Shadow deployment is a technique used to release new software features by running them alongside the current system without affecting real users. This approach allows you to test new updates in a live environment, gather performance data, and identify issues before full-scale rollout. Explore the rest of the article to learn how shadow deployment can enhance your development process and reduce deployment risks.
Table of Comparison
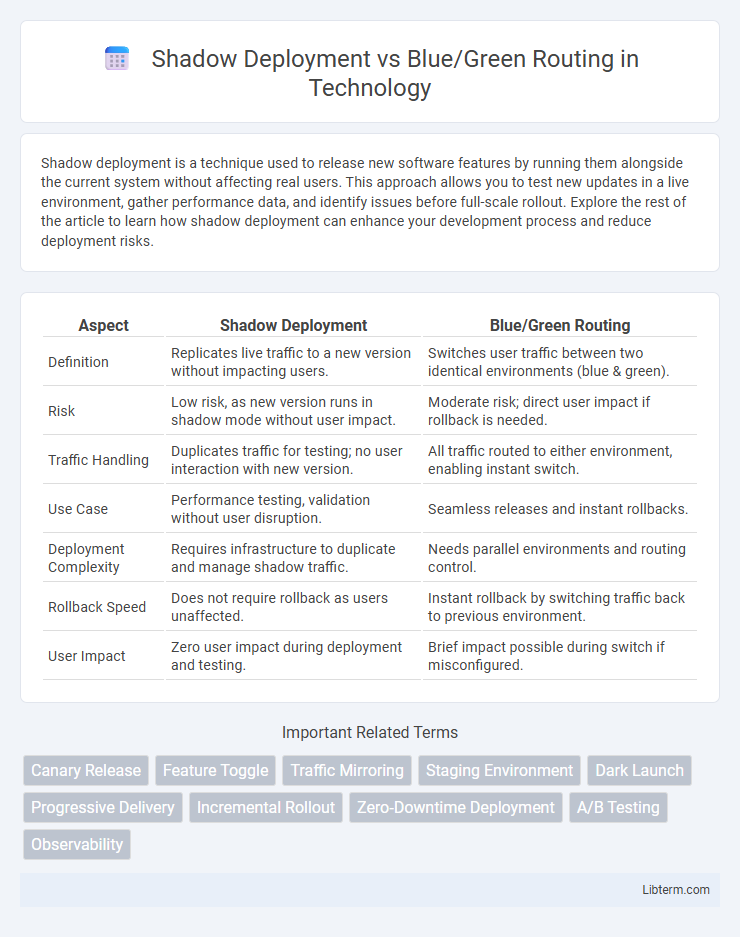
| Aspect | Shadow Deployment | Blue/Green Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Replicates live traffic to a new version without impacting users. | Switches user traffic between two identical environments (blue & green). |
| Risk | Low risk, as new version runs in shadow mode without user impact. | Moderate risk; direct user impact if rollback is needed. |
| Traffic Handling | Duplicates traffic for testing; no user interaction with new version. | All traffic routed to either environment, enabling instant switch. |
| Use Case | Performance testing, validation without user disruption. | Seamless releases and instant rollbacks. |
| Deployment Complexity | Requires infrastructure to duplicate and manage shadow traffic. | Needs parallel environments and routing control. |
| Rollback Speed | Does not require rollback as users unaffected. | Instant rollback by switching traffic back to previous environment. |
| User Impact | Zero user impact during deployment and testing. | Brief impact possible during switch if misconfigured. |
Introduction to Deployment Strategies
Shadow deployment and blue/green routing are advanced deployment strategies optimizing application rollouts and minimizing downtime. Shadow deployment directs real user traffic to a new version in parallel without affecting production, enabling real-world testing and monitoring. Blue/green routing involves two identical environments where one runs the current version and the other hosts the new release, allowing instant switching and rollback with minimal risk.
What is Shadow Deployment?
Shadow deployment is a technique where new software versions run alongside the current system without handling live user traffic, allowing developers to test features and monitor performance in a real-world environment without impacting end users. This approach enables comparison of behaviors and detection of issues before full release, minimizing risks associated with deployment. Unlike blue/green routing, shadow deployment does not involve traffic switching but duplicates requests to assess the new version silently.
What is Blue/Green Routing?
Blue/Green Routing is a deployment strategy that reduces downtime and risk by running two identical production environments, called Blue and Green. Traffic is routed entirely to the current active environment (Blue), while the new version is deployed and tested in the inactive environment (Green), enabling instant switching once validated. This approach ensures seamless user experience by quickly rolling back to the previous stable environment if issues arise during deployment.
Key Differences Between Shadow Deployment and Blue/Green Routing
Shadow Deployment directs real user traffic to a new version without impacting the primary environment, enabling testing in production with minimal risk, while Blue/Green Routing switches traffic between two identical environments to facilitate instant rollbacks. Shadow Deployment helps in gradual exposure and monitoring by duplicating live traffic to the shadow environment, whereas Blue/Green Routing provides a clear cutover point by shifting all traffic atomically. The core difference lies in Shadow Deployment's parallel testing approach versus Blue/Green Routing's environment swapping strategy for deployment and rollback.
Use Cases for Shadow Deployment
Shadow deployment excels in testing new features or updates in production without impacting live user traffic, enabling teams to validate performance and identify issues under real-world conditions. It is particularly useful for risk-averse environments requiring continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines to ensure stability before full release. In contrast to blue/green routing, shadow deployment allows parallel processing of requests silently, making it ideal for monitoring and gradual rollout scenarios.
Use Cases for Blue/Green Routing
Blue/Green Routing is ideal for zero-downtime deployments and instant rollbacks, commonly used in production environments requiring high availability and minimal risk during upgrades. It facilitates seamless traffic switching between identical application versions, making it suitable for scenarios like e-commerce platforms or financial services where uptime and user experience are critical. This approach enables thorough testing of new releases in a live environment without affecting the active user base, ensuring stability and reliability.
Pros and Cons of Shadow Deployment
Shadow deployment allows testing new features in production without impacting live user traffic, enabling real-time data collection and performance evaluation. However, it may increase resource consumption and complexity, as duplicated traffic needs to be managed carefully to avoid data inconsistencies or backend overload. Unlike blue/green routing, shadow deployment does not offer instant rollback, which can delay issue resolution if the new version has critical bugs.
Pros and Cons of Blue/Green Routing
Blue/Green Routing enables seamless traffic switching between two identical environments, minimizing downtime and reducing deployment risks by allowing instant rollback if issues arise. This strategy enhances system reliability and user experience but requires double the infrastructure resources, increasing operational costs. Its main drawback is the complexity of maintaining two synchronized environments, which can lead to configuration drift and management overhead.
Choosing the Right Deployment Strategy
Choosing the right deployment strategy hinges on your tolerance for risk, traffic control needs, and rollback complexity. Shadow deployment allows testing new features by mirroring traffic to the new system without affecting production, ideal for validating without user impact. Blue/Green routing provides a seamless switch between environments, minimizing downtime and simplifying rollbacks, making it preferable for critical applications requiring high availability and instant fallback.
Best Practices for Modern Application Deployments
Shadow deployment enables safe testing of new features by routing a copy of live traffic to a parallel environment without impacting users, ensuring robust validation under real-world conditions. Blue/green routing switches traffic between two identical production environments to minimize downtime and facilitate instant rollback during deployment, enhancing application availability and reliability. Best practices include automated traffic management, comprehensive monitoring, and gradual rollouts to reduce risks and ensure seamless transitions in modern application deployments.
Shadow Deployment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com