WebSockets provide a full-duplex communication channel over a single, long-lived connection, enabling real-time data exchange between a client and server with low latency. This technology is essential for interactive applications such as online gaming, live chat, and financial trading platforms. Discover how WebSockets can enhance Your application's performance and user experience by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
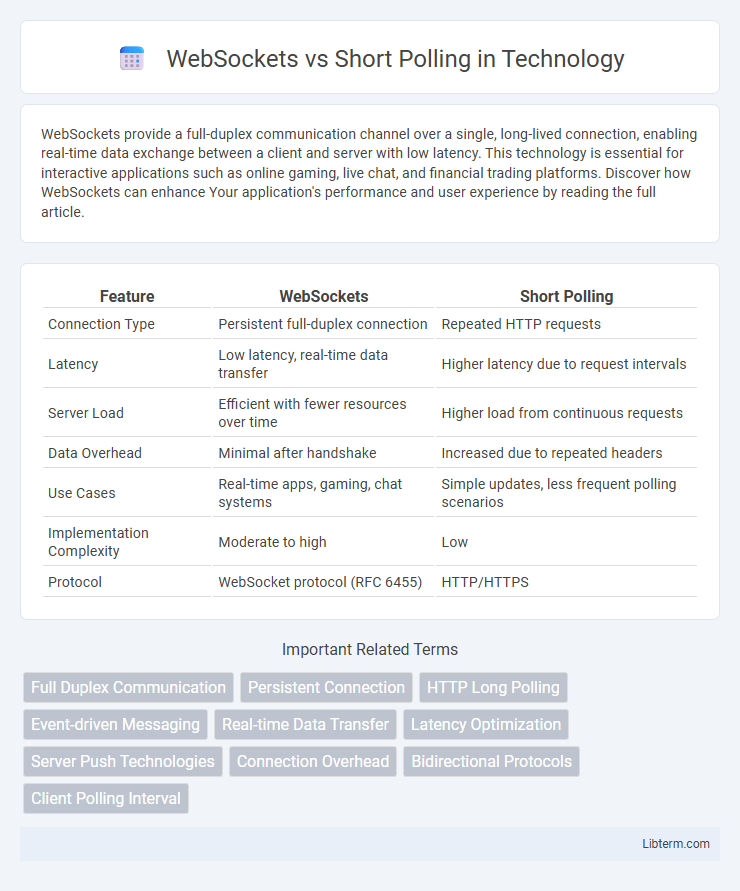
| Feature | WebSockets | Short Polling |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Type | Persistent full-duplex connection | Repeated HTTP requests |
| Latency | Low latency, real-time data transfer | Higher latency due to request intervals |
| Server Load | Efficient with fewer resources over time | Higher load from continuous requests |
| Data Overhead | Minimal after handshake | Increased due to repeated headers |
| Use Cases | Real-time apps, gaming, chat systems | Simple updates, less frequent polling scenarios |
| Implementation Complexity | Moderate to high | Low |
| Protocol | WebSocket protocol (RFC 6455) | HTTP/HTTPS |
Introduction to WebSockets and Short Polling
WebSockets establish a persistent, full-duplex communication channel between client and server, enabling real-time data exchange with low latency and minimal overhead. Short polling repeatedly sends HTTP requests at fixed intervals to check for new data, resulting in higher latency and increased network traffic. WebSockets are preferred for applications requiring instant updates, while short polling suits simpler scenarios with less frequent data changes.
How WebSockets Work
WebSockets establish a persistent, full-duplex communication channel between the client and server over a single TCP connection, allowing real-time bidirectional data exchange without repeated HTTP requests. The protocol begins with an HTTP handshake that upgrades the connection to WebSocket, enabling low-latency interactions essential for live applications like chat or gaming. Unlike short polling, which repeatedly sends HTTP requests at intervals, WebSockets maintain an open connection, reducing overhead and server load for continuous data streams.
How Short Polling Works
Short polling works by the client repeatedly sending HTTP requests to the server at regular intervals to check for new data or updates. Each request waits for a server response and then immediately sends another request after a fixed delay, resulting in increased latency and higher network overhead compared to WebSockets. This method can lead to inefficient resource usage and slower real-time communication in applications requiring frequent updates.
Key Differences Between WebSockets and Short Polling
WebSockets establish a full-duplex communication channel that allows real-time, bidirectional data transfer between client and server, minimizing latency and reducing unnecessary HTTP requests. Short polling repeatedly sends client-side requests at fixed intervals, causing increased latency and server load due to constant connection overhead. Key differences include WebSockets' persistent connection versus short polling's repetitive HTTP request mechanism, real-time data delivery in WebSockets compared to delayed updates in short polling, and improved network efficiency with WebSockets through lower resource consumption.
Performance Comparison
WebSockets offer superior performance over short polling by maintaining a persistent, full-duplex connection between client and server, significantly reducing latency and overhead associated with repeated HTTP requests. Short polling repeatedly initiates new HTTP connections at set intervals, causing increased network traffic and higher server load, which can degrade responsiveness under scale. WebSockets minimize data transfer and enable real-time communication, making them more efficient for interactive applications requiring low latency and continuous data updates.
Scalability Considerations
WebSockets offer superior scalability compared to short polling by establishing a persistent, full-duplex connection that reduces overhead and server load during continuous data exchanges. Short polling generates frequent HTTP requests, leading to increased latency and higher resource consumption on servers, especially under heavy user traffic. In large-scale applications, WebSockets minimize network congestion and optimize real-time communication efficiency, making them more suitable for scalable, high-demand environments.
Security Implications
WebSockets maintain persistent, full-duplex communication channels, which require robust security measures such as TLS encryption and strict origin validation to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks and unauthorized access. Short polling, while simpler and less resource-intensive, transmits data at frequent intervals without a constant connection, reducing the exposure time but risking data interception if HTTPS is not enforced. Both methods demand secure authentication and authorization protocols, but WebSockets' continuous connection necessitates vigilant monitoring for potential vulnerabilities like cross-site WebSocket hijacking.
Use Cases for WebSockets
WebSockets provide real-time, bidirectional communication ideal for use cases such as online gaming, live sports updates, and collaborative editing tools where immediate data exchange is crucial. They outperform short polling by maintaining a persistent connection, reducing latency and server load during continuous data streams. Applications requiring instant feedback and efficient bandwidth utilization benefit most from WebSockets over short polling.
Use Cases for Short Polling
Short Polling is ideal for applications with low-frequency updates or situations where server push is not feasible, such as legacy systems or environments with strict firewall rules. It suits use cases like periodic status checks in dashboards, simple chat applications with minimal traffic, and scenarios requiring predictable, controlled server load. Short Polling also works well when the overhead of maintaining persistent connections is undesirable or impractical.
Choosing the Right Technology for Your Application
WebSockets provide full-duplex communication ideal for real-time applications like gaming and live chat, offering lower latency and reduced overhead compared to short polling. Short polling suits simpler, less time-sensitive interactions by repeatedly requesting updates at intervals, which can increase server load and latency. Selecting the right technology depends on application requirements for immediacy, scalability, and resource efficiency, with WebSockets favored for continuous streams of data and short polling appropriate for infrequent updates.
WebSockets Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com