Password authentication is a fundamental security mechanism that verifies a user's identity by requiring a secret combination of characters. Strong passwords, combined with best practices such as regular updates and avoiding common phrases, significantly enhance protection against unauthorized access. Discover how to create and manage robust passwords effectively by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
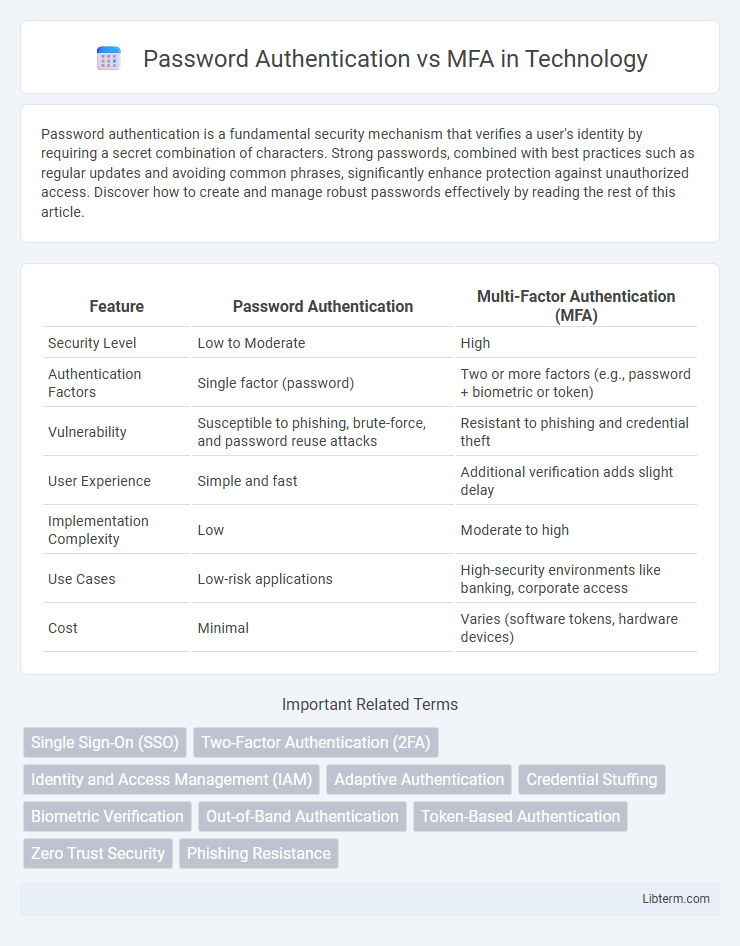
| Feature | Password Authentication | Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) |
|---|---|---|
| Security Level | Low to Moderate | High |
| Authentication Factors | Single factor (password) | Two or more factors (e.g., password + biometric or token) |
| Vulnerability | Susceptible to phishing, brute-force, and password reuse attacks | Resistant to phishing and credential theft |
| User Experience | Simple and fast | Additional verification adds slight delay |
| Implementation Complexity | Low | Moderate to high |
| Use Cases | Low-risk applications | High-security environments like banking, corporate access |
| Cost | Minimal | Varies (software tokens, hardware devices) |
Introduction to Password Authentication vs MFA
Password authentication relies on a single factor--something the user knows, typically a password or PIN--making it vulnerable to attacks such as phishing, brute force, and credential stuffing. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) combines two or more independent credentials, such as passwords, hardware tokens, biometric verification, or one-time codes, significantly enhancing security by requiring multiple forms of identity verification. Implementing MFA reduces the risks of unauthorized access by ensuring that even if one factor is compromised, additional layers prevent breaches.
Understanding Password Authentication
Password authentication relies on a single factor--usually a secret string--used to verify user identity, making it vulnerable to attacks such as phishing, brute force, and credential stuffing. Its simplicity and widespread implementation across platforms make it a common method for secure access, but its dependence on users choosing strong, unique passwords is a critical limitation. Improving security involves combining passwords with additional factors, but understanding password authentication is essential for appreciating these layered defenses.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) enhances security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors, such as something they know (password), something they have (a smartphone or hardware token), or something they are (biometric data like fingerprints). This layered approach reduces the risk of unauthorized access compared to traditional password authentication, which relies solely on a single factor. Implementing MFA significantly mitigates risks associated with password theft, phishing, and credential reuse attacks.
Key Differences Between Passwords and MFA
Password authentication relies solely on a single factor--typically something the user knows, such as a password or PIN--making it vulnerable to phishing, brute force, and credential stuffing attacks. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) enhances security by requiring two or more independent credentials from different categories: something the user knows (password), something the user has (a hardware token or smartphone app), or something the user is (biometric verification). This layered approach significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, as compromising one factor alone is insufficient for authentication.
Security Risks of Password-Only Systems
Password-only authentication systems face significant security risks due to vulnerabilities like password reuse, phishing attacks, and brute-force attempts, which can lead to unauthorized access and data breaches. Without additional layers of verification, stolen or compromised passwords provide direct entry points for cybercriminals, increasing the likelihood of identity theft and financial fraud. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) mitigates these risks by requiring multiple forms of verification, substantially enhancing account security beyond the limitations of password-only methods.
Advantages of Implementing MFA
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) significantly enhances security by requiring multiple verification methods, making unauthorized access exponentially harder compared to password-only authentication. It reduces the risk of credential theft, phishing attacks, and brute force attempts by combining something you know (password) with something you have (token) or something you are (biometric). Organizations deploying MFA experience lower data breach incidents, improved regulatory compliance, and increased user trust through stronger account protection.
User Experience: Passwords vs MFA
Passwords offer a straightforward login process but often suffer from weak security and frequent reset frustrations, impacting user experience negatively. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) enhances security by requiring additional verification methods such as biometrics or one-time codes, which can add slight complexity but significantly reduce unauthorized access risks. User experience improves with MFA when systems use seamless methods like push notifications or biometric scans, minimizing delays while maximizing protection.
MFA Adoption Challenges and Solutions
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adoption often faces challenges such as user resistance due to complexity, increased implementation costs, and integration difficulties with legacy systems. Organizations can overcome these obstacles by providing user-friendly MFA options like biometrics and adaptive authentication, investing in comprehensive employee training, and selecting scalable solutions compatible with existing infrastructure. Emphasizing seamless user experiences and robust support frameworks accelerates MFA acceptance and enhances overall security posture.
Best Practices for Transitioning to MFA
Transitioning from password authentication to multi-factor authentication (MFA) significantly enhances security by adding an extra verification layer such as biometrics or one-time codes. Best practices include conducting a thorough risk assessment, educating users on MFA benefits, and implementing MFA gradually starting with high-risk accounts to ensure smooth adoption. Leveraging adaptive authentication technologies and continuous monitoring further strengthens protection during and after the transition phase.
Future Trends in Authentication Methods
Password authentication remains widely used but faces growing vulnerabilities due to sophisticated cyberattacks and phishing schemes. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is leading the evolution by integrating biometric data, behavioral analytics, and hardware tokens to enhance security beyond traditional passwords. Future trends emphasize passwordless authentication, leveraging technologies like AI-driven identity verification and decentralized identity management to provide seamless and highly secure user experiences.
Password Authentication Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com