Zero Trust is a cybersecurity framework that assumes no user or device is trustworthy by default, requiring continuous verification before granting access to resources. It minimizes the risk of data breaches by enforcing strict identity verification and least-privilege access policies. Explore the rest of the article to understand how implementing Zero Trust can strengthen your organization's security posture.
Table of Comparison
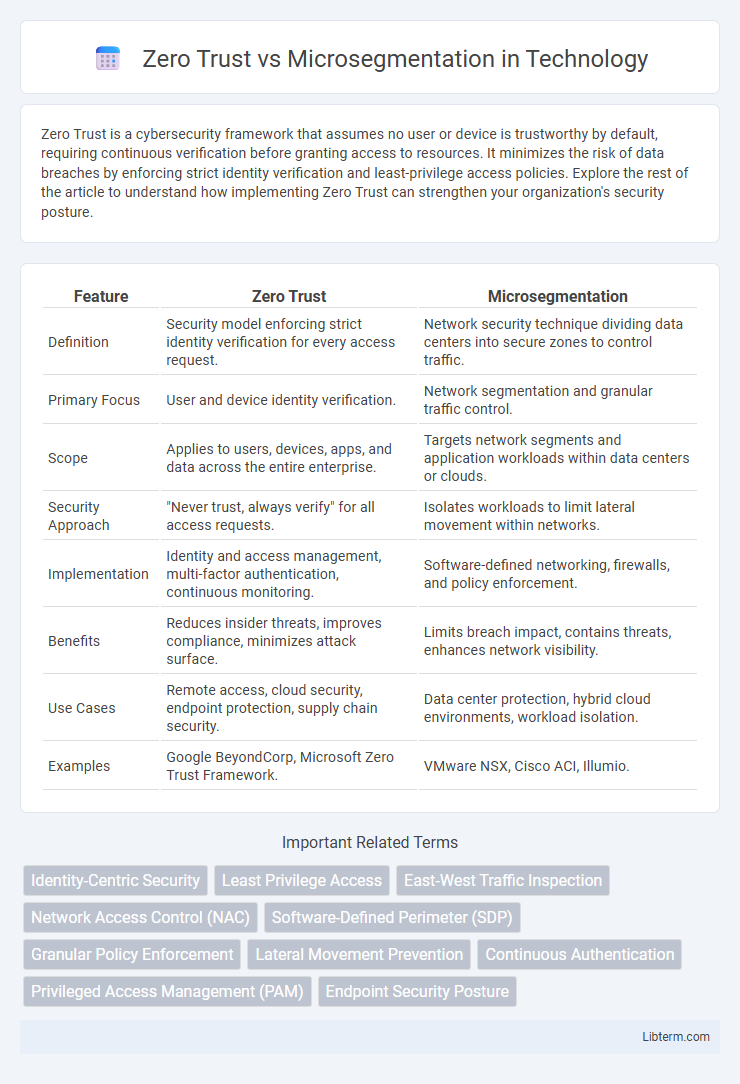
| Feature | Zero Trust | Microsegmentation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Security model enforcing strict identity verification for every access request. | Network security technique dividing data centers into secure zones to control traffic. |
| Primary Focus | User and device identity verification. | Network segmentation and granular traffic control. |
| Scope | Applies to users, devices, apps, and data across the entire enterprise. | Targets network segments and application workloads within data centers or clouds. |
| Security Approach | "Never trust, always verify" for all access requests. | Isolates workloads to limit lateral movement within networks. |
| Implementation | Identity and access management, multi-factor authentication, continuous monitoring. | Software-defined networking, firewalls, and policy enforcement. |
| Benefits | Reduces insider threats, improves compliance, minimizes attack surface. | Limits breach impact, contains threats, enhances network visibility. |
| Use Cases | Remote access, cloud security, endpoint protection, supply chain security. | Data center protection, hybrid cloud environments, workload isolation. |
| Examples | Google BeyondCorp, Microsoft Zero Trust Framework. | VMware NSX, Cisco ACI, Illumio. |
Understanding Zero Trust: Core Principles
Zero Trust security operates on the core principle of "never trust, always verify," enforcing strict identity verification for every user and device attempting to access resources. It relies on continuous monitoring, least-privilege access, and granular policy enforcement to minimize attack surfaces and prevent lateral movement within networks. Microsegmentation supports Zero Trust by dividing networks into isolated segments, enhancing the precision and effectiveness of access controls and threat containment.
Defining Microsegmentation: Key Concepts
Microsegmentation is a network security technique that divides a data center or cloud environment into distinct security segments at a granular level, isolating workloads to prevent lateral movement of threats. This approach uses policies based on identity, context, and application to enforce strict access controls within the microsegments. By implementing microsegmentation, organizations can effectively minimize attack surfaces, mitigate insider threats, and enhance compliance with zero trust security frameworks.
Zero Trust vs Microsegmentation: Main Differences
Zero Trust is a comprehensive cybersecurity framework that requires continuous verification of user identities and strict access controls across the entire network, emphasizing "never trust, always verify." Microsegmentation is a network security technique that divides the network into smaller, isolated segments to minimize lateral movement of threats within a compromised environment. The main difference lies in Zero Trust's holistic approach to security policies beyond just network segmentation, while Microsegmentation specifically enhances network isolation to enforce granular security boundaries.
Security Approaches: Perimeter vs Internal Controls
Zero Trust security eliminates implicit trust by continuously verifying every user and device inside and outside the network perimeter, emphasizing strict identity verification and least-privilege access controls. Microsegmentation enhances internal controls by dividing the network into isolated, granular segments, ensuring that threats cannot move laterally between workloads or applications. Together, these approaches shift focus from traditional perimeter defense to robust internal security, reducing attack surfaces and limiting breach impact.
Benefits of Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture offers robust security by continuously verifying user identities and device health, minimizing trust zones to reduce attack surfaces and prevent unauthorized access. It enables granular access controls and real-time monitoring, which limit lateral movement of threats within networks. Implementing Zero Trust enhances data protection, regulatory compliance, and reduces the risk of data breaches by enforcing strict authentication and access policies across all network resources.
Advantages of Microsegmentation in Network Security
Microsegmentation enhances network security by creating granular security zones that isolate workloads, significantly reducing the attack surface and limiting lateral movement of threats. This approach enables precise policy enforcement based on workload identity and behavior, improving threat detection and response capabilities. Microsegmentation's ability to provide detailed visibility into east-west traffic within data centers supports compliance with regulatory requirements and strengthens overall network resilience.
Implementation Challenges: Zero Trust and Microsegmentation
Implementing Zero Trust requires continuous verification and stringent access controls, often complicated by legacy systems and diverse user environments. Microsegmentation faces challenges in accurately mapping network dependencies and maintaining dynamic policies at scale. Both approaches demand substantial resource allocation, skilled personnel, and integration with existing security architectures to be effective.
Real-World Use Cases: Zero Trust vs Microsegmentation
Zero Trust frameworks enforce strict identity verification for every access request, reducing insider threats and securing cloud environments in organizations like Google and Microsoft. Microsegmentation divides network perimeters into isolated segments, minimizing lateral movement during breaches, which is critical in data centers and financial institutions managing sensitive transactions. Real-world adoption shows Zero Trust's effectiveness in user authentication contrasts with Microsegmentation's role in granular network isolation, both essential for comprehensive cybersecurity.
Integrating Zero Trust and Microsegmentation
Integrating Zero Trust and microsegmentation enhances cybersecurity by enforcing strict access controls and isolating network segments to contain potential threats. Zero Trust principles require continuous verification of user identity and device health, while microsegmentation divides the network into granular zones, minimizing lateral movement of attackers. Together, they provide a robust layered defense that reduces attack surfaces and improves overall threat detection and response capabilities.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Factors to Consider
Choosing between Zero Trust and Microsegmentation requires evaluating organizational security needs, existing infrastructure, and compliance requirements. Zero Trust emphasizes continuous verification and strict access controls across the entire network, ideal for environments with diverse and dynamic endpoints. Microsegmentation offers granular network segmentation to contain breaches, making it suitable for environments needing detailed internal traffic control and minimizing lateral movement risks.
Zero Trust Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com