Heterogeneous clusters combine different types of hardware or nodes to enhance computing power, efficiency, and flexibility in various applications. These clusters optimize performance by leveraging the unique strengths of each component, making them ideal for diverse workloads and scalable solutions. Discover how leveraging a heterogeneous cluster can transform your system's capabilities in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
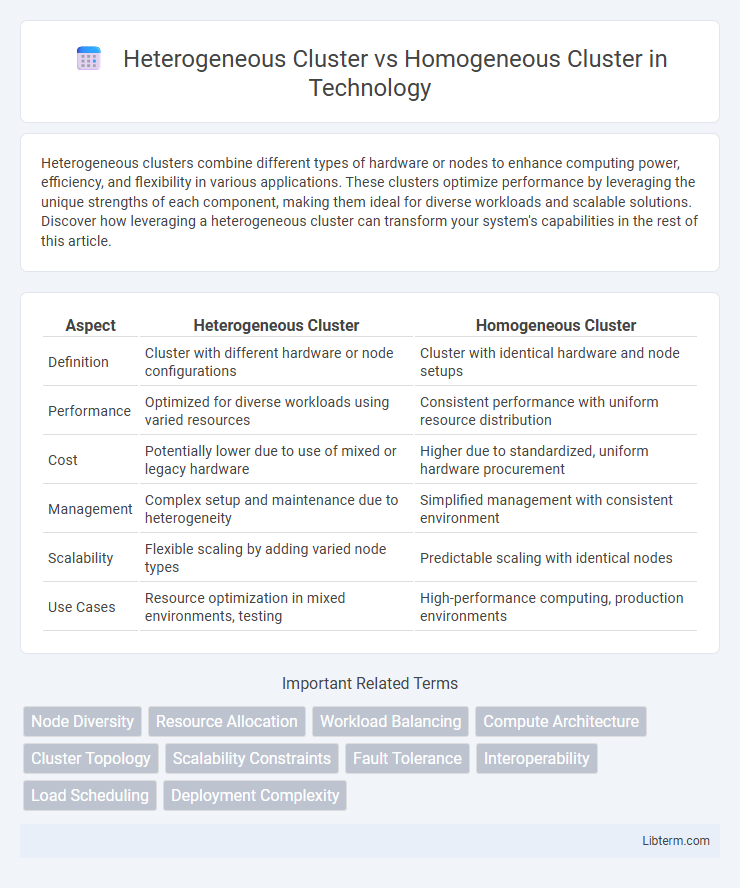
| Aspect | Heterogeneous Cluster | Homogeneous Cluster |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cluster with different hardware or node configurations | Cluster with identical hardware and node setups |
| Performance | Optimized for diverse workloads using varied resources | Consistent performance with uniform resource distribution |
| Cost | Potentially lower due to use of mixed or legacy hardware | Higher due to standardized, uniform hardware procurement |
| Management | Complex setup and maintenance due to heterogeneity | Simplified management with consistent environment |
| Scalability | Flexible scaling by adding varied node types | Predictable scaling with identical nodes |
| Use Cases | Resource optimization in mixed environments, testing | High-performance computing, production environments |
Introduction to Clustering in Computing
Clustering in computing involves grouping a set of nodes to work together as a single system, enhancing performance, reliability, and resource utilization. A homogeneous cluster consists of identical hardware and software configurations, ensuring uniform performance and simplified management. In contrast, a heterogeneous cluster combines diverse systems with different architectures or operating systems, offering flexibility and cost efficiency but requiring sophisticated management and resource allocation strategies.
Defining Homogeneous Clusters
Homogeneous clusters consist of identical or similar hardware and software configurations, ensuring uniform performance and simplified management across all nodes. These clusters optimize workload distribution by standardizing resources, leading to predictable system behavior and easier troubleshooting. Homogeneous environments are particularly beneficial for applications requiring consistent processing speeds and synchronized task execution.
Understanding Heterogeneous Clusters
Heterogeneous clusters consist of interconnected computers with varying hardware specifications, operating systems, or performance capacities, optimizing resource utilization across diverse workloads. This contrasts with homogeneous clusters, which use uniform nodes to simplify management but may limit flexibility and scalability. Understanding heterogeneous clusters is crucial for environments requiring cost-efficient computing power and adaptability to different application needs.
Key Differences between Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Clusters
Heterogeneous clusters consist of nodes with varying hardware configurations, such as different CPU architectures, memory capacities, or storage types, while homogeneous clusters feature identical or nearly identical nodes. This diversity in heterogeneous clusters allows for specialized task allocation based on node capabilities, enhancing overall system flexibility and resource optimization. Homogeneous clusters, in contrast, simplify management and load balancing due to uniform performance and predictable behavior across all nodes.
Performance Comparison: Heterogeneous vs Homogeneous
Heterogeneous clusters combine different types of processors and hardware configurations, often delivering superior performance for specialized workloads by leveraging varied computational strengths. Homogeneous clusters, consisting of identical nodes, provide consistent and predictable performance with simplified management and uniform resource allocation. Performance comparisons indicate heterogeneous clusters excel in environments requiring diverse processing tasks, while homogeneous clusters benefit applications needing scalability and repeatability.
Scalability and Flexibility Considerations
Heterogeneous clusters offer enhanced scalability by integrating diverse hardware and software resources, allowing organizations to optimize performance for varied workloads. Homogeneous clusters provide predictability and ease of management but may face limitations in scaling efficiently due to uniform configurations. Flexibility in heterogeneous clusters enables seamless adaptation to changing demands, while homogeneous clusters often require significant reconfiguration to accommodate growth or new applications.
Cost Analysis in Cluster Deployment
Heterogeneous clusters leverage diverse hardware components, often reducing upfront capital expenditures by integrating cost-effective or existing resources, while homogeneous clusters typically involve uniform, higher-cost equipment for optimized performance. Operational costs in heterogeneous clusters can increase due to management complexity and compatibility issues, whereas homogeneous clusters benefit from streamlined maintenance and predictable scalability expenses. Selecting between the two depends on workload requirements and budget constraints, with heterogeneous clusters offering flexible cost savings and homogeneous clusters providing consistent performance-to-cost ratios.
Use Cases and Applications
Heterogeneous clusters, integrating diverse hardware and architectures, excel in environments requiring specialized processing such as scientific simulations, big data analytics, and machine learning, where different node types optimize workload efficiency. Homogeneous clusters, composed of identical nodes, are ideal for applications needing uniform performance and simplified management, including web hosting, high-performance computing (HPC), and database services. Choosing between these cluster types depends on specific use cases, balancing flexibility and cost-efficiency against performance consistency and ease of administration.
Challenges in Cluster Management
Managing heterogeneous clusters presents challenges such as resource allocation complexity due to diverse hardware specifications, inconsistent performance metrics across nodes, and difficulties in maintaining uniform software environments. Homogeneous clusters simplify management with standardized hardware and software configurations, but they may face scalability limitations and reduced flexibility in handling varied workloads. Both cluster types require robust monitoring tools to address fault tolerance and workload balancing efficiently.
Choosing the Right Cluster for Your Needs
Choosing the right cluster depends on workload diversity and resource flexibility requirements. Heterogeneous clusters combine different hardware types, offering tailored performance and efficiency for varied tasks, while homogeneous clusters provide uniform hardware, ensuring simplicity and predictability in large-scale parallel processing. Evaluating cost, scalability, and specific application demands helps determine whether a heterogeneous setup or a homogeneous environment aligns better with your computational goals.
Heterogeneous Cluster Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com