Data Fabric seamlessly integrates data management across cloud and on-premises environments, ensuring unified access and improved data quality. It leverages advanced automation and AI-driven analytics to enhance data governance, security, and real-time insights. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Data Fabric can transform your organization's data strategy.
Table of Comparison
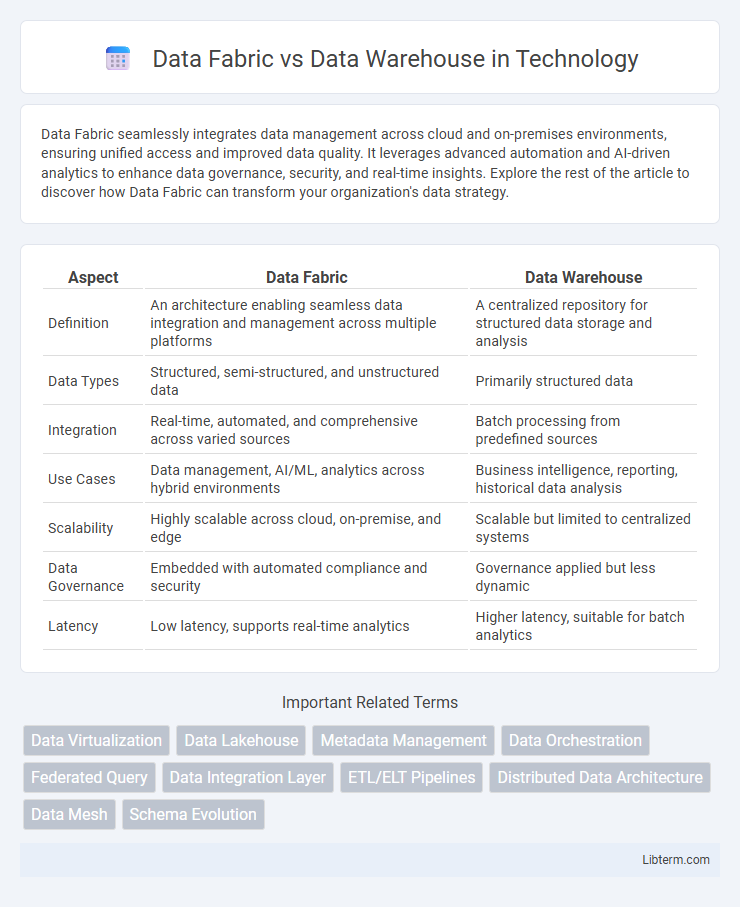
| Aspect | Data Fabric | Data Warehouse |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An architecture enabling seamless data integration and management across multiple platforms | A centralized repository for structured data storage and analysis |
| Data Types | Structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data | Primarily structured data |
| Integration | Real-time, automated, and comprehensive across varied sources | Batch processing from predefined sources |
| Use Cases | Data management, AI/ML, analytics across hybrid environments | Business intelligence, reporting, historical data analysis |
| Scalability | Highly scalable across cloud, on-premise, and edge | Scalable but limited to centralized systems |
| Data Governance | Embedded with automated compliance and security | Governance applied but less dynamic |
| Latency | Low latency, supports real-time analytics | Higher latency, suitable for batch analytics |
Introduction to Data Fabric and Data Warehouse
Data Fabric is an integrated architecture designed to provide seamless data access, management, and orchestration across diverse data environments, combining on-premises, cloud, and hybrid data sources. Data Warehouse, on the other hand, is a centralized repository that stores structured data from multiple sources, optimized for query performance and analytics. While Data Warehouses focus on consolidating and analyzing historical data, Data Fabric emphasizes real-time data integration and agility across a distributed data ecosystem.
Core Concepts: Data Fabric Explained
Data Fabric integrates diverse data sources and management tools into a unified architecture, enabling seamless access, governance, and real-time analytics across hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Data Warehouse centralizes structured data into a single repository optimized for batch processing and historical analysis, primarily supporting business intelligence. Core to Data Fabric is its adaptive metadata layer and automation, which streamline data discovery, integration, and orchestration beyond traditional storage-centric approaches found in Data Warehouses.
Core Concepts: Data Warehouse Explained
A Data Warehouse is a centralized repository that stores large volumes of structured data from multiple sources, optimized for query and analysis to support business intelligence. It integrates data through Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) processes to ensure consistency and accuracy across historical datasets. The architecture emphasizes schema-on-write, enabling fast, reliable reporting and analytics on well-defined, cleaned data.
Architecture Comparison: Data Fabric vs Data Warehouse
Data Fabric architecture integrates various data sources across on-premises and cloud environments through metadata-driven automation, enabling real-time data discovery, governance, and integration. Data Warehouse architecture centralizes structured data into a single repository optimized for query performance and historical analysis, relying on ETL processes for data ingestion and transformation. Unlike the static, schema-defined structure of Data Warehouses, Data Fabric offers dynamic, scalable, and federated data management supporting diverse data types and use cases.
Data Integration Approaches
Data Fabric employs a unified data integration approach that dynamically connects diverse data sources across cloud and on-premises environments, enabling seamless access and real-time data processing. In contrast, Data Warehouse relies on a centralized integration model, consolidating structured data into a single repository optimized for analytics and reporting. Data Fabric's flexible architecture supports complex, heterogeneous data integration, while Data Warehouse prioritizes schema-on-write methods and predefined ETL workflows.
Scalability and Flexibility Differences
Data fabric offers superior scalability by integrating diverse data sources through a unified architecture that supports real-time processing and dynamic data management across hybrid and multi-cloud environments. In contrast, data warehouses are typically less flexible, relying on structured schemas and batch processing that limit adaptability to rapidly changing data types and volumes. The flexibility of data fabric enables seamless scaling and on-demand access to both structured and unstructured data, making it ideal for complex, evolving data ecosystems.
Real-Time Data Processing Capabilities
Data fabric architecture enables real-time data processing by seamlessly integrating diverse data sources and supporting continuous data flows, facilitating immediate analytics and decision-making. Data warehouses primarily rely on batch processing, which can introduce latency and delay access to the most current data for analysis. The real-time capabilities of data fabric platforms offer superior agility for dynamic business environments compared to traditional data warehouse systems.
Security and Governance Features
Data Fabric integrates comprehensive security and governance features by enabling consistent policy enforcement, real-time data lineage tracking, and automated compliance across distributed data environments. Data Warehouses traditionally implement rigid access controls and auditing mechanisms but often lack the dynamic, end-to-end governance capabilities necessary for modern hybrid and multi-cloud architectures. Enterprises prioritize Data Fabric solutions for enhanced data protection, unified metadata management, and adaptive security protocols that align with regulatory requirements such as GDPR and HIPAA.
Use Cases: When to Choose Data Fabric or Data Warehouse
Data warehouses excel in structured data storage and complex querying for historical analysis, making them ideal for business intelligence, reporting, and regulatory compliance use cases. Data fabric supports real-time data integration across diverse sources and formats, enabling agile analytics, data governance, and hybrid or cloud-native environments. Organizations should choose data warehouses for stable, centralized storage with consistent data models, while data fabrics suit dynamic, multi-source ecosystems requiring seamless data accessibility and orchestration.
Future Trends in Data Management
Data Fabric offers a dynamic, AI-driven architecture enabling seamless data integration and real-time access across distributed environments, contrasting with the more static and centralized nature of Data Warehouses. Future trends highlight the rise of Data Fabric as it supports hybrid cloud ecosystems and enhances data governance through automation and metadata-driven intelligence. As enterprises demand more agile and scalable data solutions, Data Fabric's ability to unify diverse data sources and facilitate advanced analytics is reshaping the landscape of data management.
Data Fabric Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com