Resilience by design integrates robust strategies and adaptive frameworks to ensure systems withstand and recover from disruptions effectively. Emphasizing proactive planning and flexibility, it enhances durability across various industries and environments. Discover how resilience by design can transform your approach by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
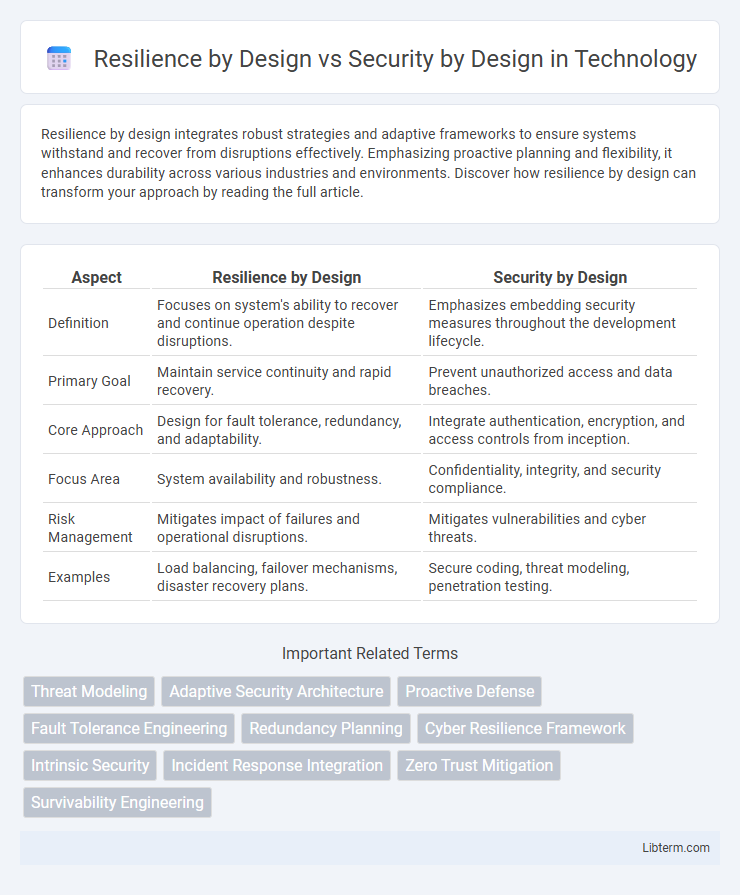
| Aspect | Resilience by Design | Security by Design |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on system's ability to recover and continue operation despite disruptions. | Emphasizes embedding security measures throughout the development lifecycle. |
| Primary Goal | Maintain service continuity and rapid recovery. | Prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. |
| Core Approach | Design for fault tolerance, redundancy, and adaptability. | Integrate authentication, encryption, and access controls from inception. |
| Focus Area | System availability and robustness. | Confidentiality, integrity, and security compliance. |
| Risk Management | Mitigates impact of failures and operational disruptions. | Mitigates vulnerabilities and cyber threats. |
| Examples | Load balancing, failover mechanisms, disaster recovery plans. | Secure coding, threat modeling, penetration testing. |
Understanding Resilience by Design
Resilience by Design emphasizes creating systems that maintain continuous operation and quickly recover from disruptions by integrating adaptive capabilities and redundancy. It prioritizes anticipating and mitigating the impact of unforeseen events, ensuring system robustness beyond mere prevention. This approach contrasts with Security by Design, which focuses primarily on protecting against known threats through proactive security measures.
Defining Security by Design
Security by Design integrates robust protection mechanisms into the core architecture of systems, ensuring vulnerabilities are minimized from the outset. It emphasizes proactive identification and mitigation of security risks through principles such as least privilege, secure defaults, and defense in depth. This approach contrasts with Resilience by Design, which prioritizes system recovery and continuity after attacks or failures.
Core Principles of Resilience by Design
Resilience by Design emphasizes the core principles of adaptability, redundancy, and rapid recovery to ensure systems can withstand and quickly bounce back from disruptions. Unlike Security by Design, which focuses on preventing threats through access controls and vulnerability mitigation, Resilience by Design prioritizes system robustness and continuous operation under stress. Key elements include proactive risk management, dynamic response strategies, and integrated fail-safes to maintain essential functions during unforeseen events.
Fundamental Tenets of Security by Design
Security by Design centers on embedding core principles such as least privilege, defense in depth, and secure defaults throughout the development lifecycle to proactively prevent vulnerabilities. It prioritizes strong authentication, data encryption, and rigorous access controls to protect systems from unauthorized access and data breaches. This approach ensures that security is not an afterthought but a foundational element, contrasting with Resilience by Design, which emphasizes recovery and continuity after an incident.
Key Differences: Resilience vs Security Approaches
Resilience by Design emphasizes creating systems that can adapt, recover, and continue functioning during and after disruptions, focusing on flexibility and redundancy. Security by Design prioritizes protecting systems against threats by implementing preventive controls, encryption, and access restrictions to minimize vulnerabilities. The key difference lies in resilience optimizing for system survivability and recovery, while security optimizes for threat prevention and attack mitigation.
Integrating Resilience and Security in System Architecture
Integrating resilience and security in system architecture requires embedding fault tolerance and adaptive recovery mechanisms alongside robust cybersecurity measures to ensure continuous operation under attack or failure conditions. Resilience by Design emphasizes system adaptability and rapid recovery from disruptions, while Security by Design focuses on preventing unauthorized access and vulnerabilities from the outset. Combining these approaches enhances overall system integrity, enabling both proactive defense and reactive recovery in complex IT environments.
Benefits of a Resilience-Focused Approach
Resilience by Design emphasizes the capacity of systems to adapt, recover, and continue functioning during and after disruptions, reducing downtime and mitigating operational risks more effectively than traditional Security by Design. This approach enhances overall system robustness by anticipating potential failures and embedding redundancy, ensuring sustained service availability and business continuity. Organizations adopting resilience-focused strategies experience improved incident response, faster recovery times, and greater long-term stability in complex threat environments.
Limitations of Security-Only Frameworks
Security-only frameworks often emphasize threat prevention and access controls but fail to address system recovery and adaptability after breaches, leading to prolonged downtime and increased damage. Resilience by Design incorporates redundancy, fault tolerance, and rapid response strategies, mitigating the limitations found in traditional security models. Ignoring resilience aspects limits an organization's ability to maintain critical operations during and after cyber incidents.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Resilience by Design and Security by Design are both critical frameworks in cybersecurity, with case studies highlighting their effectiveness in different contexts. For example, Netflix employs Resilience by Design to maintain service availability during failures through chaos engineering, while Microsoft integrates Security by Design principles to embed security at every development stage, reducing vulnerabilities in Windows OS. These real-world applications demonstrate how proactive strategies in both resilience and security architectures significantly improve system robustness and protection against threats.
Best Practices for Combining Resilience and Security by Design
Combining Resilience by Design and Security by Design involves implementing best practices that integrate proactive threat mitigation with robust system recovery strategies. Emphasizing continuous risk assessment, secure coding standards, and redundant architecture ensures both resistance to cyberattacks and quick restoration of operations. Incorporating automated monitoring, incident response planning, and rigorous vulnerability management enhances overall system robustness and data protection.
Resilience by Design Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com