Auto Scaling dynamically adjusts your cloud resources to meet fluctuating demand, ensuring optimal performance while controlling costs. By automatically increasing or decreasing compute capacity, it maintains application availability and reliability without manual intervention. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Auto Scaling can enhance your infrastructure efficiency and business continuity.
Table of Comparison
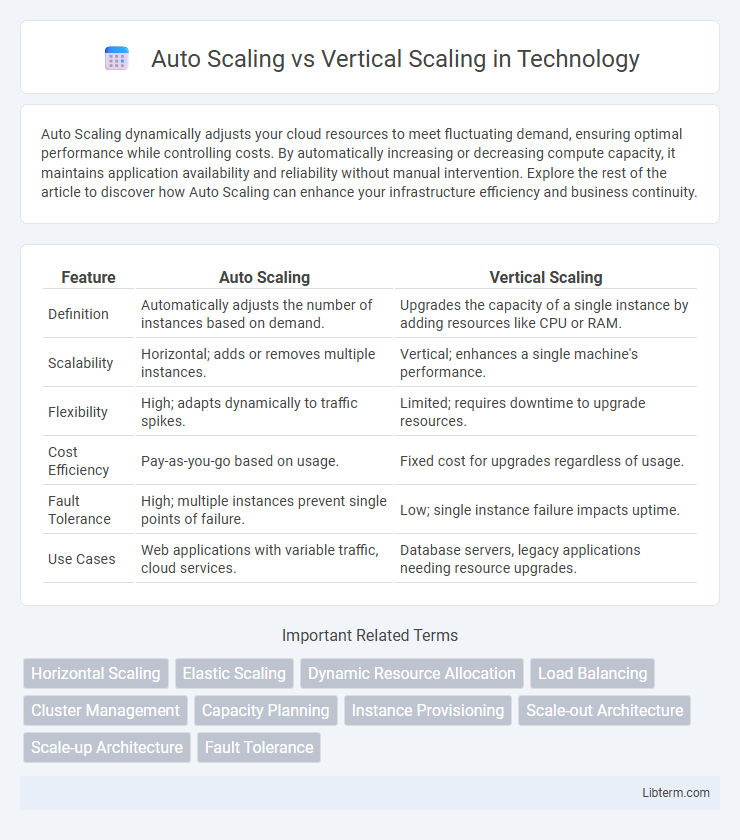
| Feature | Auto Scaling | Vertical Scaling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automatically adjusts the number of instances based on demand. | Upgrades the capacity of a single instance by adding resources like CPU or RAM. |
| Scalability | Horizontal; adds or removes multiple instances. | Vertical; enhances a single machine's performance. |
| Flexibility | High; adapts dynamically to traffic spikes. | Limited; requires downtime to upgrade resources. |
| Cost Efficiency | Pay-as-you-go based on usage. | Fixed cost for upgrades regardless of usage. |
| Fault Tolerance | High; multiple instances prevent single points of failure. | Low; single instance failure impacts uptime. |
| Use Cases | Web applications with variable traffic, cloud services. | Database servers, legacy applications needing resource upgrades. |
Introduction to Scaling in Cloud Computing
Auto scaling dynamically adjusts computing resources by adding or removing instances based on real-time demand, optimizing cost and performance in cloud environments. Vertical scaling involves increasing the capacity of a single server by upgrading CPU, RAM, or storage, enhancing performance without altering the number of instances. Both scaling methods are essential for maintaining system availability and efficiency under varying workloads in cloud computing.
What is Auto Scaling?
Auto Scaling is a cloud computing feature that automatically adjusts the number of active servers or instances based on current demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency. It dynamically adds or removes resources horizontally by increasing or decreasing server count, rather than upgrading a single server's capacity. This approach enhances application availability and fault tolerance by distributing workloads across multiple instances.
What is Vertical Scaling?
Vertical scaling, also known as scaling up, involves increasing the capacity of a single server or machine by adding more CPU, RAM, or storage resources to handle higher workloads. This approach enhances performance within a single instance but has limitations due to hardware constraints and potential downtime during upgrades. Vertical scaling is ideal for applications requiring powerful resources without the complexity of managing multiple machines.
Key Differences Between Auto Scaling and Vertical Scaling
Auto Scaling adjusts the number of active servers dynamically based on real-time demand, enhancing reliability and cost efficiency by adding or removing instances automatically. Vertical Scaling, or scaling up, involves increasing the resource capacity (CPU, RAM) of a single server to handle increased load but is limited by hardware constraints and often requires downtime. Auto Scaling suits distributed cloud environments for elastic workloads, while Vertical Scaling is ideal for applications requiring more power on a single machine without architecture complexity.
Performance and Resource Optimization
Auto Scaling dynamically adjusts the number of computing instances based on real-time traffic demands, enhancing performance by distributing workload and preventing resource bottlenecks. Vertical Scaling increases the capacity of a single server by adding more CPU, RAM, or storage, optimizing resource allocation for applications with predictable, steady workloads. Auto Scaling offers superior resilience and cost efficiency during variable usage patterns, while Vertical Scaling maximizes performance for intensive tasks requiring high resource concentration on one machine.
Cost Comparison: Auto vs Vertical Scaling
Auto Scaling offers cost efficiency by dynamically allocating resources based on real-time demand, reducing waste during low-usage periods. Vertical Scaling typically incurs higher expenses as it involves upgrading existing hardware or infrastructure regardless of fluctuating workloads. Businesses with variable traffic see better cost management and scalability benefits through Auto Scaling compared to the fixed, often costly investments of Vertical Scaling.
Use Cases for Auto Scaling
Auto Scaling is ideal for applications with unpredictable or fluctuating workloads, such as e-commerce platforms during sales events, real-time analytics, and microservices architectures that require dynamic resource allocation. It efficiently handles traffic spikes by automatically launching or terminating instances, ensuring high availability and cost optimization without manual intervention. This makes Auto Scaling indispensable for cloud environments like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud where workload variability demands rapid scalability.
Use Cases for Vertical Scaling
Vertical scaling, or scaling up, enhances a server's capacity by increasing CPU, RAM, or storage to handle higher workloads within a single machine, making it ideal for applications with fixed infrastructure or licensing constraints. It suits use cases like database management systems requiring high memory and processing power, legacy applications designed for single-node architectures, and development environments needing rapid resource boosts without architectural changes. Vertical scaling minimizes application downtime and simplifies management when hardware upgrades are sufficient to meet performance demands.
Pros and Cons of Each Scaling Method
Auto Scaling enhances application availability and fault tolerance by dynamically adjusting resources based on demand, enabling cost efficiency and improved performance during traffic spikes; however, it requires complex setup and may introduce latency during scaling events. Vertical Scaling involves upgrading existing hardware to increase capacity, offering simplicity and compatibility with legacy applications but is limited by physical server constraints and potential downtime during upgrades. Choosing between these methods depends on scalability needs, budget, and application architecture, with Auto Scaling suited for distributed systems and Vertical Scaling fitting monolithic applications.
Choosing the Right Scaling Strategy for Your Application
Choosing the right scaling strategy for your application depends on workload patterns and resource requirements; auto scaling (horizontal scaling) dynamically adds or removes instances to handle variable traffic efficiently, providing fault tolerance and improved performance in cloud environments like AWS or Azure. Vertical scaling involves upgrading existing server capabilities such as CPU, RAM, or storage, suitable for applications with steady workloads requiring enhanced power without architectural changes. Evaluating cost, latency, and complexity helps determine whether horizontal expansion or vertical enhancement best supports your application's scalability and reliability goals.
Auto Scaling Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com