Resource pools maximize efficiency by grouping available assets to allocate them effectively across projects. Managing your resource pool ensures optimal utilization, reduces downtime, and improves overall productivity in your organization. Discover how to create and optimize resource pools to enhance your project management skills throughout the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
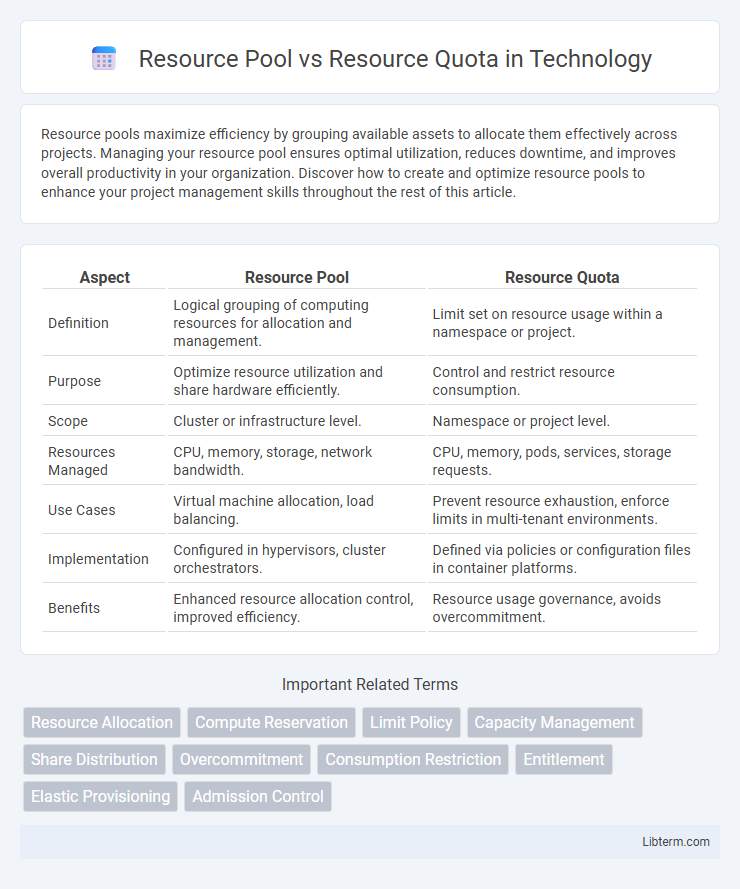
| Aspect | Resource Pool | Resource Quota |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Logical grouping of computing resources for allocation and management. | Limit set on resource usage within a namespace or project. |
| Purpose | Optimize resource utilization and share hardware efficiently. | Control and restrict resource consumption. |
| Scope | Cluster or infrastructure level. | Namespace or project level. |
| Resources Managed | CPU, memory, storage, network bandwidth. | CPU, memory, pods, services, storage requests. |
| Use Cases | Virtual machine allocation, load balancing. | Prevent resource exhaustion, enforce limits in multi-tenant environments. |
| Implementation | Configured in hypervisors, cluster orchestrators. | Defined via policies or configuration files in container platforms. |
| Benefits | Enhanced resource allocation control, improved efficiency. | Resource usage governance, avoids overcommitment. |
Introduction to Resource Pool vs Resource Quota
Resource Pool and Resource Quota are fundamental concepts in cloud resource management that help optimize allocation and control of computing resources. Resource Pools aggregate resources like CPU, memory, and storage into manageable collections, enabling efficient distribution and prioritization among multiple users or workloads. Resource Quotas, on the other hand, enforce limits on resource consumption within namespaces or projects to prevent overallocation and ensure fair usage across the environment.
Understanding Resource Pools
Resource pools are a method of partitioning and managing computing resources such as CPU and memory within a virtualization environment, allowing administrators to allocate resources efficiently among virtual machines or applications. Unlike resource quotas, which impose strict limits on resource consumption, resource pools provide flexible resource allocation and prioritization, enabling dynamic adjustment based on workload demands. Effective use of resource pools ensures optimized performance and scalability in data center operations by controlling resource distribution at granular levels.
Defining Resource Quotas
Resource quotas are administrative limits set within cloud platforms or container orchestration systems, defining the maximum amount of resources, such as CPU, memory, and storage, that a namespace or project can consume. Unlike resource pools that aggregate and manage available resources for allocation, resource quotas actively restrict resource usage to prevent overconsumption and ensure fair distribution among users or teams. Kubernetes, for example, implements resource quotas to enforce boundaries on resource requests and limits, enhancing cluster stability and operational efficiency.
Key Differences Between Resource Pools and Resource Quotas
Resource Pools allocate and manage CPU and memory resources within a virtualized environment, allowing administrators to control resource distribution among virtual machines by setting limits, reservations, and shares. Resource Quotas, on the other hand, are primarily used in container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes to restrict the overall resource consumption, including CPU, memory, and storage, within a namespace or project to prevent resource overuse. Key differences include Resource Pools focusing on prioritizing and partitioning resources within virtual infrastructure, while Resource Quotas enforce hard limits on resource usage within multi-tenant container clusters for better governance.
Advantages of Using Resource Pools
Resource pools simplify complex resource management by aggregating CPU and memory resources, allowing for efficient allocation and prioritization based on workload requirements. They enhance resource utilization by enabling dynamic adjustment within the pool without affecting the overall infrastructure, leading to improved performance and scalability. Resource pools also provide isolation and control, ensuring that critical applications receive guaranteed resources, which reduces contention and supports service level agreements (SLAs).
Benefits of Implementing Resource Quotas
Implementing resource quotas ensures precise control over resource allocation, preventing resource exhaustion and promoting fair distribution among projects or teams. Resource quotas help maintain system stability by limiting CPU, memory, and storage usage, which reduces the risk of performance degradation caused by resource contention. Organizations benefit from improved cost management and predictable capacity planning by enforcing strict limits on resource consumption through quotas.
Use Cases: When to Choose Resource Pool
Resource pools are ideal for managing and allocating resources within virtualized environments, especially when organizing resources by department, project, or team to ensure predictable performance and control. Use resource pools when you need hierarchical resource management, flexible resource distribution, or want to enforce resource shares and limits among virtual machines. Resource quotas, by contrast, are better suited for setting strict usage limits within namespaces or containers, making resource pools preferable for dynamic scaling and workload prioritization in complex virtual infrastructure.
Use Cases: When to Choose Resource Quota
Resource Quotas are ideal for environments requiring strict limits on resource consumption per namespace, ensuring fair resource allocation among multiple teams or projects within a Kubernetes cluster. Use cases include multi-tenant clusters where preventing resource overuse and maintaining stability are critical, such as shared development platforms or production environments with limited compute capacity. Resource Pools, in contrast, are better suited for managing resources at a broader level, making Resource Quotas the preferred choice when granular control and enforcement of consumption limits in isolated namespaces are necessary.
Performance Impacts and Management Strategies
Resource Pools organize and allocate compute resources within virtualized environments, enhancing workload performance by enabling fine-grained CPU and memory distribution among virtual machines. Resource Quotas enforce limits on resource consumption in container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes, preventing resource contention by capping CPU, memory, and storage usage per namespace or project. Effective management strategies involve balancing Resource Pool configurations to avoid overallocation, while setting precise Resource Quotas ensures fair resource distribution and mitigates performance degradation due to resource starvation or overcommitment.
Best Practices for Resource Allocation and Control
Resource pools organize and allocate CPU and memory resources efficiently among virtual machines or workloads, ensuring prioritized access based on predefined shares, limits, and reservations. Resource quotas enforce strict limits on resource consumption within namespaces or projects, preventing overallocation by capping CPU, memory, and storage usage. Best practices include combining resource pools for performance isolation with quotas for enforcing organizational policies, regularly monitoring usage metrics to adjust allocations dynamically, and avoiding overallocation to maintain system stability and optimal resource utilization.
Resource Pool Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com