DevOps engineers streamline software development and IT operations by implementing automation, continuous integration, and continuous delivery pipelines to accelerate product releases and improve reliability. They leverage cloud platforms, scripting languages, and infrastructure as code to optimize system performance and reduce downtime. Discover how DevOps expertise can transform your workflow by diving deeper into this article.
Table of Comparison
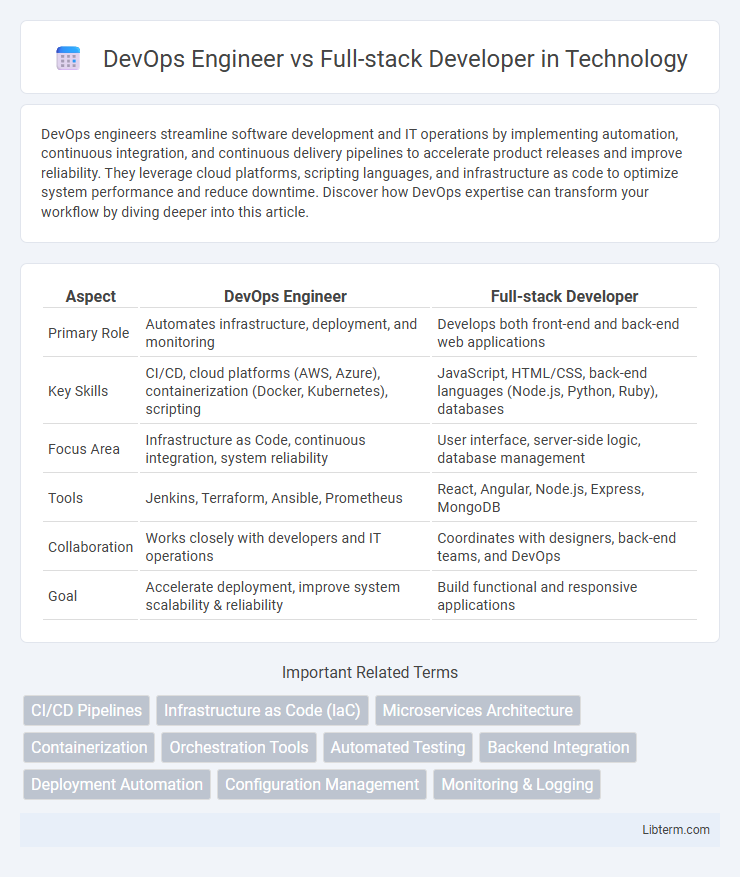
| Aspect | DevOps Engineer | Full-stack Developer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Automates infrastructure, deployment, and monitoring | Develops both front-end and back-end web applications |
| Key Skills | CI/CD, cloud platforms (AWS, Azure), containerization (Docker, Kubernetes), scripting | JavaScript, HTML/CSS, back-end languages (Node.js, Python, Ruby), databases |
| Focus Area | Infrastructure as Code, continuous integration, system reliability | User interface, server-side logic, database management |
| Tools | Jenkins, Terraform, Ansible, Prometheus | React, Angular, Node.js, Express, MongoDB |
| Collaboration | Works closely with developers and IT operations | Coordinates with designers, back-end teams, and DevOps |
| Goal | Accelerate deployment, improve system scalability & reliability | Build functional and responsive applications |
Introduction to DevOps Engineers and Full-stack Developers
DevOps Engineers specialize in automating and streamlining the software development lifecycle through continuous integration, deployment, and infrastructure management using tools like Jenkins, Docker, and Kubernetes. Full-stack Developers handle both front-end and back-end development, working with technologies such as JavaScript, React, Node.js, and databases to build complete web applications. The roles differ in focus, with DevOps emphasizing operational efficiency and system reliability, while Full-stack Developers concentrate on designing and coding comprehensive user-facing functionalities.
Core Responsibilities of DevOps Engineers
DevOps Engineers specialize in automating infrastructure, managing CI/CD pipelines, and ensuring system reliability through monitoring and incident response. They integrate development and operations teams by streamlining software deployment processes and maintaining cloud environments like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. Their core responsibilities include configuration management, container orchestration using tools like Kubernetes and Docker, and fostering collaboration to accelerate delivery cycles and minimize downtime.
Key Duties of Full-stack Developers
Full-stack developers are responsible for designing and implementing both client-side and server-side software, ensuring seamless integration between front-end interfaces and back-end systems. They develop user-facing features, manage databases, and optimize application performance across multiple platforms and devices. Proficiency in languages such as JavaScript, Python, and SQL, along with frameworks like React and Node.js, enables full-stack developers to deliver end-to-end software solutions.
Skill Set Comparison: DevOps vs Full-stack
DevOps Engineers specialize in infrastructure automation, continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, cloud platforms like AWS or Azure, and containerization tools such as Docker and Kubernetes. Full-stack Developers possess expertise in both front-end technologies (JavaScript, React, Angular) and back-end development (Node.js, Python, Ruby), along with database management and API design. While DevOps focuses on optimizing software delivery and operational stability, Full-stack Developers concentrate on building functional and scalable web applications across client and server environments.
Tools and Technologies: Differences and Overlaps
DevOps Engineers primarily utilize tools like Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes, and Terraform to automate infrastructure, manage CI/CD pipelines, and ensure scalable deployments, whereas Full-stack Developers focus on technologies such as JavaScript, React, Node.js, and databases like MongoDB or SQL for building front-end and back-end applications. Both roles overlap in using version control systems like Git and containerization tools like Docker, facilitating collaboration and consistent development environments. Understanding these toolsets highlights the distinct yet complementary nature of DevOps engineering's operational focus and full-stack development's software creation expertise.
Workflow and Collaboration Styles
DevOps Engineers streamline continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines, emphasizing automated testing, infrastructure as code, and monitoring to ensure reliable software deployment. Full-stack Developers engage in end-to-end software creation, handling both front-end and back-end development, focusing on coding, debugging, and iterative feature implementation. Collaboration in DevOps involves cross-functional teams with frequent communication between development and IT operations, while Full-stack Developers often collaborate closely with product managers and designers for rapid feature development and user experience enhancements.
Career Pathways and Growth Opportunities
DevOps Engineers specialize in automation, continuous integration, and infrastructure management, enabling seamless software delivery and system reliability, which opens career pathways towards roles like Site Reliability Engineer or Cloud Architect. Full-stack Developers possess expertise in both front-end and back-end development, allowing them to progress into positions such as Technical Lead or Software Architect, with strong growth potential in product development and user experience design. Both careers offer robust growth opportunities driven by evolving technology trends, with DevOps focusing on operational efficiency and Full-stack emphasizing comprehensive software solutions.
Impact on Software Development Lifecycle
DevOps Engineers streamline the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) by automating deployment pipelines, monitoring performance, and ensuring continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) that lead to faster, more reliable releases. Full-stack Developers influence SDLC through comprehensive coding expertise across front-end and back-end layers, enabling rapid development of feature-rich applications with seamless user experiences. Both roles enhance collaboration and efficiency, but DevOps emphasizes operational stability while Full-stack Developers focus on end-to-end application creation within SDLC.
Salary and Job Market Trends
DevOps Engineers command an average salary of $115,000 annually, driven by growing demand for automation and cloud infrastructure expertise, while Full-stack Developers earn around $105,000, reflecting their broad skill set in both front-end and back-end development. The job market for DevOps Engineers is expanding rapidly due to digital transformation initiatives and increased adoption of CI/CD pipelines, whereas Full-stack Developers remain essential for agile product development and diverse technology stacks. Market trends indicate higher growth rates for DevOps roles, projecting a 22% increase by 2030 compared to 13% for Full-stack Developers according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Choosing the Right Role: DevOps Engineer or Full-stack Developer
Choosing the right role between a DevOps Engineer and a Full-stack Developer depends on individual skills and career goals, as DevOps Engineers specialize in automation, continuous integration, and infrastructure management, while Full-stack Developers focus on both front-end and back-end application development. DevOps roles require expertise in tools like Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes, and cloud platforms such as AWS or Azure, whereas Full-stack Developers need proficiency in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and frameworks like React or Node.js. Understanding project requirements and personal strengths helps determine whether to pursue a path centered on deployment pipelines and system reliability or one focused on software design and user experience.
DevOps Engineer Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com