Single cloud environments simplify IT infrastructure by consolidating resources into one unified platform, enhancing efficiency and reducing operational costs. They provide seamless integration, improved scalability, and centralized management, making it easier to monitor and secure your data. Discover more about how single cloud solutions can transform your business in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
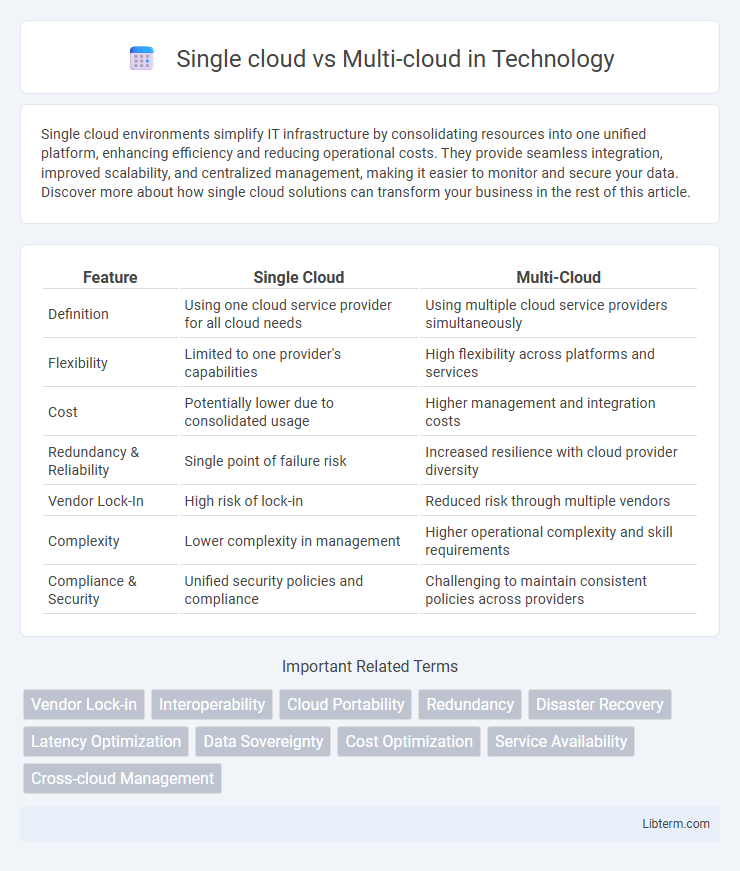
| Feature | Single Cloud | Multi-Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Using one cloud service provider for all cloud needs | Using multiple cloud service providers simultaneously |
| Flexibility | Limited to one provider's capabilities | High flexibility across platforms and services |
| Cost | Potentially lower due to consolidated usage | Higher management and integration costs |
| Redundancy & Reliability | Single point of failure risk | Increased resilience with cloud provider diversity |
| Vendor Lock-In | High risk of lock-in | Reduced risk through multiple vendors |
| Complexity | Lower complexity in management | Higher operational complexity and skill requirements |
| Compliance & Security | Unified security policies and compliance | Challenging to maintain consistent policies across providers |
Introduction to Single Cloud and Multi-Cloud
Single cloud environments utilize one cloud service provider, offering streamlined management, consistent security policies, and simplified billing structures. Multi-cloud strategies deploy services across multiple cloud providers to enhance redundancy, optimize performance, and avoid vendor lock-in. Enterprises adopting multi-cloud benefit from tailored solutions but face increased complexity in integration and governance.
Defining Single Cloud Architecture
Single cloud architecture refers to the deployment of computing resources and services within one cloud provider's ecosystem, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP). This approach centralizes infrastructure management, reducing complexity and optimizing performance by leveraging the provider's integrated tools and services. Organizations often choose single cloud architectures for streamlined security, compliance, and cost management, benefiting from the provider's native capabilities and continuous innovation.
Understanding Multi-Cloud Environments
Multi-cloud environments involve using multiple cloud service providers to optimize performance, reduce risks, and avoid vendor lock-in, contrasting with a single cloud approach that relies on one provider. Understanding multi-cloud strategies requires evaluating interoperability, data integration, and consistent security policies across platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. Organizations adopting multi-cloud benefit from increased flexibility, scalability, and redundancy while facing challenges in management complexity and cost control.
Key Differences: Single Cloud vs Multi-Cloud
Single cloud environments centralize resources within one provider, simplifying management and reducing vendor complexity but may increase risk of downtime or vendor lock-in. Multi-cloud strategies distribute workloads across multiple providers, enhancing redundancy, flexibility, and resilience while potentially increasing integration challenges and operational overhead. Key differences lie in risk management, scalability options, and cost structures aligned with organizational needs.
Benefits of Single Cloud Strategy
A single cloud strategy offers streamlined management by centralizing resources within one cloud provider, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing complexity. It ensures consistent security protocols and compliance standards across the infrastructure, minimizing risk and simplifying governance. Cost optimization is achieved through volume discounts and simplified billing, making budgeting and financial forecasting more predictable.
Advantages of Multi-Cloud Adoption
Multi-cloud adoption offers enhanced resilience by distributing workloads across multiple cloud providers, reducing the risk of service outages. It enables organizations to leverage best-of-breed services tailored to specific business needs, optimizing performance and cost efficiency. Increased data sovereignty and compliance management are achievable by selecting regional cloud providers aligned with regulatory requirements.
Challenges of Single Cloud Deployment
Single cloud deployment poses challenges such as vendor lock-in, which limits flexibility and increases dependency on a single provider's ecosystem and pricing policies. Scalability can be restricted by the capacity and geographic distribution of the chosen cloud, potentially impacting performance and disaster recovery options. Security concerns arise from concentrating critical workloads in one environment, increasing the risk of data breaches and service outages.
Security and Compliance Considerations
Single cloud environments simplify security management by centralizing control and reducing the attack surface, which streamlines compliance with standards like GDPR and HIPAA. Multi-cloud strategies increase complexity due to varied security protocols and disparate compliance requirements across providers, necessitating robust governance frameworks and continuous monitoring. Organizations must implement unified security policies and automated compliance tools to mitigate risks and ensure data protection in multi-cloud architectures.
Cost Implications: Single Cloud vs Multi-Cloud
Single cloud environments often benefit from volume discounts and simplified management, leading to lower operational costs and predictable billing. Multi-cloud strategies incur higher expenses due to complex integration, data transfer fees, and vendor-specific training requirements across platforms. Organizations must weigh the increased flexibility and risk mitigation of multi-cloud setups against the efficiency and cost advantages of a single cloud provider.
Choosing the Best Cloud Strategy for Your Business
Selecting the best cloud strategy involves evaluating single cloud and multi-cloud options based on scalability, cost efficiency, and vendor risk. Single cloud solutions offer simplified management and deep integration with a specific provider's tools, ideal for businesses prioritizing streamlined operations. Multi-cloud strategies enhance redundancy and flexibility by leveraging multiple cloud vendors like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, supporting risk mitigation and optimizing workloads across diverse platforms.
Single cloud Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com