The hub and spoke model centralizes operations through a main hub, improving efficiency and reducing costs by connecting multiple spokes or branches. This system optimizes logistics, transportation, and communication networks, making it ideal for businesses and airlines aiming to streamline processes. Discover how implementing the hub and spoke model can transform your operations by reading the full article.
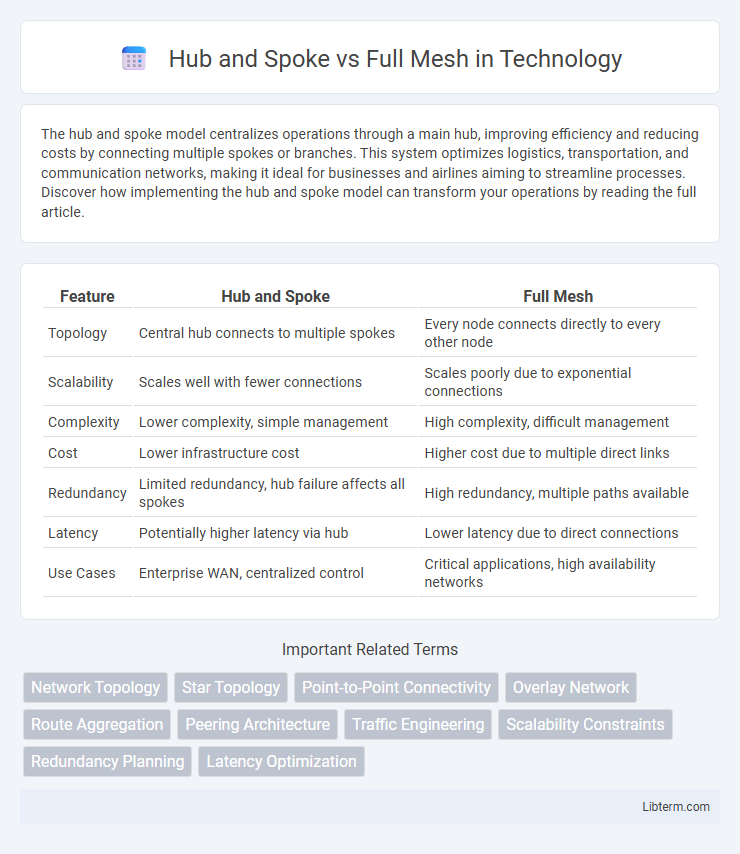
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hub and Spoke | Full Mesh |
|---|---|---|
| Topology | Central hub connects to multiple spokes | Every node connects directly to every other node |
| Scalability | Scales well with fewer connections | Scales poorly due to exponential connections |
| Complexity | Lower complexity, simple management | High complexity, difficult management |
| Cost | Lower infrastructure cost | Higher cost due to multiple direct links |
| Redundancy | Limited redundancy, hub failure affects all spokes | High redundancy, multiple paths available |
| Latency | Potentially higher latency via hub | Lower latency due to direct connections |
| Use Cases | Enterprise WAN, centralized control | Critical applications, high availability networks |
Introduction to Network Topologies: Hub and Spoke vs Full Mesh
Hub and Spoke and Full Mesh are two fundamental network topologies used to design communication systems. In a Hub and Spoke topology, all devices connect centrally through a single hub, simplifying management but creating a potential single point of failure. Full Mesh topology connects every device directly to all others, enhancing redundancy and fault tolerance at the cost of increased complexity and higher infrastructure requirements.
Defining the Hub and Spoke Topology
The Hub and Spoke topology features a central hub node that connects multiple peripheral spoke nodes, enabling streamlined communication and simplified management within a network. This design optimizes resource allocation by consolidating network traffic through the hub, reducing complexity compared to Full Mesh configurations where every node connects to every other node. Hub and Spoke topology is commonly used in VPNs and enterprise networks to centralize control and improve scalability.
Understanding Full Mesh Network Architecture
Full Mesh Network Architecture connects every node directly to all other nodes, ensuring maximum redundancy and minimal latency through multiple communication paths. This configuration enhances fault tolerance, as the failure of one link or node does not interrupt network connectivity. Compared to Hub and Spoke, Full Mesh delivers superior performance in critical environments requiring high availability and consistent data transmission.
Key Differences Between Hub and Spoke and Full Mesh
Hub and Spoke topology centralizes network traffic through a single hub node, optimizing management and reducing complexity, whereas Full Mesh topology requires every node to connect directly with every other node, ensuring maximum redundancy and fault tolerance. Hub and Spoke is typically more cost-effective and scalable for large networks but may create bottlenecks at the hub, while Full Mesh delivers superior performance and reliability at the expense of higher infrastructure costs and complexity. The choice between these topologies depends on the balance between network resilience, cost, and scalability requirements.
Advantages of the Hub and Spoke Model
The Hub and Spoke model simplifies network management by centralizing traffic through a single hub, reducing complexity and making troubleshooting more efficient. It offers cost savings in infrastructure by minimizing the number of required connections compared to Full Mesh, which demands direct links between all nodes. Scalability is enhanced as adding new spokes requires only one connection to the hub, avoiding exponential growth in network links.
Benefits of Full Mesh Topology
Full Mesh topology offers unparalleled network reliability by providing multiple redundant paths between all nodes, minimizing the risk of communication failure. It enhances communication efficiency through direct connections, reducing latency and improving data transfer speeds for critical applications. Moreover, Full Mesh supports scalable and flexible network growth, allowing easy integration of new nodes without disrupting existing connections.
Drawbacks and Limitations of Hub and Spoke
Hub and Spoke network topology suffers from a single point of failure at the central hub, which can lead to complete network downtime if the hub experiences issues. Scalability is limited since all traffic must pass through the hub, causing potential bottlenecks and increased latency during peak loads. This architecture also lacks redundancy and direct communication between spokes, resulting in reduced fault tolerance and lower overall network performance compared to Full Mesh topologies.
Challenges Associated With Full Mesh Networks
Full mesh networks face significant challenges including high complexity and scalability issues due to the exponential growth of connections as nodes increase, which significantly raises maintenance and management costs. Network redundancy in full mesh adds robustness but leads to increased bandwidth consumption and complicated routing protocols, making troubleshooting more difficult. These factors often result in higher infrastructure expenses and require specialized expertise to maintain optimal performance compared to hub and spoke models.
Use Cases: When to Choose Hub and Spoke or Full Mesh
Hub and Spoke topology is ideal for organizations with centralized control, simplified management, and predictable traffic patterns, such as branch offices connecting to a main data center. Full Mesh topology suits scenarios requiring high availability, direct communication between all nodes, and low latency, like financial trading platforms or global enterprise networks. Choose Hub and Spoke for cost-efficiency and ease of scalability, while Full Mesh is preferred for mission-critical applications demanding redundancy and minimal downtime.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Topology for Your Needs
Choosing between Hub and Spoke and Full Mesh topologies depends on your network size, scalability requirements, and budget constraints. Hub and Spoke offers simplicity and cost-effectiveness for smaller or centralized networks, while Full Mesh provides maximum redundancy and low latency ideal for large, highly available systems. Evaluating these factors ensures optimal performance and resource allocation tailored to your specific operational goals.
Hub and Spoke Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com