Clear-box testing focuses on evaluating the internal structures and workings of an application, ensuring every code path and logic condition is thoroughly verified. This testing method helps identify hidden bugs and security vulnerabilities by analyzing the source code directly. Discover how clear-box testing can improve your software quality in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
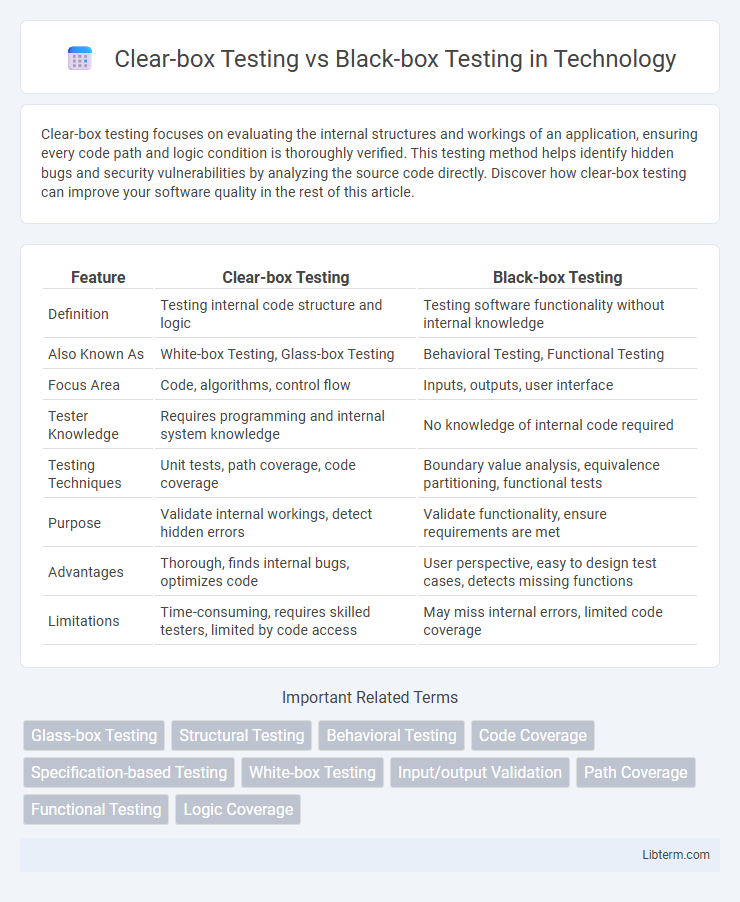
| Feature | Clear-box Testing | Black-box Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Testing internal code structure and logic | Testing software functionality without internal knowledge |
| Also Known As | White-box Testing, Glass-box Testing | Behavioral Testing, Functional Testing |
| Focus Area | Code, algorithms, control flow | Inputs, outputs, user interface |
| Tester Knowledge | Requires programming and internal system knowledge | No knowledge of internal code required |
| Testing Techniques | Unit tests, path coverage, code coverage | Boundary value analysis, equivalence partitioning, functional tests |
| Purpose | Validate internal workings, detect hidden errors | Validate functionality, ensure requirements are met |
| Advantages | Thorough, finds internal bugs, optimizes code | User perspective, easy to design test cases, detects missing functions |
| Limitations | Time-consuming, requires skilled testers, limited by code access | May miss internal errors, limited code coverage |
Introduction to Software Testing Approaches
Clear-box testing involves evaluating the internal structures and working mechanisms of software, allowing testers to verify code flow, logic, and system architecture precision. Black-box testing focuses on assessing software functionality without knowledge of internal code, emphasizing input-output correctness and user experience validation. Both methodologies are crucial in comprehensive software testing strategies to ensure robustness and quality assurance.
What is Clear-box Testing?
Clear-box testing, also known as white-box testing, involves examining the internal structures or workings of an application, focusing on code logic, paths, and conditions. Testers require knowledge of the source code to create test cases targeting specific functions, branches, and statements. This testing method is essential for identifying hidden errors, optimizing code efficiency, and ensuring comprehensive coverage of all execution paths.
What is Black-box Testing?
Black-box testing evaluates software functionality without any knowledge of the internal code structure, focusing solely on input-output behavior to ensure the application meets specified requirements. This method involves testing user interfaces, APIs, and system integrations to identify discrepancies, errors, and missing functionalities from an end-user perspective. It is widely used in functional, acceptance, and system testing phases to validate software behavior against defined use cases and business rules.
Key Differences Between Clear-box and Black-box Testing
Clear-box testing involves detailed analysis of internal code structures and logic, allowing testers to design test cases based on the software's internal workings, while black-box testing evaluates software functionality without any knowledge of the internal code, focusing solely on input-output behaviors. Clear-box testing requires access to source code for path coverage and branch testing, whereas black-box testing emphasizes requirement validation and user experience through functional testing techniques. The main differences lie in transparency, testing approach, and test design criteria, with clear-box being white-box and code-driven, and black-box being specification-driven and behavior-oriented.
Advantages of Clear-box Testing
Clear-box testing offers the advantage of thorough code coverage by examining internal structures and logic, enabling early detection of hidden errors. It enhances defect identification within specific paths, conditions, and branches, ensuring high accuracy and reliability in software validation. Clear-box testing also facilitates optimization of code quality and efficient debugging, reducing maintenance costs over time.
Advantages of Black-box Testing
Black-box testing offers the advantage of evaluating software functionality without requiring knowledge of the internal code structure, making it accessible to testers with varying technical expertise. It effectively identifies discrepancies between user requirements and actual behavior by focusing on input-output validation, enhancing user-centric quality assurance. This method also enables testing of large and complex applications by simulating real-world scenarios, thus improving overall software reliability and user satisfaction.
Limitations of Clear-box Testing
Clear-box testing faces significant limitations due to its reliance on comprehensive knowledge of the internal code structure, making it time-consuming and impractical for large or complex systems. It often fails to detect unimplemented functionalities or missing requirements since it primarily validates what exists within the code rather than what the system should do. The method also requires skilled testers with programming expertise, limiting its applicability in environments where such resources are scarce.
Limitations of Black-box Testing
Black-box testing faces limitations such as its inability to uncover hidden code errors and internal security vulnerabilities due to lack of access to source code. Test coverage can be incomplete because it relies exclusively on functional requirements and external outputs, potentially missing edge cases or unhandled exceptions. These constraints make black-box testing less effective for identifying structural issues compared to clear-box testing methodologies.
When to Use Clear-box vs Black-box Testing
Clear-box testing is ideal when detailed knowledge of the internal code structure, logic, and paths is available, enabling thorough validation of control flow and data handling. Black-box testing is preferred when the focus is on verifying functionality against requirements without access to internal implementation, making it suitable for user acceptance and system integration testing. Use clear-box testing during unit and security testing phases, while black-box testing excels in functional, usability, and regression testing scenarios.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Testing Method
Clear-box testing offers in-depth code coverage by examining internal structures and logic, ideal for identifying hidden errors and ensuring code quality. Black-box testing focuses on functionality and user experience by validating software behavior against requirements, making it essential for end-user acceptance. Selecting the right testing method depends on project goals, development stage, and resource availability, often combining both to maximize defect detection and software reliability.
Clear-box Testing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com