SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is an open standard for exchanging authentication and authorization data between parties, particularly between identity providers and service providers. It enables single sign-on (SSO) functionality, allowing users to access multiple applications with one set of credentials securely. Discover how SAML can enhance Your organization's security and streamline user access by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
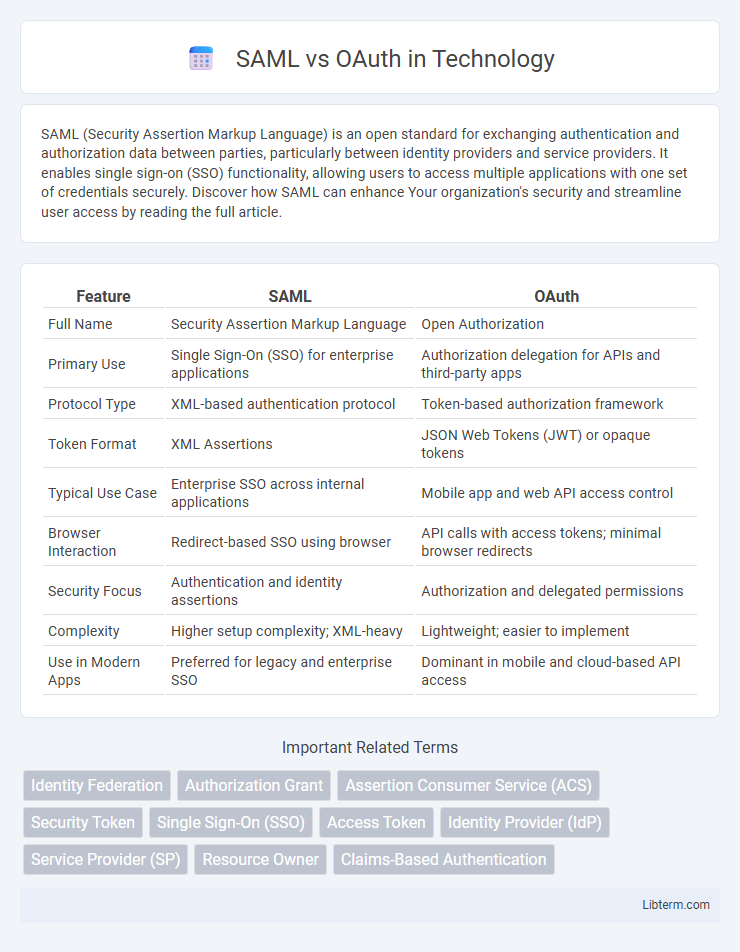
| Feature | SAML | OAuth |
|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Security Assertion Markup Language | Open Authorization |
| Primary Use | Single Sign-On (SSO) for enterprise applications | Authorization delegation for APIs and third-party apps |
| Protocol Type | XML-based authentication protocol | Token-based authorization framework |
| Token Format | XML Assertions | JSON Web Tokens (JWT) or opaque tokens |
| Typical Use Case | Enterprise SSO across internal applications | Mobile app and web API access control |
| Browser Interaction | Redirect-based SSO using browser | API calls with access tokens; minimal browser redirects |
| Security Focus | Authentication and identity assertions | Authorization and delegated permissions |
| Complexity | Higher setup complexity; XML-heavy | Lightweight; easier to implement |
| Use in Modern Apps | Preferred for legacy and enterprise SSO | Dominant in mobile and cloud-based API access |
Introduction to SAML and OAuth
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is an XML-based framework designed for exchanging authentication and authorization data between identity providers and service providers, primarily used in enterprise single sign-on (SSO) scenarios. OAuth is an open standard for access delegation that enables third-party applications to obtain limited access to user resources on HTTP services without revealing user credentials. Both protocols enhance security by enabling centralized authentication but serve different purposes: SAML focuses on identity authentication, while OAuth emphasizes authorization and delegated access.
What is SAML?
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is an open standard for exchanging authentication and authorization data between parties, particularly between an identity provider and a service provider. It enables single sign-on (SSO) by allowing users to authenticate once and gain access to multiple applications without re-entering credentials. SAML uses XML-based assertions to securely transfer user identity information and access rights.
What is OAuth?
OAuth is an open standard for access delegation commonly used to grant websites or applications limited access to user information without exposing passwords. It enables secure authorization by allowing users to log in through third-party services like Google or Facebook, providing tokens that grant specific permissions. OAuth is primarily designed for authorization, facilitating resource access control across distributed systems and APIs.
Key Differences Between SAML and OAuth
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) primarily serves as a protocol for Single Sign-On (SSO) by exchanging authentication and authorization data between an identity provider and a service provider, often used in enterprise environments. OAuth functions as an authorization framework that enables third-party applications to obtain limited access to user resources without exposing credentials, commonly used for delegated access in web and mobile applications. Key differences include SAML's reliance on XML-based assertions and its focus on user identity verification, whereas OAuth uses JSON and tokens for access delegation without directly handling authentication.
Use Cases: When to Use SAML vs OAuth
SAML is best suited for enterprise single sign-on (SSO) scenarios where secure identity federation between organizations is required, such as accessing corporate intranets and cloud-based applications within a trusted ecosystem. OAuth excels in delegated authorization use cases, enabling third-party applications to access user resources on platforms like Google or Facebook without sharing user credentials. Choosing SAML over OAuth depends on the need for identity assertion in authentication workflows, while OAuth prioritizes granting limited access tokens for resource authorization.
Authentication vs Authorization Explained
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) primarily facilitates authentication by enabling secure single sign-on (SSO) for users across different domains, transmitting identity assertions between identity providers and service providers. OAuth, in contrast, focuses on authorization, granting third-party applications limited access to user resources without exposing credentials by issuing tokens. Understanding their distinct roles clarifies that SAML verifies user identity, while OAuth controls resource access permissions.
Security Considerations: SAML vs OAuth
SAML and OAuth both provide robust security frameworks, but their mechanisms differ significantly: SAML uses XML-based assertions primarily for single sign-on (SSO) with strong identity verification, while OAuth uses token-based authorization to grant access without sharing credentials. SAML's reliance on signed XML messages ensures message integrity and authenticity, making it ideal for enterprise environments requiring rigorous identity proofing. OAuth, often used in mobile and web applications, must implement additional layers like HTTPS and token expiration to mitigate risks such as token interception and replay attacks.
Implementation Challenges and Best Practices
Implementing SAML poses challenges such as complex XML-based assertions, intricate configuration requirements, and limited support for mobile applications, while OAuth implementation faces difficulties managing token security, scope definition, and handling various grant types effectively. Best practices for SAML include thorough metadata exchange, rigorous certificate management, and extensive testing in various identity provider scenarios. For OAuth, recommended strategies involve using secure token storage, strict scope enforcement, and employing Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE) to enhance authorization code flow security.
Industry Adoption and Real-World Examples
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) dominates enterprise environments for single sign-on (SSO) in sectors like finance and government, with companies such as Salesforce and Microsoft utilizing SAML for secure identity federation. OAuth, favored in consumer-facing applications and API authorization, powers platforms like Google, Facebook, and Twitter to enable third-party app access without sharing passwords. Both protocols achieve broad industry adoption but serve distinct purposes: SAML excels in identity assertions within controlled enterprise settings, while OAuth is optimized for delegated authorization in web and mobile app ecosystems.
Conclusion: Choosing Between SAML and OAuth
Choosing between SAML and OAuth depends on the specific use case, with SAML being ideal for enterprise single sign-on (SSO) scenarios requiring robust identity federation and secure authentication. OAuth excels in delegated authorization, enabling applications to access resources on behalf of users without sharing credentials, making it suitable for mobile and web app integrations. Understanding the security requirements, user experience, and system architecture is crucial to selecting the appropriate protocol.
SAML Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com