SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is a protocol that enables secure single sign-on (SSO) by allowing users to authenticate across multiple applications with one set of credentials. It simplifies identity management and enhances security by relying on trusted identity providers to exchange authentication data. Discover how implementing SAML can streamline Your access management and improve overall security in the full article.
Table of Comparison
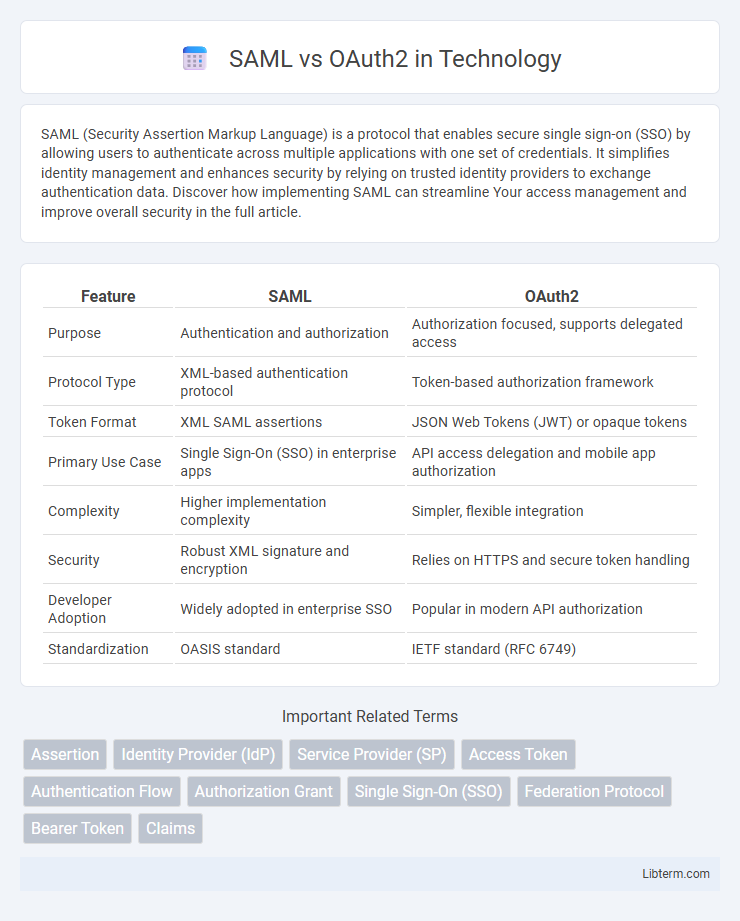
| Feature | SAML | OAuth2 |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Authentication and authorization | Authorization focused, supports delegated access |
| Protocol Type | XML-based authentication protocol | Token-based authorization framework |
| Token Format | XML SAML assertions | JSON Web Tokens (JWT) or opaque tokens |
| Primary Use Case | Single Sign-On (SSO) in enterprise apps | API access delegation and mobile app authorization |
| Complexity | Higher implementation complexity | Simpler, flexible integration |
| Security | Robust XML signature and encryption | Relies on HTTPS and secure token handling |
| Developer Adoption | Widely adopted in enterprise SSO | Popular in modern API authorization |
| Standardization | OASIS standard | IETF standard (RFC 6749) |
Introduction to SAML and OAuth2
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is an XML-based protocol primarily used for single sign-on (SSO) and exchanging authentication and authorization data between an identity provider and a service provider. OAuth2 is an authorization framework that enables third-party applications to obtain limited access to an HTTP service on behalf of a user without sharing credentials. Both SAML and OAuth2 serve different purposes in identity and access management, with SAML focusing on federated identity and OAuth2 emphasizing delegated authorization for API access.
Understanding SAML: Core Concepts
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is a protocol primarily used for single sign-on (SSO) by exchanging authentication and authorization data between identity providers and service providers. It relies on XML-based assertions to securely convey user identity information, enabling seamless access across different domains. SAML's core components include assertions, protocols, bindings, and profiles, which together facilitate secure federation and trust management in enterprise environments.
What Is OAuth2 and How Does It Work?
OAuth2 is an authorization framework that enables third-party applications to obtain limited access to user resources without exposing credentials. It works by issuing access tokens after user authentication, allowing clients to interact securely with resource servers on behalf of users. The protocol supports multiple grant types such as authorization code, implicit, client credentials, and password, catering to different use cases and security levels.
Key Differences Between SAML and OAuth2
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is primarily used for single sign-on (SSO) and exchanging authentication and authorization data between identity providers and service providers using XML-based assertions. OAuth2, on the other hand, is an authorization framework designed to grant third-party applications limited access to user resources via access tokens, commonly using JSON and RESTful APIs. Key differences include SAML's emphasis on enterprise SSO with robust identity federation, whereas OAuth2 focuses on delegated authorization for API access with lighter protocols and token-based mechanisms.
Authentication vs Authorization Explained
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) primarily facilitates authentication by enabling single sign-on (SSO) through secure exchange of identity assertions between an identity provider and a service provider. OAuth2 serves as an authorization framework that grants third-party applications limited access to user resources without exposing credentials, typically through access tokens issued by an authorization server. Understanding the distinction is crucial: SAML confirms user identity (authentication), while OAuth2 controls resource permissions (authorization).
Use Cases: When to Use SAML or OAuth2
SAML is best suited for enterprise single sign-on (SSO) scenarios that require secure, federated identity exchange between organizations, such as access to corporate intranets or legacy systems. OAuth2 excels in delegated authorization for modern web and mobile applications, enabling users to grant third-party apps limited access to resources without sharing credentials. Use SAML when strict security and identity federation across trusted domains are necessary, and choose OAuth2 for scalable API authorization and user consent in consumer-facing services.
Security Considerations for SAML and OAuth2
SAML provides strong authentication through XML-based assertions and is often used in enterprise environments requiring single sign-on (SSO) with high assurance of identity, leveraging digital signatures and encrypted tokens to protect data integrity and confidentiality. OAuth2, designed primarily for authorization, relies on bearer tokens which can be susceptible to interception if not properly secured with TLS, and requires careful implementation of scopes and token expiration to minimize risk. Both protocols demand rigorous security practices, including secure token storage, frequent rotation of credentials, and comprehensive validation checks to prevent attacks such as token theft, replay, or impersonation.
Implementation Challenges and Best Practices
Implementing SAML presents challenges like complex XML-based message handling, extensive configuration requirements, and compatibility issues with modern web applications, often requiring robust identity provider (IdP) and service provider (SP) coordination. OAuth2 implementation demands careful management of token lifecycles, secure authorization flows, and protection against threats such as token leakage and CSRF attacks, with emphasis on correctly implementing authorization code grants and refresh tokens. Best practices involve thorough testing, strict adherence to protocol specifications, and leveraging established libraries and frameworks to mitigate security risks and streamline integration efforts.
SAML vs OAuth2: Performance and Scalability
SAML operates with XML-based assertions, which often result in higher processing overhead and latency compared to OAuth2's lightweight JSON tokens, impacting performance efficiency. OAuth2's design supports scalable, stateless token validation suitable for modern microservices and mobile applications, enabling faster authentication and authorization workflows. SAML's reliance on SOAP and XML can limit scalability in high-demand environments, whereas OAuth2's JSON and bearer token mechanism offer enhanced scalability and better integration with cloud-native architectures.
Choosing the Right Protocol for Your Application
Selecting between SAML and OAuth2 depends on your application's specific needs for security and user experience; SAML excels in enterprise single sign-on (SSO) scenarios with robust identity assertion, while OAuth2 is ideal for delegated authorization in mobile and web applications. Consider SAML for applications requiring strong, standardized authentication across organizational boundaries, and OAuth2 when enabling access to APIs with token-based, granular permissions. Evaluating factors such as protocol complexity, token format, and user flow will ensure the chosen protocol aligns with both technical requirements and user convenience.
SAML Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com