Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a specialized hardware chip designed to enhance computer security by securely generating, storing, and managing cryptographic keys. It plays a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive information like passwords, encryption keys, and digital certificates from unauthorized access and tampering. To understand how TPM can protect your data and improve system integrity, keep reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
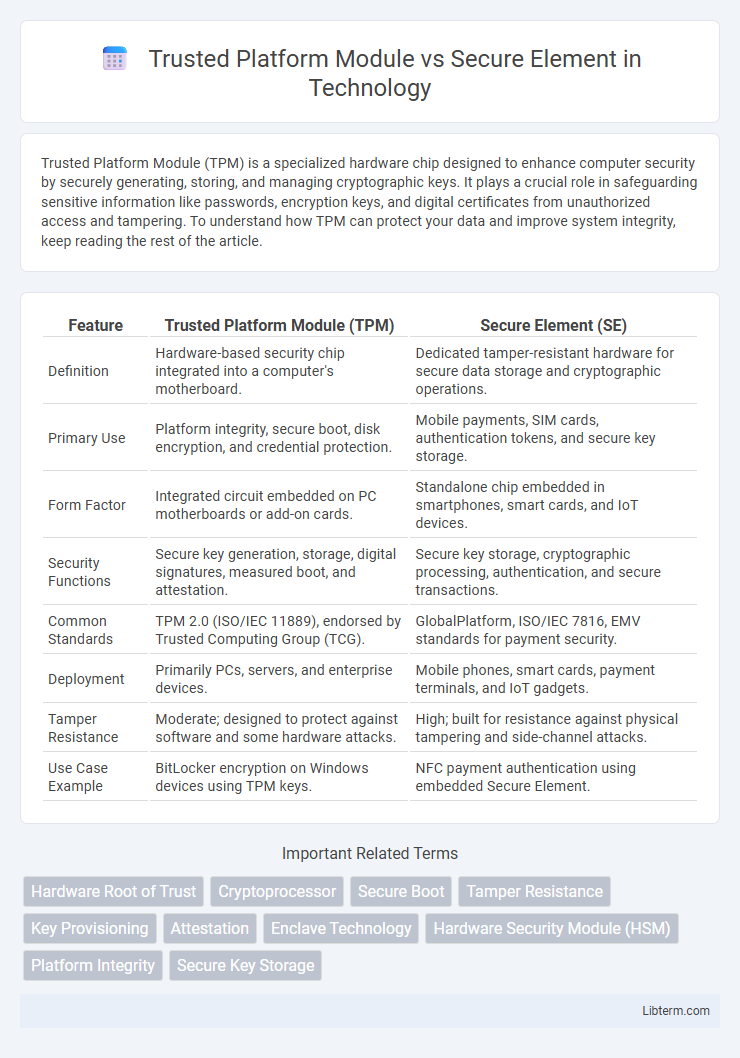
| Feature | Trusted Platform Module (TPM) | Secure Element (SE) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hardware-based security chip integrated into a computer's motherboard. | Dedicated tamper-resistant hardware for secure data storage and cryptographic operations. |
| Primary Use | Platform integrity, secure boot, disk encryption, and credential protection. | Mobile payments, SIM cards, authentication tokens, and secure key storage. |
| Form Factor | Integrated circuit embedded on PC motherboards or add-on cards. | Standalone chip embedded in smartphones, smart cards, and IoT devices. |
| Security Functions | Secure key generation, storage, digital signatures, measured boot, and attestation. | Secure key storage, cryptographic processing, authentication, and secure transactions. |
| Common Standards | TPM 2.0 (ISO/IEC 11889), endorsed by Trusted Computing Group (TCG). | GlobalPlatform, ISO/IEC 7816, EMV standards for payment security. |
| Deployment | Primarily PCs, servers, and enterprise devices. | Mobile phones, smart cards, payment terminals, and IoT gadgets. |
| Tamper Resistance | Moderate; designed to protect against software and some hardware attacks. | High; built for resistance against physical tampering and side-channel attacks. |
| Use Case Example | BitLocker encryption on Windows devices using TPM keys. | NFC payment authentication using embedded Secure Element. |
Introduction to Trusted Platform Module (TPM) and Secure Element (SE)
Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a dedicated microcontroller designed to secure hardware through integrated cryptographic keys, enhancing device integrity and platform trustworthiness. Secure Element (SE) is a tamper-resistant hardware chip that securely stores cryptographic keys and sensitive data, commonly used in mobile payments and identity verification. Both TPM and SE provide robust hardware-based security but serve different ecosystem roles, with TPM focusing on system authentication and SE emphasizing secure storage and transaction protection.
Core Functionality: TPM vs Secure Element
The Trusted Platform Module (TPM) primarily offers hardware-based cryptographic functions such as secure key storage, platform integrity measurement, and attestation, enhancing system security at the motherboard level. The Secure Element (SE) focuses on securely storing sensitive data like cryptographic keys and executing secure applications within an isolated chip environment, often used in mobile payments and identity verification. TPMs integrate deeply with operating systems for platform integrity, while Secure Elements provide isolated, tamper-resistant environments for trustworthy transaction processing and data protection.
Security Architecture Comparison
Trusted Platform Module (TPM) and Secure Element (SE) both provide robust hardware-based security but differ in architecture and application scope. TPM is primarily designed for platform integrity, offering secure cryptographic key storage and attestation capabilities integrated into motherboards, while SE is a tamper-resistant chip focused on secure transactions in mobile and payment systems, managing sensitive data independently from the primary processor. SE typically operates in a more isolated environment with dedicated firmware, making it resilient against a broader range of physical and software attacks compared to the platform-bound TPM.
Use Cases and Applications in Industry
Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is widely used in enterprise environments for hardware-based cryptographic operations, secure boot processes, and integrity measurement, ensuring trusted computing in servers and personal computers. Secure Element (SE) excels in mobile devices and payment systems, providing isolated environments for sensitive data storage and cryptographic key management, crucial for contactless payments, mobile wallets, and IoT security. Both technologies complement each other in industries like finance, healthcare, and telecommunications by enhancing device authentication, data protection, and compliance with regulatory standards.
Hardware Integration and Compatibility
Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a dedicated microcontroller integrated into a computer's motherboard, designed to securely generate and store cryptographic keys, ensuring tight hardware-level integration primarily in PCs and servers. Secure Element (SE) is a tamper-resistant hardware chip embedded in mobile devices, smart cards, or IoT devices, optimized for versatile platform compatibility and secure execution of applications. While TPM offers standardized hardware security mainly in computing environments, Secure Elements provide flexible integration across diverse hardware ecosystems, enhancing security for mobile and connected devices.
Performance and Scalability Differences
Trusted Platform Module (TPM) offers strong hardware-based security with moderate scalability, primarily designed for individual devices and platform-level encryption tasks. Secure Element (SE) provides superior performance in cryptographic operations with enhanced scalability, supporting multiple applications and secure transactions across diverse devices and environments. TPM is optimized for root-of-trust functions with fixed hardware specs, while SE's flexible architecture allows integration in various form factors, boosting scalability for large-scale deployments.
Certification and Compliance Standards
Trusted Platform Module (TPM) and Secure Element (SE) differ significantly in certification and compliance standards, with TPM typically adhering to ISO/IEC 11889 and Common Criteria (CC) certifications targeting hardware-based cryptographic security. Secure Elements often comply with GlobalPlatform specifications and Common Criteria Protection Profiles tailored for secure applications such as payment and identity verification. Both technologies prioritize meeting industry-specific regulations, but SE's compliance scope is broader in mobile and financial services, while TPM is favored in PC and server environments for platform trust.
Cost Considerations and Implementation
Trusted Platform Modules (TPMs) typically offer a lower cost solution for hardware-based security, integrating seamlessly with standard computing devices and benefiting from widespread industry support. Secure Elements (SEs), while more expensive, provide enhanced security by isolating cryptographic processes in dedicated tamper-resistant chips commonly used in mobile devices and payment systems. Implementation complexity varies; TPMs are easier to deploy in PCs and servers due to firmware standards, whereas SEs require specialized hardware design and integration, increasing initial development expenses.
Pros and Cons: TPM vs Secure Element
Trusted Platform Module (TPM) offers robust hardware-based security for device integrity, key storage, and cryptographic operations, making it ideal for system-level protection but is typically limited to PCs and servers. Secure Elements (SE) provide highly tamper-resistant environments for sensitive data and secure transactions, commonly used in mobile devices and payment systems, with the advantage of broader application scope but can be more costly to integrate. TPMs excel in platform authentication and secure boot processes, while SEs offer superior flexibility and isolation for secure applications, highlighting a trade-off between standardized system security and specialized, high-assurance use cases.
Future Trends in Hardware Security Solutions
Trusted Platform Module (TPM) and Secure Element (SE) technologies are evolving to address increasing demands for hardware-based security in IoT and mobile devices. Future trends emphasize enhanced cryptographic capabilities, integration with AI-driven threat detection, and expanded support for post-quantum encryption standards. These advancements aim to provide robust, scalable hardware security solutions that protect sensitive data and ensure device integrity against emerging cyber threats.
Trusted Platform Module Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com