Lambda functions offer a concise way to create anonymous functions in programming, primarily used for short, simple operations without the need for defining a formal function. They enhance code readability and efficiency, especially in languages like Python, by allowing you to embed small function logic inline. Discover how lambda functions can streamline your coding tasks and improve your programming workflow in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
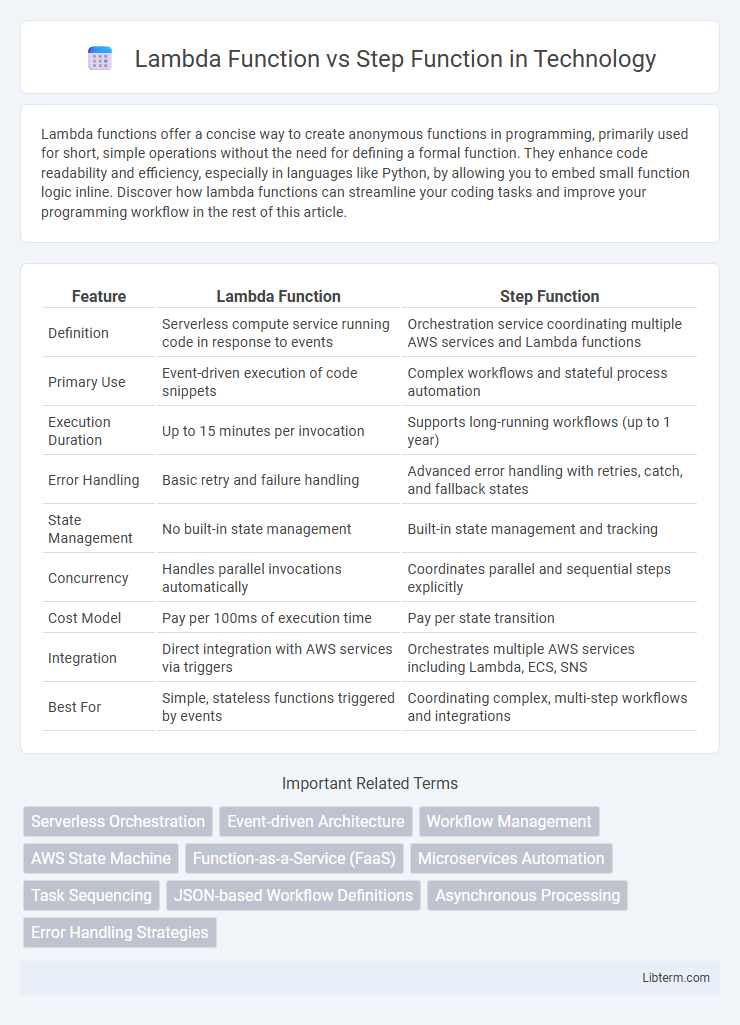
| Feature | Lambda Function | Step Function |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Serverless compute service running code in response to events | Orchestration service coordinating multiple AWS services and Lambda functions |
| Primary Use | Event-driven execution of code snippets | Complex workflows and stateful process automation |
| Execution Duration | Up to 15 minutes per invocation | Supports long-running workflows (up to 1 year) |
| Error Handling | Basic retry and failure handling | Advanced error handling with retries, catch, and fallback states |
| State Management | No built-in state management | Built-in state management and tracking |
| Concurrency | Handles parallel invocations automatically | Coordinates parallel and sequential steps explicitly |
| Cost Model | Pay per 100ms of execution time | Pay per state transition |
| Integration | Direct integration with AWS services via triggers | Orchestrates multiple AWS services including Lambda, ECS, SNS |
| Best For | Simple, stateless functions triggered by events | Coordinating complex, multi-step workflows and integrations |
Introduction to Lambda and Step Functions
AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service that runs code in response to events and automatically manages the underlying compute resources, enabling scalable and cost-efficient application development. AWS Step Functions orchestrate multiple AWS services by coordinating Lambda functions and other components into workflows, allowing developers to build complex, distributed applications with visual state machines. Both services optimize cloud computing by simplifying event-driven and workflow-based system architectures, enhancing reliability and maintainability.
What is AWS Lambda?
AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service that runs code in response to events and automatically manages the underlying compute resources. It enables developers to execute backend code without provisioning or managing servers, supporting various programming languages including Python, Node.js, and Java. Lambda integrates seamlessly with other AWS services like S3, DynamoDB, and API Gateway to enable event-driven application architectures.
What are AWS Step Functions?
AWS Step Functions is a serverless orchestration service that enables developers to design and execute complex workflows by coordinating multiple AWS Lambda functions and other AWS services. It simplifies the management of distributed applications by providing state machines that define the sequence, branching, and error handling of tasks. Step Functions enhance application scalability and reliability by automating retries and enabling visual workflow monitoring and debugging.
Key Differences Between Lambda and Step Functions
AWS Lambda executes individual, short-lived functions triggered by events, ideal for single-task processing with automatic scaling and built-in fault tolerance. AWS Step Functions orchestrate multiple Lambda functions or other AWS services into complex workflows, managing sequence, parallel execution, and error handling across distributed components. Lambda focuses on code execution, while Step Functions coordinate workflows, providing state management, retries, and visualization of multi-step processes.
Use Cases for Lambda Functions
Lambda functions excel in serverless computing scenarios requiring event-driven, short-lived code execution such as real-time file processing, API request handling, and data transformation tasks. They are ideal for microservices architectures where lightweight, stateless functions respond rapidly to triggers like changes in databases or message queues. Lambda's scalability and pay-per-use pricing make it cost-effective for workloads with unpredictable or intermittent traffic patterns.
Use Cases for Step Functions
Step Functions are ideal for orchestrating complex workflows that involve multiple AWS Lambda functions, handling retries, parallel execution, and error handling seamlessly. Use cases include automating order processing, managing ETL pipelines, and coordinating microservices in serverless applications. Step Functions enable stateful, long-running tasks that require human approval or integration with other AWS services for enhanced operational control.
Performance Comparison
AWS Lambda functions provide fast, event-driven compute with sub-second execution times ideal for lightweight, stateless tasks. Step Functions coordinate multiple Lambda executions and other AWS services into complex workflows, introducing orchestration overhead that may impact latency but enhances fault tolerance and scalability. Performance differences hinge on execution complexity and orchestration needs, with Lambda excelling in real-time processing and Step Functions optimizing multi-step, long-running processes.
Cost Analysis: Lambda vs Step Functions
AWS Lambda charges are based on the number of requests and duration of function execution with millisecond granularity, making it cost-effective for short, stateless tasks. Step Functions incur costs per state transition, which can add up significantly in complex workflows with many steps, potentially increasing expenses compared to Lambda alone. For workloads with simple or moderate orchestration, Lambda offers lower overall costs, but highly orchestrated or long-running processes may justify Step Functions' added expense due to better workflow management and error handling.
Best Practices for Integration
Integrating AWS Lambda functions with Step Functions requires following best practices such as designing modular and idempotent Lambda functions to ensure reliable retries and error handling within workflows. Use versioning and aliases in Lambda to manage deployments seamlessly, while Step Functions should be structured with clear state transitions and error catchers to maintain orchestration clarity and recoverability. Monitor Lambda execution metrics alongside Step Functions' state machine executions to optimize performance and cost efficiency in complex serverless applications.
Deciding Between Lambda and Step Functions
Choosing between AWS Lambda and Step Functions depends on the complexity and orchestration needs of your application. Lambda is ideal for running individual, stateless functions with short execution times, while Step Functions excel at coordinating multiple Lambda functions or other AWS services into complex workflows with built-in retry and error handling. Evaluate the control flow, scalability, and state management requirements to determine the best fit for your serverless architecture.
Lambda Function Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com