SaltStack automates IT infrastructure management, enabling rapid deployment, configuration, and orchestration across diverse systems. It enhances operational efficiency by providing real-time remote execution and event-driven automation. Discover how SaltStack can streamline your infrastructure and boost productivity by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
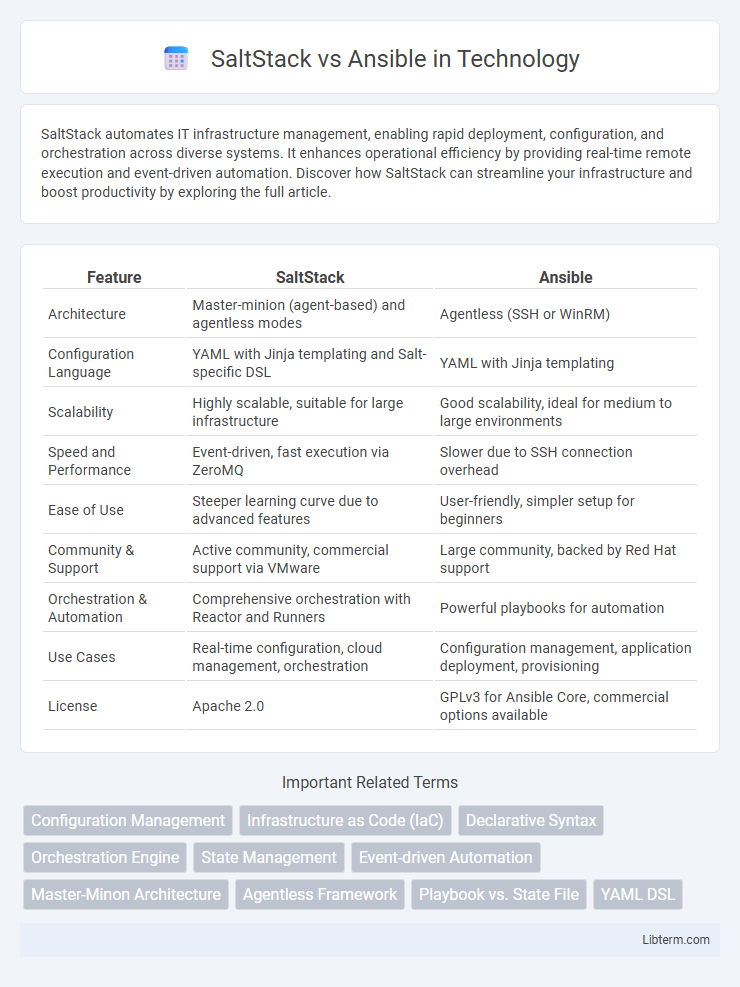
| Feature | SaltStack | Ansible |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Master-minion (agent-based) and agentless modes | Agentless (SSH or WinRM) |
| Configuration Language | YAML with Jinja templating and Salt-specific DSL | YAML with Jinja templating |
| Scalability | Highly scalable, suitable for large infrastructure | Good scalability, ideal for medium to large environments |
| Speed and Performance | Event-driven, fast execution via ZeroMQ | Slower due to SSH connection overhead |
| Ease of Use | Steeper learning curve due to advanced features | User-friendly, simpler setup for beginners |
| Community & Support | Active community, commercial support via VMware | Large community, backed by Red Hat support |
| Orchestration & Automation | Comprehensive orchestration with Reactor and Runners | Powerful playbooks for automation |
| Use Cases | Real-time configuration, cloud management, orchestration | Configuration management, application deployment, provisioning |
| License | Apache 2.0 | GPLv3 for Ansible Core, commercial options available |
Introduction to SaltStack and Ansible
SaltStack is an open-source automation and configuration management tool designed for remote execution and infrastructure orchestration, emphasizing speed and scalability through an event-driven communication model. Ansible is an agentless automation platform that simplifies IT tasks such as configuration management, application deployment, and orchestration using human-readable YAML playbooks. Both tools enable infrastructure as code but differ in architecture; SaltStack relies on a master-minion model while Ansible uses SSH for managing nodes without requiring additional software agents.
Core Architecture and Design
SaltStack employs a master-minion architecture with an event-driven, asynchronous communication model using ZeroMQ, enabling rapid execution and real-time monitoring across large infrastructures. Ansible utilizes a simpler agentless design, relying on SSH for secure, sequential task execution and a push-based model, which simplifies onboarding and reduces infrastructure overhead. SaltStack's modular, scalable design excels in high-speed, parallel task execution, while Ansible emphasizes ease of use and broad compatibility across diverse environments.
Installation and Setup Process
SaltStack's installation typically involves deploying a master and agents (minions), with setup relying on a secure, encrypted communication model using ZeroMQ, often requiring more initial configuration for scalability in large environments. Ansible uses an agentless architecture managed over SSH, simplifying installation since it only requires Python on the target nodes and straightforward configuration via inventory files and YAML playbooks. SaltStack excels in real-time monitoring through persistent connections, while Ansible prioritizes ease of use and quick setup without agent installations.
Configuration Management Approach
SaltStack employs a master-minion architecture facilitating real-time configuration management with event-driven automation, enabling rapid state enforcement across large infrastructures. Ansible uses an agentless, push-based approach leveraging SSH for configuration tasks, simplifying deployment and reducing overhead. SaltStack excels in scalability and dynamic environments, while Ansible prioritizes simplicity and ease of use in managing configurations.
Scalability and Performance
SaltStack excels in scalability with its event-driven architecture and high-speed communication protocol, enabling efficient management of thousands of nodes simultaneously. Ansible, while simpler to implement, relies on agentless SSH connections which may introduce latency and limit performance in very large infrastructures. For enterprises requiring real-time orchestration and rapid execution across extensive environments, SaltStack typically offers superior scalability and faster performance.
State Management and Orchestration
SaltStack excels in real-time state management and event-driven orchestration through its reactor system, enabling dynamic responses to infrastructure changes. Ansible provides efficient orchestration with playbooks that define desired states but relies on push-based execution without persistent agents, making it simpler yet less responsive to asynchronous events. Both tools support configuration management, yet SaltStack's pull-based architecture offers more granular control over state enforcement and scalability in complex environments.
Community Support and Ecosystem
SaltStack and Ansible both boast robust community support, with Ansible having a larger and more active user base due to its widespread adoption and backing by Red Hat. The Ansible ecosystem offers extensive collections of modules, plugins, and roles, fostering rapid development and problem-solving, while SaltStack provides a strong plugin system and flexible execution modules that appeal to advanced automation users. SaltStack's integration with cloud providers and infrastructure tools complements its modular architecture, but Ansible's greater number of third-party integrations and extensive documentation give it an edge in ecosystem maturity and ongoing community contributions.
Security Features Comparison
SaltStack offers robust security features including agent-based architecture with encrypted communication using ZeroMQ and AES encryption, while Ansible relies on agentless architecture with SSH for secure connections. SaltStack supports role-based access control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA), enhancing granular security management, whereas Ansible Tower (AWX) provides RBAC and credential vault features. Both tools offer integration with external authentication systems like LDAP and support encrypted secrets management, but SaltStack's event-driven automation allows for real-time security monitoring and response.
Use Cases and Industry Adoption
SaltStack excels in real-time event-driven automation and infrastructure management, making it ideal for complex, large-scale IT environments like telecommunications and financial services. Ansible is widely adopted for application deployment, configuration management, and cloud provisioning across industries such as healthcare, retail, and technology due to its agentless architecture and simplicity. Both tools have strong community support, but Ansible's integration with Red Hat and extensive ecosystem drives broader adoption in enterprise DevOps workflows.
Pros, Cons, and Final Recommendation
SaltStack excels in real-time infrastructure automation with its event-driven architecture, offering fast scalability and robust remote execution. Ansible provides agentless configuration management with a simple YAML syntax, enhancing ease of use and integration within DevOps pipelines. For organizations requiring rapid, large-scale automation with complex orchestration, SaltStack is ideal; Ansible suits teams prioritizing simplicity and agentless design.
SaltStack Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com