A Virtual Private Network (VPN) enhances your online privacy by encrypting your internet connection and masking your IP address, preventing unauthorized access to your sensitive data. By routing your internet traffic through secure servers, a VPN allows you to bypass geographic restrictions and access content safely from anywhere in the world. Discover how a VPN can protect your digital life and improve your online experience in the full article.
Table of Comparison
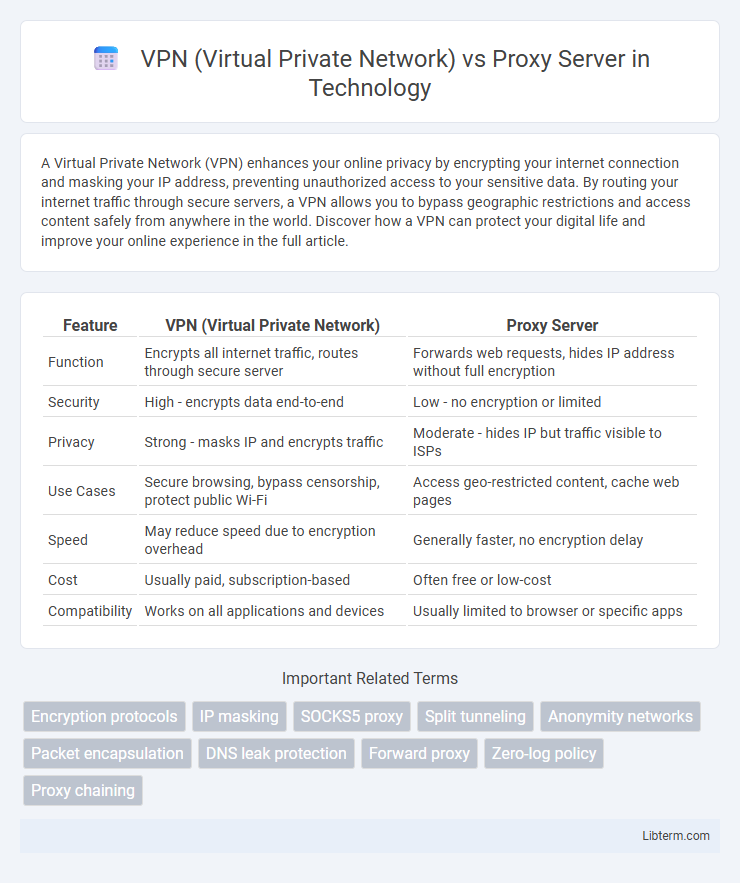
| Feature | VPN (Virtual Private Network) | Proxy Server |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Encrypts all internet traffic, routes through secure server | Forwards web requests, hides IP address without full encryption |
| Security | High - encrypts data end-to-end | Low - no encryption or limited |
| Privacy | Strong - masks IP and encrypts traffic | Moderate - hides IP but traffic visible to ISPs |
| Use Cases | Secure browsing, bypass censorship, protect public Wi-Fi | Access geo-restricted content, cache web pages |
| Speed | May reduce speed due to encryption overhead | Generally faster, no encryption delay |
| Cost | Usually paid, subscription-based | Often free or low-cost |
| Compatibility | Works on all applications and devices | Usually limited to browser or specific apps |
Introduction to VPNs and Proxy Servers
VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) create a secure, encrypted tunnel between the user's device and the internet, protecting data from hackers and ensuring privacy by masking the IP address. Proxy servers act as intermediaries for internet requests, forwarding traffic on behalf of the user but typically without encryption, offering basic anonymity and access to geo-restricted content. While both tools help mask IP addresses, VPNs provide comprehensive security and privacy features that proxy servers lack.
How VPNs Work: Encryption and Privacy
VPNs create a secure tunnel by encrypting all internet traffic between the user's device and the VPN server, ensuring data privacy and protection from interception. This encryption uses protocols like OpenVPN, WireGuard, or IPSec to safeguard sensitive information and mask the user's IP address. Unlike proxy servers that only reroute specific traffic or browser data without encryption, VPNs provide comprehensive privacy by securing all network activity on the device.
How Proxy Servers Function: Filtering and Hiding IPs
Proxy servers function by acting as intermediaries between a user's device and the internet, filtering requests to control access to specific content and enhancing privacy by masking the original IP address. They intercept web traffic, enabling the blocking of harmful sites, caching data for faster loading, and anonymizing user identity to bypass geo-restrictions or censorship. Unlike VPNs, proxies typically do not encrypt traffic, focusing instead on IP address substitution and content filtering to offer basic anonymity and control.
Key Differences Between VPNs and Proxy Servers
VPNs encrypt all internet traffic by routing it through secure servers, ensuring comprehensive privacy and data protection across all applications and devices. Proxy servers act as intermediaries for specific applications or browsers without encrypting traffic, primarily masking the IP address for targeted anonymity. Unlike VPNs, proxies do not provide full network security or encryption, making them less effective for safeguarding sensitive information or avoiding ISP tracking.
Security Features: VPNs vs Proxy Servers
VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) encrypt all internet traffic through secure tunnels using protocols like OpenVPN, IPsec, and WireGuard, providing strong protection against eavesdropping, data interception, and man-in-the-middle attacks. Proxy servers primarily route specific application traffic without encryption, making them less effective at safeguarding data from cyber threats or securing entire device connections. VPNs also mask IP addresses and locations at the network level, enhancing privacy, whereas proxy servers typically only mask IPs for individual applications, offering limited security coverage.
Online Privacy: Which Option Offers Better Anonymity?
VPNs encrypt internet traffic through secure tunnels, masking IP addresses and providing robust anonymity by routing data through remote servers. Proxy servers hide your IP by acting as intermediaries but typically lack encryption, exposing data to potential interception. For enhanced online privacy and better anonymity, VPNs are the preferred choice over proxy servers.
Unblocking Content and Bypassing Geo-Restrictions
VPNs encrypt internet traffic and route it through remote servers, effectively unblocking content and bypassing geo-restrictions with enhanced security and privacy. Proxy servers only mask IP addresses and reroute traffic without encryption, making them less effective for bypassing sophisticated geo-blocks and more vulnerable to detection. For consistent access to restricted content and improved anonymity, VPNs offer superior performance compared to proxy servers.
Performance and Speed Comparison
VPNs typically provide secure, encrypted connections that can slightly reduce internet speed due to encryption overhead, while proxy servers often offer faster performance by simply routing traffic without encryption. VPNs are better suited for privacy and security, as their encryption can slow down connection speeds compared to proxies, which prioritize speed over confidentiality. Evaluating performance, proxies deliver lower latency and quicker load times, but VPNs enable safer browsing at a modest speed trade-off.
Use Cases: When to Choose VPN or Proxy Server
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is ideal for securing sensitive data, encrypting internet traffic, and ensuring privacy on public Wi-Fi networks, making it essential for remote work and secure connections. Proxy servers suit scenarios requiring IP masking for geo-restricted content access or low-risk anonymity in web browsing without the need for full encryption. Choosing between a VPN and a proxy depends on whether robust security and data protection or simple IP address masking for content access is the primary goal.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) offers comprehensive security by encrypting all internet traffic and masking your IP address, making it ideal for privacy-conscious users and secure remote access. Proxy servers, while useful for bypassing geo-restrictions and improving web access speed, do not provide encryption or full anonymity, limiting their effectiveness for sensitive activities. Selecting between a VPN and a proxy depends on your priority for security, privacy, speed, and the specific use case, with VPNs generally favored for robust protection and proxies suited for less critical, location-based access.
VPN (Virtual Private Network) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com