Encryption safeguards your data by converting it into a coded format, making unauthorized access nearly impossible. It is essential for protecting sensitive information across various platforms, including emails, online transactions, and personal communications. Discover how encryption can enhance your digital security by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
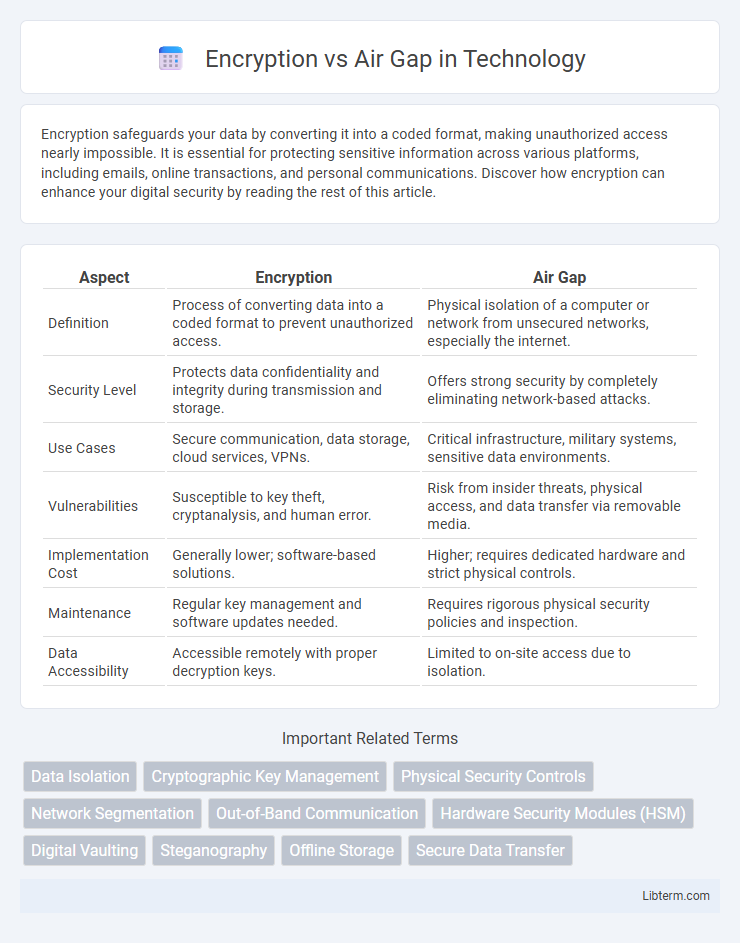
| Aspect | Encryption | Air Gap |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of converting data into a coded format to prevent unauthorized access. | Physical isolation of a computer or network from unsecured networks, especially the internet. |
| Security Level | Protects data confidentiality and integrity during transmission and storage. | Offers strong security by completely eliminating network-based attacks. |
| Use Cases | Secure communication, data storage, cloud services, VPNs. | Critical infrastructure, military systems, sensitive data environments. |
| Vulnerabilities | Susceptible to key theft, cryptanalysis, and human error. | Risk from insider threats, physical access, and data transfer via removable media. |
| Implementation Cost | Generally lower; software-based solutions. | Higher; requires dedicated hardware and strict physical controls. |
| Maintenance | Regular key management and software updates needed. | Requires rigorous physical security policies and inspection. |
| Data Accessibility | Accessible remotely with proper decryption keys. | Limited to on-site access due to isolation. |
Introduction to Data Security: Encryption vs Air Gap
Encryption transforms data into a coded format requiring a decryption key, ensuring confidentiality and secure communication across networks. Air gap physically isolates critical systems from unsecured networks, preventing unauthorized digital access and cyber threats. Both methods serve as fundamental strategies in data security, with encryption focusing on protecting data in transit and air gap emphasizing isolation for sensitive information.
Defining Encryption: Principles and Methods
Encryption involves converting data into a coded format using algorithms such as AES or RSA, ensuring confidentiality and protection from unauthorized access. It relies on cryptographic keys to both encode and decode information, with symmetric and asymmetric methods serving different security needs. Strong encryption protocols are essential for safeguarding data in transit and at rest, especially when compared to physical isolation methods like air gaps.
Understanding Air Gap Security
Air gap security isolates critical systems by physically separating them from unsecured networks, preventing unauthorized access and data breaches. Unlike encryption, which protects data by encoding it, an air gap ensures no direct or wireless connection exists, making remote cyberattacks extremely difficult. This method is highly effective for safeguarding sensitive information in environments like military installations, financial institutions, and critical infrastructure.
Key Differences Between Encryption and Air Gap
Encryption secures data by converting it into a coded format using algorithms and keys, ensuring information remains confidential during storage or transmission. An air gap physically isolates a system by disconnecting it from unsecured networks, eliminating external access and reducing cyberattack risks. Unlike encryption, which protects data in transit or at rest, an air gap focuses on preventing unauthorized network access altogether.
Use Cases: When to Use Encryption
Encryption is essential for protecting sensitive data in transit and at rest, especially in cloud storage, email communications, and online transactions where data traverses potentially insecure networks. Enterprises handling personal identifiable information (PII), financial data, or intellectual property benefit from encryption to ensure confidentiality and compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA. Unlike air gaps, encryption allows secure data exchange between remote systems while maintaining strong defense against interception and unauthorized access.
Use Cases: When to Implement Air Gap
Air gap security is essential for protecting highly sensitive data and critical infrastructure that require physical isolation from external networks, such as classified government systems or nuclear power plant controls. Unlike encryption, which secures data in transit or at rest on connected networks, air gapping prevents any digital connection, making it ideal for environments where absolute isolation is necessary to eliminate cyberattack vectors. Implement air gap strategies in scenarios demanding maximum security assurance, including military communication networks, secure financial transaction systems, and industrial control systems managing critical processes.
Strengths and Limitations of Encryption
Encryption provides robust data protection by converting information into unreadable code, ensuring confidentiality and integrity even during data transmission. Its strength lies in enabling secure communication over untrusted networks and safeguarding data at rest or in motion with algorithms like AES and RSA. Limitations include vulnerability to key management failures, potential susceptibility to quantum computing attacks, and performance overhead impacting system efficiency.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Air Gap Solutions
Air gap solutions provide robust security by physically isolating critical systems from network connections, effectively preventing remote cyberattacks and unauthorized access. However, this isolation complicates data transfer and system updates, often requiring manual intervention that increases operational overhead and the risk of human error. While air gaps enhance protection for sensitive environments, they can limit real-time data accessibility and integration with modern digital workflows.
Combining Encryption and Air Gap for Maximum Protection
Combining encryption with air gap security creates a robust defense against unauthorized data access and cyber threats by ensuring sensitive information is both physically isolated and cryptographically protected. Encryption secures data at rest and in transit using algorithms like AES-256, while air gaps physically separate critical systems from networks, preventing remote attacks and malware infiltration. Employing both methods enhances data integrity and confidentiality, making it extremely difficult for attackers to breach systems or exfiltrate information.
Choosing the Right Security Strategy for Your Data
Choosing the right security strategy for your data depends on the threat landscape and operational needs. Encryption ensures data confidentiality and integrity across networks by converting information into unreadable code accessible only with decryption keys. Air gap security physically isolates critical systems from unsecured networks, preventing remote cyberattacks but requiring strict physical access controls and maintenance protocols.
Encryption Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com