Latency-based routing improves the speed and performance of your network by directing user requests to the server with the lowest latency, ensuring faster response times and enhanced user experience. This technique dynamically measures network delays to optimize routing decisions, reducing load times and minimizing packet loss. Discover how to implement latency-based routing effectively to boost your system's efficiency in the full article.
Table of Comparison
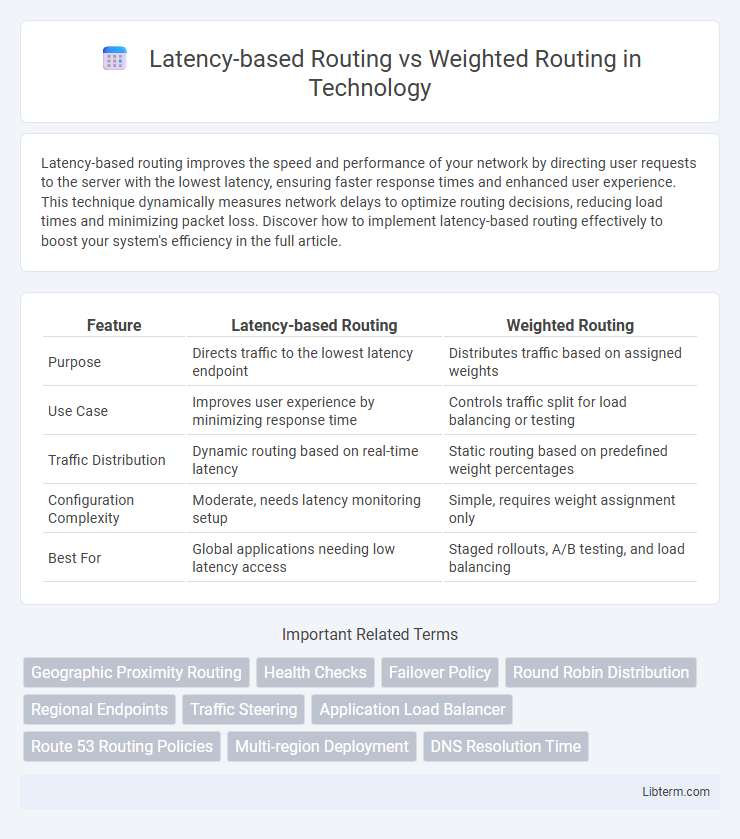
| Feature | Latency-based Routing | Weighted Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Directs traffic to the lowest latency endpoint | Distributes traffic based on assigned weights |
| Use Case | Improves user experience by minimizing response time | Controls traffic split for load balancing or testing |
| Traffic Distribution | Dynamic routing based on real-time latency | Static routing based on predefined weight percentages |
| Configuration Complexity | Moderate, needs latency monitoring setup | Simple, requires weight assignment only |
| Best For | Global applications needing low latency access | Staged rollouts, A/B testing, and load balancing |
Introduction to Routing Strategies
Latency-based routing directs internet traffic to the server with the lowest network latency, enhancing user experience by minimizing response time. Weighted routing distributes traffic based on assigned weights to each server, optimizing resource utilization and balancing workloads according to capacity or priority. Both strategies improve performance and reliability by directing traffic intelligently within global server networks.
What is Latency-Based Routing?
Latency-based routing directs user traffic to the server endpoint that provides the lowest network latency, optimizing website and application performance by minimizing delay. It relies on real-time measurements of latency between the user's location and various server regions to dynamically route requests. This method enhances user experience by reducing load times, particularly for global applications distributed across multiple data centers.
Understanding Weighted Routing
Weighted routing distributes traffic across multiple resources based on assigned weights, enabling granular control over load balancing and resource utilization. This method allows for gradual traffic shifts during deployments, minimizing disruption by directing a specific percentage of users to different endpoints. Latency-based routing, in contrast, routes users based on the lowest network latency to enhance performance by directing traffic to the closest or fastest-performing resource.
Key Differences Between Latency and Weighted Routing
Latency-based routing directs user traffic to the endpoint with the lowest network latency, optimizing for speed and responsiveness by measuring real-time connection delays. Weighted routing distributes traffic according to predefined weights assigned to each endpoint, allowing granular control over traffic allocation regardless of latency. The key difference lies in latency-based routing prioritizing performance metrics dynamically, whereas weighted routing emphasizes traffic distribution based on fixed proportions.
Performance Impacts on User Experience
Latency-based routing directs user requests to the server with the lowest network latency, significantly reducing load times and improving responsiveness for applications requiring real-time interaction. Weighted routing distributes traffic based on predefined weights across multiple servers, enabling load balancing and redundancy but potentially leading to varied latency experiences depending on server locations. Choosing latency-based routing optimizes performance for end-users by minimizing delay, while weighted routing enhances reliability and resource utilization with less focus on immediate user experience.
Use Cases for Latency-Based Routing
Latency-based routing improves user experience by directing traffic to the fastest responding server, ideal for global applications requiring low response times like video streaming and online gaming. It reduces latency by considering real-time network performance and geographic distance between the user and server. Weighted routing, by comparison, is better suited for distributing traffic among multiple servers based on predefined proportions to balance load rather than minimize latency.
When to Choose Weighted Routing
Weighted Routing is ideal when distributing traffic proportionally across multiple endpoints to optimize resource utilization or test new deployments gradually. It allows precise control over traffic allocation percentages, making it suitable for scenarios like blue-green deployments or A/B testing where different versions of an application receive specific traffic loads. This routing method provides flexibility in balancing server loads and managing gradual traffic shifts without relying on network latency metrics.
Scalability and Reliability Considerations
Latency-based routing enhances scalability by dynamically directing user requests to the lowest-latency endpoints, thus efficiently distributing traffic across global servers and reducing response times. Weighted routing offers granular control over traffic distribution by assigning specific weights to resources, which supports scalability through load balancing but may introduce complexity in managing dynamic workloads. Reliability in latency-based routing depends on real-time network performance metrics, ensuring traffic is routed to optimal endpoints, while weighted routing relies on predefined weights that require continuous adjustment to maintain system resilience under varying load conditions.
Security Implications in Routing Decisions
Latency-based routing enhances security by directing traffic to the lowest-latency server, reducing the window for potential interception or man-in-the-middle attacks during data transmission. Weighted routing distributes traffic based on assigned values, which can complicate traffic monitoring and increase exposure to risk if weights are misconfigured, potentially leading to load imbalance and security vulnerabilities. Ensuring proper configuration and continuous monitoring of routing policies is critical to maintaining robust security postures in both latency-based and weighted routing scenarios.
Choosing the Right Routing Strategy for Your Application
Latency-based routing directs user traffic to the endpoint with the lowest latency, ensuring faster response times for latency-sensitive applications like video streaming or online gaming. Weighted routing distributes traffic based on predefined weights, ideal for load balancing or gradual feature rollouts in web applications. Selecting the right strategy depends on prioritizing performance optimization with latency-based routing or traffic management flexibility with weighted routing.
Latency-based Routing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com