Point-to-point communication establishes a direct link between two devices, ensuring secure and efficient data transfer without interference from other network traffic. This method enhances speed and reliability, making it ideal for high-performance applications requiring dedicated connections. Discover how implementing point-to-point solutions can optimize your network by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
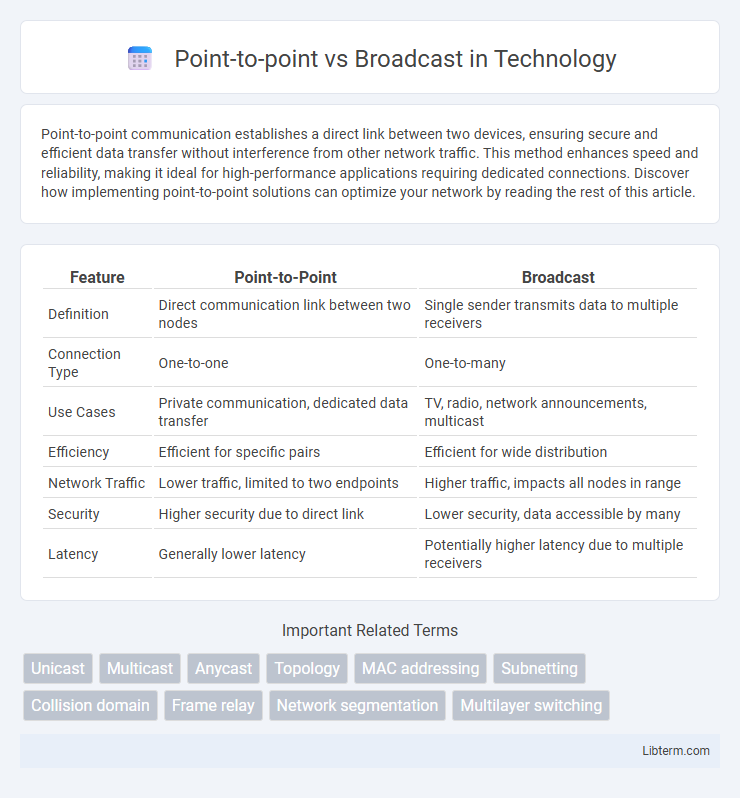
| Feature | Point-to-Point | Broadcast |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct communication link between two nodes | Single sender transmits data to multiple receivers |
| Connection Type | One-to-one | One-to-many |
| Use Cases | Private communication, dedicated data transfer | TV, radio, network announcements, multicast |
| Efficiency | Efficient for specific pairs | Efficient for wide distribution |
| Network Traffic | Lower traffic, limited to two endpoints | Higher traffic, impacts all nodes in range |
| Security | Higher security due to direct link | Lower security, data accessible by many |
| Latency | Generally lower latency | Potentially higher latency due to multiple receivers |
Understanding Point-to-Point and Broadcast Communication
Point-to-point communication involves a direct link between a single sender and a single receiver, ensuring targeted data transfer with minimal interference. Broadcast communication transmits data from one sender to multiple receivers simultaneously, maximizing reach but potentially causing network congestion. Understanding these communication models is essential for designing efficient networks and optimizing data distribution protocols.
Key Differences Between Point-to-Point and Broadcast
Point-to-point communication involves a direct link between two specific devices, ensuring dedicated interaction and minimal interference, whereas broadcast communication transmits data to all devices within a network segment simultaneously. In point-to-point, data security and reliability tend to be higher due to targeted transmission, while broadcast can cause network congestion and increased collisions due to indiscriminate message delivery. Understanding these differences is critical in network design, influencing decisions based on efficiency, scalability, and the nature of data exchange required.
Advantages of Point-to-Point Networks
Point-to-point networks provide dedicated communication channels between devices, ensuring high security and reliable data transmission by minimizing interference. This direct connection allows for faster data transfer rates and reduced latency compared to broadcast networks. Enhanced privacy and efficient bandwidth utilization make point-to-point networks ideal for sensitive or high-performance applications.
Benefits of Broadcast Transmission
Broadcast transmission enhances network efficiency by simultaneously sending data to multiple receivers, reducing bandwidth usage compared to point-to-point connections. It simplifies communication management in large-scale environments such as IPTV and emergency alert systems, where messages must reach diverse audiences quickly. This method minimizes latency and infrastructure costs by eliminating the need for multiple individual transmissions.
Common Use Cases for Point-to-Point
Point-to-point communication is widely used in scenarios requiring direct, secure connections between two devices, such as private data transfers, video conferencing, and dedicated network links in corporate environments. This model ensures low latency and high reliability by avoiding network congestion typical in broadcast systems, making it ideal for sensitive or real-time communications. Industries like finance, healthcare, and telecommunication rely heavily on point-to-point setups to maintain data integrity and confidentiality during transmissions.
Popular Applications of Broadcast Communication
Broadcast communication is widely utilized in applications such as live television and radio transmissions, where data is sent simultaneously to all receivers within a network. Popular platforms like IPTV, digital signage, and emergency alert systems leverage broadcast methods to efficiently distribute content to large audiences. Unlike point-to-point communication, broadcast enables scalable and real-time dissemination of information to multiple users without the need for individual connections.
Scalability and Efficiency Comparison
Point-to-point communication scales poorly as the number of recipients increases, leading to higher resource consumption and network congestion due to multiple redundant transmissions. Broadcast efficiently delivers data to multiple recipients simultaneously, minimizing bandwidth usage and reducing latency in large-scale networks. However, broadcast can cause unnecessary data reception on all nodes, potentially wasting resources in scenarios with selective communication needs.
Security Implications: Point-to-Point vs Broadcast
Point-to-point communication offers enhanced security by establishing a direct, exclusive connection between two endpoints, reducing the risk of interception and unauthorized access. In contrast, broadcast communication transmits data to multiple recipients simultaneously, increasing vulnerability to eavesdropping and data breaches due to the wider exposure of transmitted information. Encryption and robust authentication mechanisms are critical in both methods to mitigate security risks, but point-to-point setups inherently provide a more controlled and secure communication environment.
Cost Considerations for Network Selection
Point-to-point networks typically incur higher costs due to dedicated hardware and infrastructure required for each direct connection, making them less scalable compared to broadcast networks. Broadcast networks reduce expenses by sharing communication channels among multiple devices, lowering per-node costs and simplifying maintenance. Cost-efficiency depends on network size and traffic patterns, with broadcast networks favored for large, multi-device environments and point-to-point preferred for secure, high-throughput links.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Needs
Point-to-point communication provides direct, private data transfer between devices, ideal for secure and efficient connections in small or targeted networks. Broadcast communication sends data simultaneously to all devices within a network segment, suitable for scenarios requiring information dissemination to multiple recipients at once. Assess network size, security requirements, and application specificity to determine whether point-to-point's exclusivity or broadcast's broad reach best aligns with your operational needs.
Point-to-point Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com