Cloud computing offers scalable, on-demand access to computing resources, enabling businesses to reduce infrastructure costs and increase operational efficiency. By leveraging cloud platforms, you can enhance collaboration, data storage, and application deployment without the need for extensive physical hardware. Explore the full article to discover how cloud computing can transform your technology strategy and drive innovation.
Table of Comparison
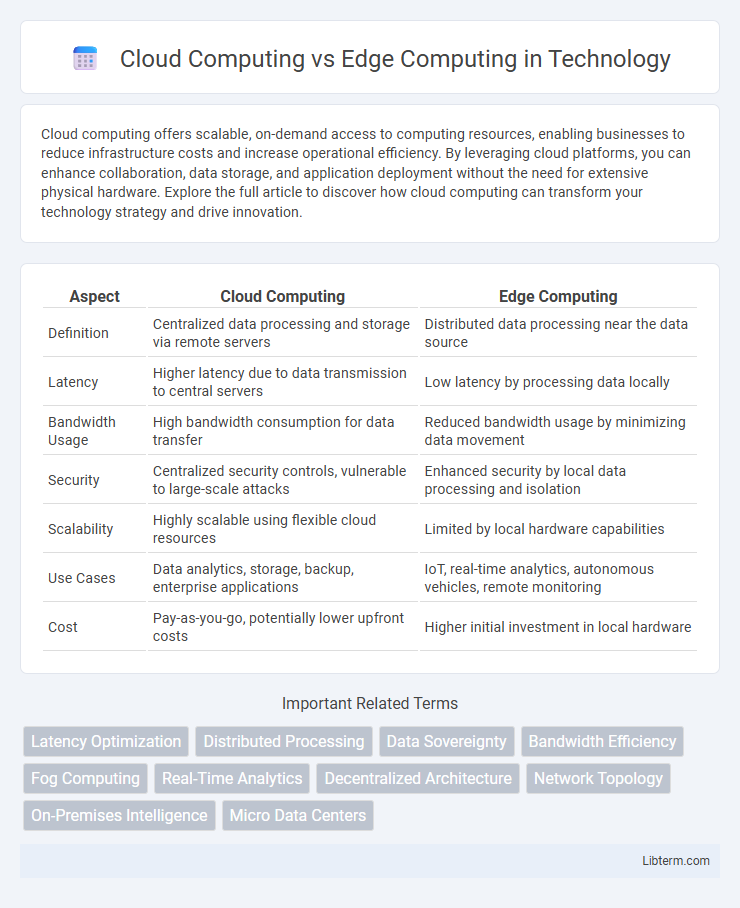
| Aspect | Cloud Computing | Edge Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Centralized data processing and storage via remote servers | Distributed data processing near the data source |
| Latency | Higher latency due to data transmission to central servers | Low latency by processing data locally |
| Bandwidth Usage | High bandwidth consumption for data transfer | Reduced bandwidth usage by minimizing data movement |
| Security | Centralized security controls, vulnerable to large-scale attacks | Enhanced security by local data processing and isolation |
| Scalability | Highly scalable using flexible cloud resources | Limited by local hardware capabilities |
| Use Cases | Data analytics, storage, backup, enterprise applications | IoT, real-time analytics, autonomous vehicles, remote monitoring |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go, potentially lower upfront costs | Higher initial investment in local hardware |
Introduction to Cloud Computing and Edge Computing
Cloud computing delivers scalable computing resources and data storage over the internet through centralized data centers, enabling on-demand access to virtualized infrastructure and services worldwide. Edge computing processes data closer to the source of generation, such as IoT devices or local gateways, reducing latency and bandwidth use by performing computations near the data origin. Combining cloud and edge computing enhances overall system efficiency by balancing centralized processing power with localized real-time analytics.
Core Concepts and Definitions
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics over the internet, enabling on-demand resource access and scalability from centralized data centers. Edge computing processes data closer to the source or end-user devices, reducing latency and bandwidth usage by performing computations at or near the data generation point. Both paradigms serve complementary roles, with cloud computing excelling in large-scale data processing and storage, while edge computing enhances real-time data processing and responsiveness in IoT, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities.
Architecture: Centralized vs Decentralized
Cloud computing architecture is centralized, relying on large data centers to process and store data, enabling scalable and resource-intensive applications. Edge computing employs a decentralized architecture by processing data closer to the data source or end-user device, reducing latency and bandwidth usage. This fundamental difference in architecture impacts data privacy, response times, and network efficiency in diverse application scenarios.
Data Processing and Latency Differences
Cloud computing processes data in centralized data centers, enabling extensive computational power and storage capacity but often experiencing higher latency due to data transmission over long distances. Edge computing performs data processing closer to the source, such as IoT devices or local edge servers, significantly reducing latency and enabling real-time analytics and faster decision-making. The trade-off involves balancing the cloud's scalability and global accessibility against the edge's low-latency responsiveness and localized data handling.
Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud computing offers exceptional scalability by leveraging vast centralized data centers that can dynamically allocate resources on demand, enabling businesses to handle fluctuating workloads efficiently. Edge computing enhances flexibility by processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and enabling real-time decision-making, which is crucial for IoT applications and remote environments. Combining cloud and edge computing allows organizations to scale infrastructure seamlessly while maintaining adaptive, low-latency operations across diverse use cases.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Cloud computing centralizes data processing in remote data centers, creating potential risks such as extended attack surfaces and data breaches due to multi-tenant environments. Edge computing processes data closer to the source by leveraging local devices, reducing latency and limiting data exposure but posing challenges in securing distributed nodes and ensuring consistent privacy policies. Implementing robust encryption, stringent access controls, and compliance with data protection regulations is critical in both models to safeguard sensitive information and maintain user privacy.
Use Cases and Industry Applications
Cloud computing excels in data storage, large-scale analytics, and centralized application hosting, making it ideal for industries like e-commerce, healthcare, and finance that require extensive data processing and scalability. Edge computing is crucial for real-time data processing and low-latency applications in sectors such as autonomous vehicles, manufacturing automation, and smart cities, where immediate decision-making and reduced bandwidth are essential. Hybrid approaches combine cloud and edge computing to optimize performance, security, and cost-efficiency across diverse industry applications.
Cost Implications and Resource Management
Cloud computing offers scalable resource management with predictable operational expenses, ideal for handling large-scale data processing and storage. Edge computing reduces latency and bandwidth costs by processing data locally, which can lower expenses related to data transmission and improve real-time application efficiency. Organizations must balance cloud's centralized resource benefits against edge's cost savings from localized processing to optimize overall infrastructure spending.
Challenges and Limitations
Cloud computing faces challenges such as latency issues, limited bandwidth, and data privacy concerns due to centralized data processing. Edge computing encounters limitations like constrained computational resources, security risks at distributed nodes, and complexity in managing numerous edge devices. Both paradigms must address scalability, interoperability, and consistent data synchronization to optimize performance and reliability.
Future Trends in Cloud and Edge Computing
Future trends in cloud computing emphasize increased adoption of hybrid and multi-cloud architectures to enhance flexibility and scalability for enterprises. Edge computing advancements focus on real-time data processing and reduced latency through distributed computing resources closer to end-users and IoT devices. Integration of AI and 5G technologies will drive innovative edge-cloud collaborations, enabling smarter, faster decision-making in industries like autonomous vehicles and smart cities.
Cloud Computing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com