Security tokens represent a revolutionary way to digitize ownership of real-world assets, combining blockchain technology with regulatory compliance. These tokens offer enhanced transparency, liquidity, and efficiency in trading traditional securities like stocks, bonds, and real estate. Discover how security tokens can transform your investment strategies by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
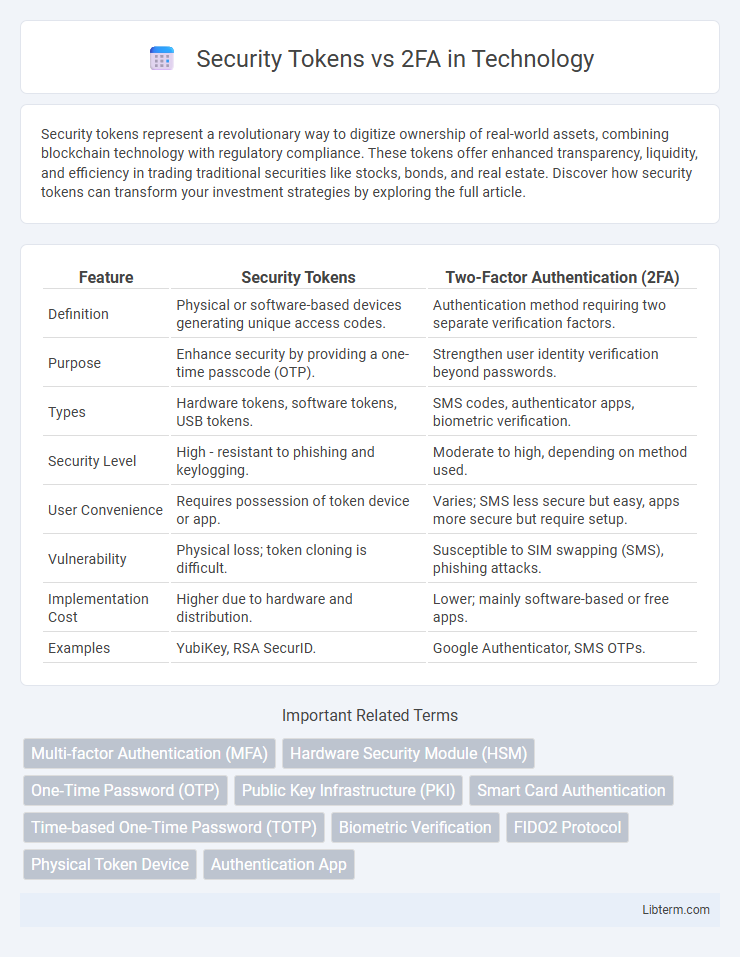
| Feature | Security Tokens | Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical or software-based devices generating unique access codes. | Authentication method requiring two separate verification factors. |
| Purpose | Enhance security by providing a one-time passcode (OTP). | Strengthen user identity verification beyond passwords. |
| Types | Hardware tokens, software tokens, USB tokens. | SMS codes, authenticator apps, biometric verification. |
| Security Level | High - resistant to phishing and keylogging. | Moderate to high, depending on method used. |
| User Convenience | Requires possession of token device or app. | Varies; SMS less secure but easy, apps more secure but require setup. |
| Vulnerability | Physical loss; token cloning is difficult. | Susceptible to SIM swapping (SMS), phishing attacks. |
| Implementation Cost | Higher due to hardware and distribution. | Lower; mainly software-based or free apps. |
| Examples | YubiKey, RSA SecurID. | Google Authenticator, SMS OTPs. |
Introduction to Security Tokens and 2FA
Security tokens are physical or digital devices used to generate unique authentication codes, enhancing access security by requiring possession of the token. Two-factor authentication (2FA) combines something a user knows, such as a password, with something they have, like a security token or a mobile device, to verify identity. These authentication methods significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access by adding an extra layer of security beyond just passwords.
What Are Security Tokens?
Security tokens are physical or digital devices used to authenticate a user's identity by generating a unique, time-sensitive code or cryptographic key, enhancing security beyond traditional passwords. Unlike 2FA methods that may rely on software or SMS, security tokens provide a stronger layer of protection against phishing and unauthorized access through hardware-based verification. Common types include USB tokens, smart cards, and mobile app-generated codes that integrate with multi-factor authentication systems.
Understanding Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) enhances security by requiring users to provide two separate forms of identification, typically something they know (password) and something they have (security token). Security tokens, including hardware devices or software-generated codes, generate time-sensitive, unique codes that prevent unauthorized access even if a password is compromised. Unlike traditional password-only systems, 2FA significantly reduces the risk of identity theft, fraud, and account breaches by adding an extra layer of authentication.
Key Differences Between Security Tokens and 2FA
Security tokens are physical or digital devices that generate unique codes for user authentication, enhancing security by requiring possession of the token. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) combines something you know, like a password, with something you have or are, such as a security token or biometric data, adding a second layer of verification. The key difference lies in security tokens being a method of generating authentication codes, while 2FA is a broader authentication framework that can incorporate security tokens, biometrics, or SMS codes as one of the factors.
Security Token Use Cases and Applications
Security tokens provide a robust authentication method by generating one-time passcodes or leveraging cryptographic keys, ensuring secure access to sensitive systems in banking, corporate networks, and cloud services. Common applications include multi-factor authentication for financial transactions, secure VPN logins, and access control in regulated industries where compliance with standards like PCI-DSS and HIPAA is critical. Security tokens enhance protection against phishing and credential theft by requiring possession of a physical or virtual device, making them essential for high-security environments.
Types of Two-Factor Authentication Methods
Two-factor authentication (2FA) enhances security by requiring users to provide two distinct forms of identification, typically combining something they know (password) with something they have or are. Common types of 2FA methods include SMS-based codes, time-based one-time passwords (TOTP) generated by authenticator apps like Google Authenticator, hardware security keys using Universal 2nd Factor (U2F) protocols, biometric verification such as fingerprint or facial recognition, and push notification approvals through mobile apps. Security tokens, often implemented as hardware devices or software-based tokens, are specifically designed to generate or store these authentication factors, offering a robust layer of defense against unauthorized access compared to SMS or biometric-only methods.
Pros and Cons of Security Tokens
Security tokens provide a strong layer of protection by generating dynamic, unique codes that reduce the risk of unauthorized access in two-factor authentication (2FA). Their pros include enhanced security, resistance to phishing attacks, and the ability to function offline without relying on SMS or email. However, cons involve potential loss or damage of physical tokens, the need for backup methods, and possible inconvenience compared to app-based or biometric 2FA options.
Advantages and Limitations of 2FA
Two-factor authentication (2FA) enhances security by requiring users to provide two distinct forms of identification, typically a password and a temporary code, reducing the risk of unauthorized access compared to single-factor authentication. Its advantages include ease of implementation, compatibility with existing systems, and significant protection against phishing and credential theft. However, limitations involve dependency on mobile devices or hardware tokens, vulnerability to SIM swapping and phishing attacks targeting the second factor, and potential user inconvenience leading to inconsistent adoption.
Choosing Between Security Tokens and 2FA
Choosing between security tokens and two-factor authentication (2FA) depends on the desired balance of security and convenience. Security tokens, such as hardware key fobs or USB devices, offer robust protection by generating unique codes or enabling biometric verification, making them highly resistant to phishing attacks compared to software-based 2FA methods like SMS or authenticator apps. Organizations prioritizing maximum security, especially in regulated industries, often prefer hardware tokens, while users seeking ease of use may opt for app-based 2FA due to its accessibility and lower cost.
Future Trends in Authentication Security
Security tokens provide a physical or digital key for secure authentication, enhancing protection against phishing and credential theft. Future trends in authentication security emphasize multi-factor systems integrating biometric data and blockchain-based security tokens for decentralized verification. Advancements include adaptive authentication leveraging AI to dynamically assess risk and strengthen user identity confirmation beyond traditional 2FA methods.
Security Tokens Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com