Automatic scaling dynamically adjusts your application's resources based on current demand to maintain optimal performance and cost-efficiency. This process ensures seamless handling of traffic spikes without manual intervention, improving user experience and minimizing downtime. Discover how automatic scaling can transform your system's reliability and scalability by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
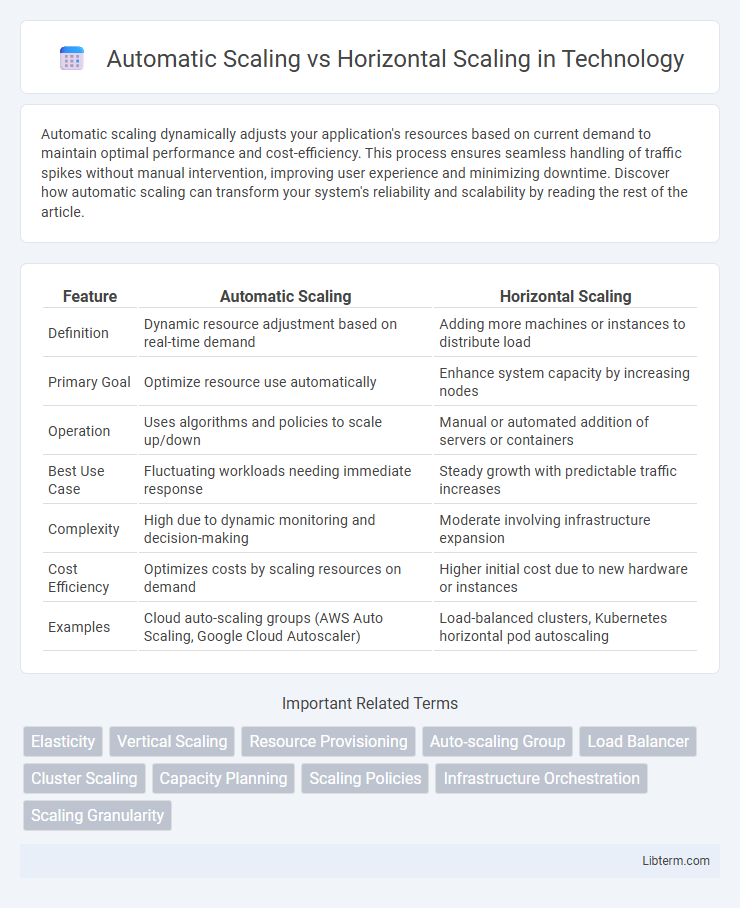
| Feature | Automatic Scaling | Horizontal Scaling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dynamic resource adjustment based on real-time demand | Adding more machines or instances to distribute load |
| Primary Goal | Optimize resource use automatically | Enhance system capacity by increasing nodes |
| Operation | Uses algorithms and policies to scale up/down | Manual or automated addition of servers or containers |
| Best Use Case | Fluctuating workloads needing immediate response | Steady growth with predictable traffic increases |
| Complexity | High due to dynamic monitoring and decision-making | Moderate involving infrastructure expansion |
| Cost Efficiency | Optimizes costs by scaling resources on demand | Higher initial cost due to new hardware or instances |
| Examples | Cloud auto-scaling groups (AWS Auto Scaling, Google Cloud Autoscaler) | Load-balanced clusters, Kubernetes horizontal pod autoscaling |
Introduction to Automatic and Horizontal Scaling
Automatic scaling dynamically adjusts computing resources based on real-time demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency without manual intervention. Horizontal scaling, also known as scaling out, involves adding or removing multiple instances of servers or nodes to handle increased workload, improving fault tolerance and load distribution. Both approaches enhance application availability and responsiveness but differ in control mechanisms and infrastructure requirements.
Defining Automatic Scaling
Automatic scaling refers to the process where cloud systems dynamically adjust computing resources based on real-time demand without manual intervention. This method leverages predefined policies and metrics like CPU utilization or request latency to add or remove instances automatically, optimizing performance and cost-efficiency. Unlike horizontal scaling, which involves adding more machines manually or through scripts, automatic scaling ensures seamless adaptability to workload fluctuations in cloud environments.
Understanding Horizontal Scaling
Horizontal scaling involves adding more machines or nodes to a system to distribute workload and improve performance, allowing applications to handle increased traffic by expanding resources horizontally rather than vertically. Automatic scaling dynamically adjusts the number of active servers or instances based on real-time demand, optimizing resource usage and cost efficiency without manual intervention. Understanding horizontal scaling is essential for designing scalable architectures that maintain high availability and fault tolerance through load balancing across multiple servers.
Key Differences Between Automatic and Horizontal Scaling
Automatic scaling dynamically adjusts computing resources based on real-time demand without manual intervention, optimizing performance and cost efficiency. Horizontal scaling involves adding or removing physical or virtual machines to handle increased loads, focusing on expanding system capacity by distributing workloads across multiple nodes. Key differences include automatic scaling's reliance on algorithms for resource allocation versus horizontal scaling's manual or predefined scaling actions, impacting responsiveness and operational overhead.
Advantages of Automatic Scaling
Automatic scaling offers the advantage of dynamically adjusting resources based on real-time demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency. It eliminates the need for manual intervention by automatically increasing or decreasing the number of instances, which minimizes downtime and supports seamless user experiences. This approach enhances resource utilization, reduces operational overhead, and allows businesses to respond swiftly to fluctuating workloads.
Benefits of Horizontal Scaling
Horizontal scaling improves system performance by adding multiple servers to distribute workload efficiently, enhancing fault tolerance and reducing downtime. It allows seamless capacity expansion without service interruption, accommodating growing traffic and data storage needs. This approach offers cost-effective scalability through commodity hardware, ensuring flexibility and resilience in dynamic environments.
Use Cases for Automatic Scaling
Automatic scaling enables cloud applications to dynamically adjust resource allocation based on real-time demand, preventing performance degradation during traffic spikes. It is ideal for e-commerce websites experiencing unpredictable visitor surges, streaming platforms handling fluctuating viewer counts, and SaaS applications requiring seamless user experience without manual intervention. This approach optimizes cost efficiency by allocating resources only when needed, improving operational agility in fluctuating workloads.
When to Choose Horizontal Scaling
Horizontal scaling is ideal when dealing with growing workloads that require distributing traffic across multiple servers to improve performance and reliability. It is preferred in cloud-native applications, microservices architectures, and systems needing high availability and fault tolerance. Choose horizontal scaling when the goal is to seamlessly add more machines to handle increased demand, rather than upgrading existing hardware components.
Challenges and Considerations
Automatic scaling dynamically adjusts resource allocation based on real-time workloads, reducing the risk of over-provisioning but facing challenges in accurately predicting demand spikes and potential latency during scaling events. Horizontal scaling involves adding or removing discrete instances to handle increased load, requiring careful management of load balancing, data consistency, and statefulness across distributed systems. Both approaches demand thorough monitoring and orchestration to ensure optimal performance and cost-efficiency while minimizing service disruption.
Conclusion: Which Scaling Method is Right for You?
Choosing between automatic scaling and horizontal scaling depends on your application's traffic patterns and resource demands. Automatic scaling offers dynamic resource adjustment based on real-time load, ideal for unpredictable workloads and cost efficiency. Horizontal scaling provides enhanced performance by adding more servers, best suited for applications requiring consistent high availability and fault tolerance.
Automatic Scaling Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com