MQTT is a lightweight messaging protocol designed for efficient communication between devices in IoT networks, enabling real-time data transfer with minimal bandwidth usage. Its publish-subscribe architecture enhances scalability and ensures reliable message delivery even in low-bandwidth or unstable environments. Discover how MQTT can transform Your IoT projects by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
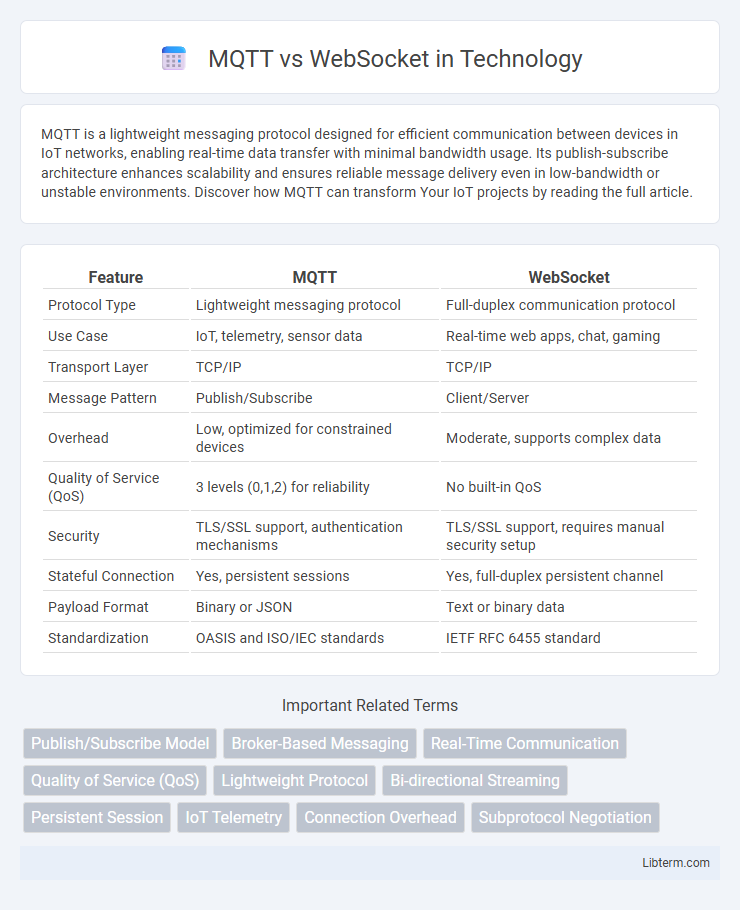
| Feature | MQTT | WebSocket |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol Type | Lightweight messaging protocol | Full-duplex communication protocol |
| Use Case | IoT, telemetry, sensor data | Real-time web apps, chat, gaming |
| Transport Layer | TCP/IP | TCP/IP |
| Message Pattern | Publish/Subscribe | Client/Server |
| Overhead | Low, optimized for constrained devices | Moderate, supports complex data |
| Quality of Service (QoS) | 3 levels (0,1,2) for reliability | No built-in QoS |
| Security | TLS/SSL support, authentication mechanisms | TLS/SSL support, requires manual security setup |
| Stateful Connection | Yes, persistent sessions | Yes, full-duplex persistent channel |
| Payload Format | Binary or JSON | Text or binary data |
| Standardization | OASIS and ISO/IEC standards | IETF RFC 6455 standard |
Introduction to MQTT and WebSocket
MQTT, or Message Queuing Telemetry Transport, is a lightweight messaging protocol designed for low-bandwidth, high-latency, or unreliable networks, commonly used in IoT applications for its efficient publish/subscribe architecture. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol over a single TCP connection, enabling real-time, bidirectional interaction between web browsers and servers. Both MQTT and WebSocket facilitate data transmission, but MQTT is optimized for constrained devices and telemetry, whereas WebSocket excels in web-based interactive applications.
Protocol Overview: MQTT vs WebSocket
MQTT is a lightweight, publish-subscribe messaging protocol designed for low-bandwidth, high-latency, or unreliable networks, commonly used in IoT applications. WebSocket provides full-duplex communication channels over a single TCP connection, enabling real-time, bidirectional data exchange primarily for web applications. While MQTT excels in asynchronous communication with minimal overhead, WebSocket offers persistent connections ideal for interactive client-server applications.
Communication Models: Publish-Subscribe vs Full Duplex
MQTT operates on a publish-subscribe communication model, enabling efficient message distribution through topics and decoupling publishers from subscribers for scalability in IoT networks. WebSocket uses a full duplex communication model, allowing bidirectional, real-time data exchange between clients and servers with low latency. MQTT's pub-sub architecture excels in scenarios requiring asynchronous messaging and device-to-cloud telemetry, while WebSocket suits interactive applications demanding continuous two-way communication.
Performance and Latency Comparison
MQTT is designed for lightweight, low-bandwidth communication, offering minimal overhead and ultra-low latency, making it ideal for IoT devices and real-time telemetry. WebSocket provides full-duplex communication over a single TCP connection, suited for interactive web applications but with higher overhead and slightly increased latency compared to MQTT. Performance benchmarks reveal MQTT can achieve faster message delivery rates and lower CPU usage than WebSocket, especially under constrained network conditions.
Scalability and Network Efficiency
MQTT offers superior scalability through its lightweight protocol design, enabling efficient handling of thousands of concurrent device connections with minimal overhead. WebSocket provides persistent full-duplex communication but typically consumes more network resources, which can limit large-scale deployments. MQTT's optimized message delivery and minimized packet size result in better network efficiency for IoT applications compared to WebSocket.
Security Features and Considerations
MQTT offers robust security features such as TLS encryption for data confidentiality and client authentication through username-password or certificate-based methods, ensuring secure message exchanges in IoT environments. WebSocket also supports TLS to encrypt data streams but primarily relies on existing web security models like same-origin policy and secure cookies for authentication and session management. Both protocols require careful configuration of access controls and secure key management to mitigate risks like man-in-the-middle attacks and unauthorized access.
Use Cases: When to Use MQTT or WebSocket
MQTT excels in IoT environments requiring lightweight, low-bandwidth communication and reliable message delivery, such as remote sensor monitoring and smart home systems. WebSocket suits real-time web applications that need full-duplex communication, including online gaming, live chat, and financial trading platforms. Choosing MQTT or WebSocket depends on specific needs for scalability, message overhead, and network conditions.
Implementation Complexity and Ecosystem
MQTT offers lower implementation complexity due to its lightweight protocol design tailored for constrained devices and efficient publish-subscribe messaging, making it ideal for IoT applications. The MQTT ecosystem features extensive support from platforms like AWS IoT, Eclipse Mosquitto, and HiveMQ, along with broad integration into embedded systems and edge devices. In contrast, WebSocket, while versatile for full-duplex communication over standard HTTP ports, demands more complex setup and lacks the specialized broker infrastructure prevalent in MQTT environments.
Cross-Platform and Device Compatibility
MQTT offers superior cross-platform support due to its lightweight protocol design specifically tailored for constrained devices and IoT environments, enabling seamless communication across diverse hardware and operating systems. WebSocket provides broad compatibility with modern web browsers and supports real-time data exchange but may demand higher computational resources, limiting its effectiveness on low-power or resource-constrained devices. Integrating MQTT with WebSocket bridges compatibility gaps by allowing MQTT messages to be transmitted over WebSocket connections, combining MQTT's efficiency with WebSocket's universal web compatibility.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Protocol
Selecting MQTT or WebSocket depends on application requirements: MQTT excels in low-bandwidth, low-power IoT scenarios due to its lightweight publish/subscribe model, optimized for reliable message delivery and minimal network overhead. WebSocket suits real-time, bidirectional communication needs in web applications, enabling persistent, full-duplex connections for instant data exchange. Evaluating factors like network conditions, message patterns, and resource constraints guides the choice between MQTT's efficiency and WebSocket's interactive capabilities.
MQTT Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com