objects that cannot be altered once created |
| Use Case | Real-time applications, live updates, interactive interfaces | Versioning, caching, concurrency control, functional programming |
| Memory Efficiency | Typically more memory-efficient due to in-place changes | May consume more memory due to copying and new instances |
| Concurrency Safety | Requires locks or synchronization to avoid conflicts | Innately thread-safe with no side effects |
| Performance | Faster for frequent updates, direct mutations | Slower for updates due to copying overhead |
| Examples | JavaScript objects, Python lists | Strings in Java, functional data structures |
Introduction to Dynamic and Immutable Concepts
Dynamic data structures allow modification after creation, enabling flexibility with changing information. Immutable objects, once created, cannot be altered, ensuring consistency and thread safety in software applications. Understanding the distinction between dynamic and immutable types is crucial for efficient memory management and designing reliable systems.
Understanding Dynamic Systems
Dynamic systems are characterized by continuous change and adaptability, allowing components to evolve and respond to varying conditions in real-time. These systems rely on feedback loops and interactions between variables to achieve equilibrium or develop complex behaviors over time. Understanding dynamic systems involves analyzing their non-linear processes, emergent properties, and sensitivity to initial conditions to predict and manage system performance effectively.
What Does Immutable Mean?
Immutable refers to data or objects that cannot be altered once created, ensuring consistent state throughout program execution. In programming, immutable structures prevent side effects and enhance thread safety by disallowing modifications after initialization. This contrasts with dynamic entities, which allow changes and offer flexibility but can introduce unpredictability and errors.
Key Differences: Dynamic vs Immutable
Dynamic data structures allow modification after creation, enabling changes in size or content, while immutable data structures remain constant once defined, preventing any alterations. Performance and safety diverge, as dynamic types offer flexibility and ease of use, but may introduce bugs or side effects, whereas immutable types enhance reliability and thread safety at the cost of increased memory use due to copying. Common examples include dynamic arrays and strings versus immutable tuples and frozen sets in languages like Python, highlighting distinct use cases based on mutability requirements.
Real-World Examples of Dynamic Approaches
Dynamic approaches in software development, such as dynamic typing in languages like Python and JavaScript, enable rapid prototyping and flexibility in real-world applications like web development and data analysis. Platforms like Node.js leverage dynamic techniques to handle asynchronous events efficiently, supporting scalable network applications. In contrast, dynamic content management systems (CMS) such as WordPress allow users to update website content in real time without redeployment, demonstrating practical benefits of dynamism in user experience and operational agility.
Real-World Applications of Immutability
Immutability is widely applied in real-world software development to ensure data consistency and enhance security, especially in blockchain technology where transaction records must remain unaltered. In functional programming, immutable data structures prevent side effects, enabling easier debugging and parallel processing. Enterprise applications leverage immutability to maintain audit trails and improve cache efficiency, resulting in more reliable and performant systems.
Advantages of Dynamic Structures
Dynamic data structures offer significant advantages such as flexible memory usage that adapts to changing data sizes, leading to efficient utilization of system resources. They enable easy insertion and deletion operations without the need for predefining the data size, which enhances performance in applications with unpredictable or variable data sets. This flexibility makes dynamic structures ideal for complex algorithms and real-time processing where data requirements frequently change.
Benefits of Immutable Systems
Immutable systems offer enhanced security by preventing unauthorized changes, ensuring data integrity and auditability. They enable reliable system recovery and rollback, reducing downtime and operational risks. These systems also simplify compliance with regulatory standards by providing consistent and verifiable states over time.
Choosing Between Dynamic and Immutable
Choosing between dynamic and immutable data structures depends on the specific use case and performance requirements. Dynamic structures offer flexibility and ease of modification, ideal for scenarios with frequent updates or varying data. Immutable structures enhance safety, predictability, and enable efficient sharing, making them suitable for concurrent programming and functional paradigms.
Future Trends in Dynamic and Immutable Design
Dynamic design, characterized by flexibility and real-time adaptability, is increasingly integrated with machine learning and AI to enable responsive user experiences in evolving digital environments. Immutable design, emphasizing data integrity and security, gains traction through blockchain technology and decentralized systems, ensuring tamper-proof records and trustless interactions. Future trends indicate a hybrid approach combining dynamic adaptability with immutable audit trails to balance innovation with reliability in software development and data management.
Dynamic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com