Network segmentation enhances security by dividing a larger network into smaller, isolated segments, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and containing potential threats within specific areas. It also improves network performance by minimizing congestion and enabling more efficient traffic management. Explore the rest of the article to discover how network segmentation can strengthen your IT infrastructure and protect your data.
Table of Comparison
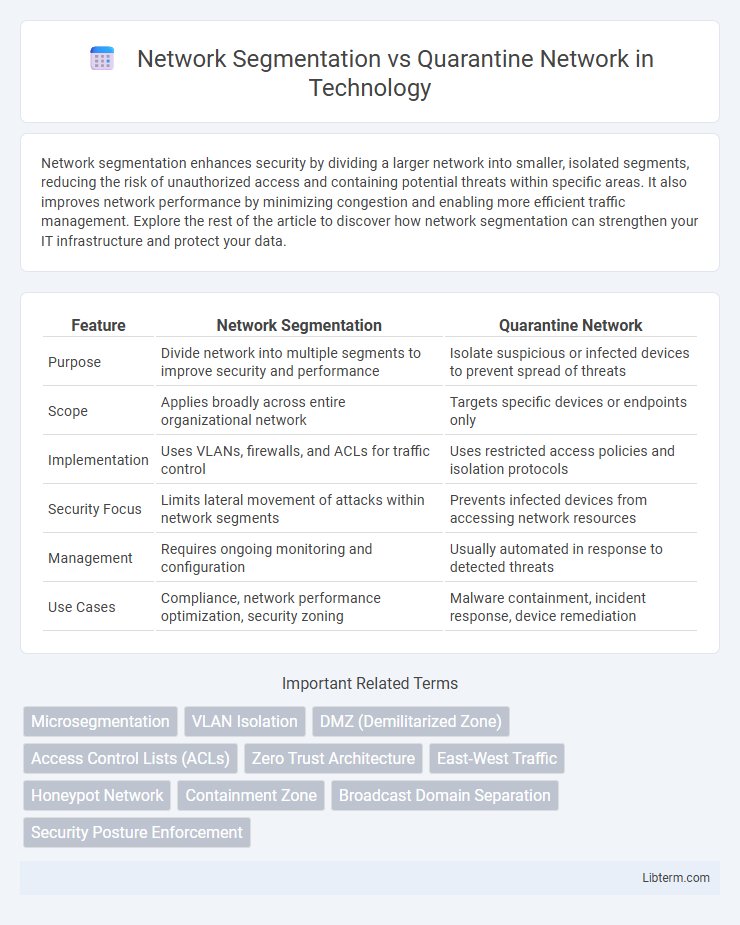
| Feature | Network Segmentation | Quarantine Network |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Divide network into multiple segments to improve security and performance | Isolate suspicious or infected devices to prevent spread of threats |
| Scope | Applies broadly across entire organizational network | Targets specific devices or endpoints only |
| Implementation | Uses VLANs, firewalls, and ACLs for traffic control | Uses restricted access policies and isolation protocols |
| Security Focus | Limits lateral movement of attacks within network segments | Prevents infected devices from accessing network resources |
| Management | Requires ongoing monitoring and configuration | Usually automated in response to detected threats |
| Use Cases | Compliance, network performance optimization, security zoning | Malware containment, incident response, device remediation |
Introduction to Network Segmentation and Quarantine Networks
Network segmentation divides a computer network into smaller, isolated segments to improve performance and enhance security by limiting access to sensitive data and reducing the attack surface. Quarantine networks isolate compromised or untrusted devices to prevent the spread of malware and protect the broader network environment. Both strategies are critical in cybersecurity frameworks, with segmentation focusing on traffic control and containment, while quarantine networks serve as temporary holding areas for devices needing remediation.
Defining Network Segmentation
Network segmentation involves dividing a computer network into smaller, isolated segments to improve security and performance by limiting access to sensitive data and reducing the attack surface. It uses VLANs, firewalls, or access control lists to separate traffic and enforce policies between segments, enabling granular control over communication pathways. Unlike quarantine networks, which isolate potentially compromised devices, network segmentation proactively structures the network to prevent unauthorized lateral movement and contain breaches.
What is a Quarantine Network?
A quarantine network is a specialized segment within an IT infrastructure designed to isolate compromised or suspicious devices to prevent the spread of malware or unauthorized access. Unlike general network segmentation that divides a network into multiple zones for performance and security management, quarantine networks specifically contain threats by restricting device communication until they are verified secure. Implementing a quarantine network enhances overall cyber defense by allowing security teams to analyze and remediate infected assets without risking contamination of critical systems.
Key Differences Between Network Segmentation and Quarantine Networks
Network segmentation divides a network into multiple subnetworks to improve performance and security by limiting access to sensitive data and reducing attack surfaces. Quarantine networks isolate compromised or suspicious devices to prevent the spread of malware and contain threats before reintegration. The key difference lies in function: network segmentation is a proactive structural approach for ongoing access control, whereas quarantine networks are reactive measures targeting compromised endpoints.
Use Cases for Network Segmentation
Network segmentation enhances security by dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments to contain threats and control traffic flow, making it ideal for protecting sensitive data in industries like finance and healthcare. Use cases include limiting access to critical systems, reducing attack surfaces, and improving compliance with regulations such as PCI DSS and HIPAA. Unlike quarantine networks that isolate compromised devices, segmentation proactively prevents lateral movement of threats within the network.
Scenarios for Implementing Quarantine Networks
Quarantine networks are crucial in scenarios where compromised or untrusted devices must be isolated immediately to prevent lateral movement of malware or unauthorized access within an enterprise environment. Common implementations include onboarding new devices that require verification before full network access, containing infected endpoints detected by intrusion prevention systems, and isolating guest or third-party devices to maintain strict security controls. By deploying quarantine networks, organizations enforce strict access policies, enabling remediation actions while minimizing risk to core network segments.
Benefits of Network Segmentation
Network segmentation enhances security by isolating sensitive data and critical systems, reducing the attack surface and limiting lateral movement of threats within the network. It improves network performance through traffic management and simplifies compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA by enforcing access controls. Segmentation also enables faster incident response by containing breaches to specific segments, minimizing overall organizational impact and downtime.
Advantages of Quarantine Networks
Quarantine Networks provide enhanced security by isolating compromised or suspicious devices from the main network, preventing the spread of malware and minimizing potential damage. They enable rapid containment and remediation of threats without disrupting overall network operations. This targeted isolation simplifies policy enforcement and improves incident response efficiency compared to broader network segmentation.
Security Challenges and Best Practices
Network segmentation and quarantine networks address security challenges by isolating devices and limiting lateral movement of threats within an organization. Effective network segmentation involves creating granular security zones using VLANs and firewalls to restrict access based on role or sensitivity, while quarantine networks isolate potentially compromised devices for forensic analysis without impacting critical operations. Best practices include continuous monitoring, strict access controls, regular policy updates, and integration with intrusion detection systems to enhance threat containment and minimize attack surfaces.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Network segmentation enhances security by dividing a large network into smaller, isolated segments to control traffic flow and limit potential attack surfaces, ideal for organizations seeking to minimize internal threats. Quarantine networks isolate suspicious devices or compromised endpoints dynamically to prevent malware spread, best suited for environments requiring rapid containment of threats. Selecting the right approach depends on an organization's size, security policies, compliance requirements, and the desired balance between proactive defense and reactive containment.
Network Segmentation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com