An Integrated Development Environment (IDE) offers a user-friendly graphical interface for coding, debugging, and managing projects, enhancing your productivity with features like autocomplete and visual debugging tools. In contrast, the Command Line Interface (CLI) allows direct interaction with the system using text-based commands, providing greater control and flexibility for experienced developers. Explore the rest of the article to understand which tool best suits your development workflow.
Table of Comparison
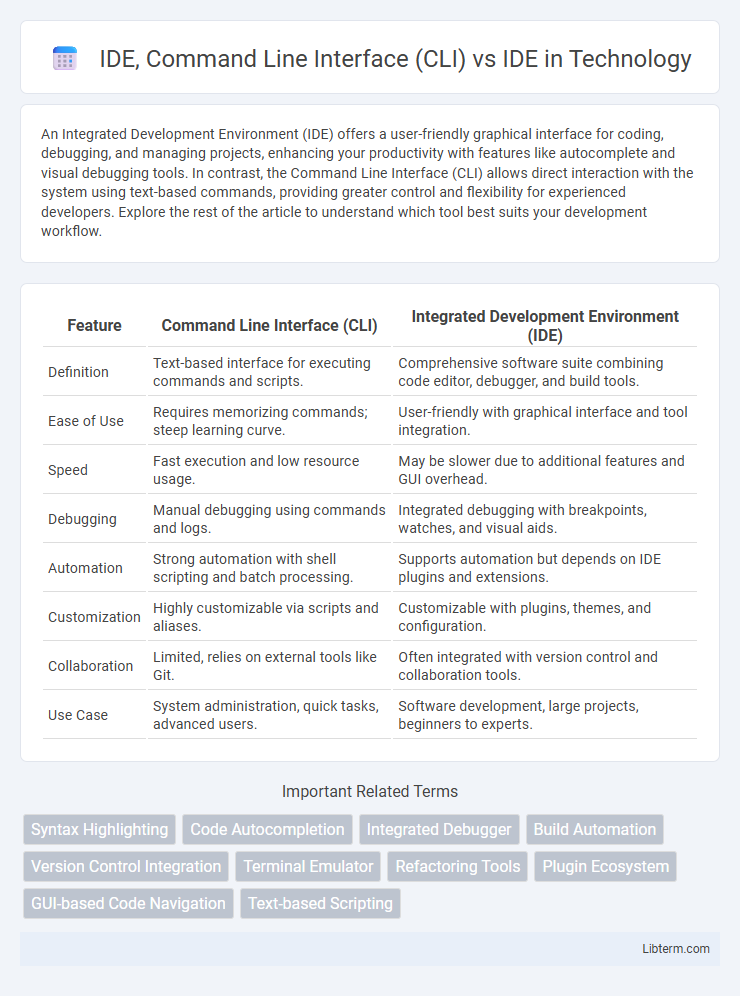
| Feature | Command Line Interface (CLI) | Integrated Development Environment (IDE) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Text-based interface for executing commands and scripts. | Comprehensive software suite combining code editor, debugger, and build tools. |
| Ease of Use | Requires memorizing commands; steep learning curve. | User-friendly with graphical interface and tool integration. |
| Speed | Fast execution and low resource usage. | May be slower due to additional features and GUI overhead. |
| Debugging | Manual debugging using commands and logs. | Integrated debugging with breakpoints, watches, and visual aids. |
| Automation | Strong automation with shell scripting and batch processing. | Supports automation but depends on IDE plugins and extensions. |
| Customization | Highly customizable via scripts and aliases. | Customizable with plugins, themes, and configuration. |
| Collaboration | Limited, relies on external tools like Git. | Often integrated with version control and collaboration tools. |
| Use Case | System administration, quick tasks, advanced users. | Software development, large projects, beginners to experts. |
Introduction to IDEs and Command Line Interfaces
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) offer a comprehensive platform combining code editing, debugging, and build automation, streamlining software development workflows with features such as syntax highlighting, code completion, and integrated version control. Command Line Interfaces (CLIs) provide a text-based input method for interacting with the operating system or development tools, emphasizing precision, scripting capabilities, and resource efficiency without the graphical overhead of IDEs. Developers often choose IDEs for complex projects requiring rich toolsets, while CLIs are preferred for quick tasks, automation, and environments with limited system resources.
Defining IDE: Features and Benefits
An Integrated Development Environment (IDE) is a comprehensive software suite that combines a code editor, compiler, debugger, and build automation tools, streamlining the development process. Key features include syntax highlighting, intelligent code completion, version control integration, and real-time error detection, which significantly enhance coding efficiency and accuracy. IDEs benefit developers by providing a unified interface that reduces context switching and accelerates debugging, testing, and deployment compared to Command Line Interfaces (CLI), which require manual command execution without visual aids.
Understanding Command Line Interface (CLI)
The Command Line Interface (CLI) enables developers to interact directly with the operating system through text-based commands, offering precise control and automation capabilities. Unlike an Integrated Development Environment (IDE), which provides graphical tools, debugging support, and code completion, CLI emphasizes efficiency and low resource usage. Mastery of CLI commands enhances workflows for tasks like version control, scripting, and build automation, crucial for professional software development.
Key Differences: CLI vs IDE
The Command Line Interface (CLI) offers direct text-based interaction with the operating system or software, enabling faster execution of commands and automation through scripting, which is favored for its lightweight performance and precision. Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) provide a comprehensive suite of developer tools including code editors, debuggers, and build automation, enhancing productivity with graphical interfaces, real-time error detection, and code completion features. Key differences revolve around usability and functionality: CLI emphasizes speed and control for experienced users, while IDE focuses on user-friendly features and integrated tools that streamline development workflows.
Productivity: Which is Faster?
Using an IDE typically enhances productivity by providing integrated tools such as code completion, debugging, and error highlighting, which streamline development processes. Conversely, CLI offers faster execution of specific tasks through direct command inputs and scripting automation, benefiting experienced developers with precise control. Ultimately, productivity depends on the complexity of the project and the developer's familiarity, with IDEs favoring rapid development and CLIs excelling in repetitive or system-level operations.
Learning Curve: CLI vs IDE Usability
The learning curve for Command Line Interface (CLI) is steeper compared to an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) due to the need to memorize commands and syntax without visual aids. IDEs enhance usability by offering features like code completion, debugging tools, and graphical interfaces that simplify coding tasks for beginners. While CLI provides powerful control and flexibility, IDEs accelerate development and reduce errors through intuitive design and built-in assistance.
Customization and Flexibility in CLI and IDE
Command Line Interface (CLI) offers extensive customization and flexibility through scripting, aliases, and command chaining, enabling developers to tailor workflows precisely to their needs. Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) provide customization within a graphical interface with plugins, themes, and settings but often impose constraints due to predefined workflows and GUI limitations. CLI excels in automation and resource efficiency, while IDEs enhance user experience with built-in tools but sacrifice some flexibility for ease of use.
Use Cases: When to Choose CLI or IDE
Command Line Interface (CLI) excels in automation, scripting, and managing remote servers, making it ideal for developers comfortable with text-based commands and for tasks requiring minimal resource usage. Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) offer robust features like code completion, debugging tools, and visual interfaces, which are best suited for complex software projects, rapid development, and beginners seeking an intuitive environment. Choosing between CLI and IDE depends on project complexity, developer proficiency, and the need for advanced debugging or automation capabilities.
Popular IDEs and CLI Tools for Developers
Popular Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) like Visual Studio Code, IntelliJ IDEA, and Eclipse offer developers robust code editing, debugging, and project management features with intuitive graphical interfaces. Command Line Interface (CLI) tools such as Git, Node.js, and Docker provide powerful, scriptable workflows and automation, favored for their speed and flexibility in version control, runtime environment management, and containerization. Developers often combine IDEs with CLI tools to leverage the strengths of both, enhancing productivity through seamless integration of visual development and command-line utilities.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Tool for Your Workflow
Selecting between a Command Line Interface (CLI) and an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) depends on the complexity of the project, user proficiency, and specific workflow needs. CLI offers lightweight, fast interactions with precise control ideal for automation and scripting, while IDEs provide comprehensive features including debugging, code completion, and visual design for enhanced productivity in large-scale projects. Developers often combine both tools to leverage CLI's flexibility and IDE's user-friendly environment, optimizing efficiency and adaptability in diverse coding scenarios.
IDE, Command Line Interface (CLI) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com