Nominal typing is a type system where compatibility and equivalence between data types are determined by explicit declarations and names rather than structure or content. This approach ensures stricter type safety by preventing unintended assignments between types that might appear similar but are distinct in purpose. Discover how nominal typing impacts your software development and why it could be crucial for maintaining robust code by exploring the details in this article.
Table of Comparison
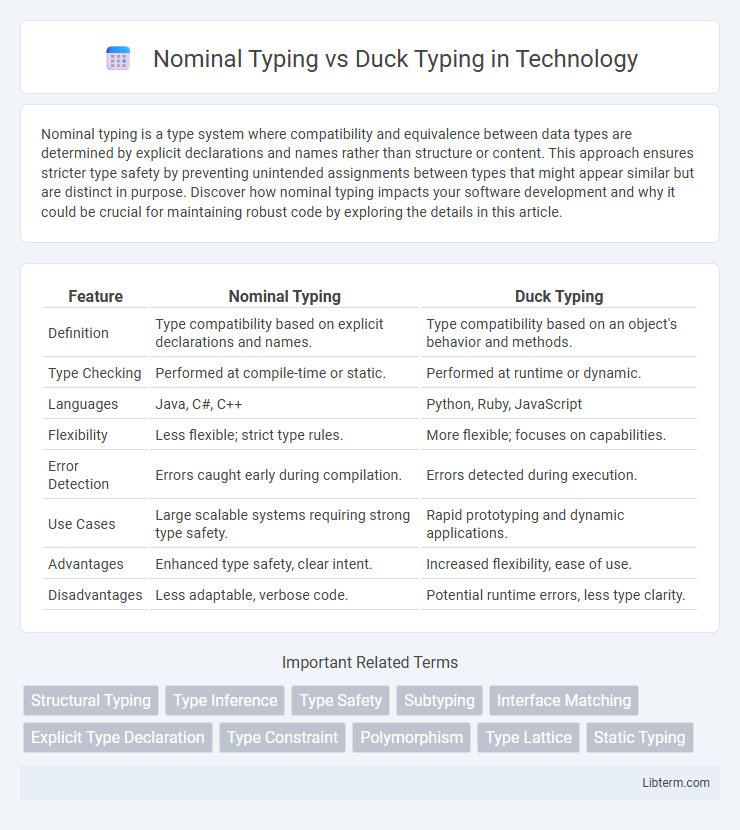
| Feature | Nominal Typing | Duck Typing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Type compatibility based on explicit declarations and names. | Type compatibility based on an object's behavior and methods. |
| Type Checking | Performed at compile-time or static. | Performed at runtime or dynamic. |
| Languages | Java, C#, C++ | Python, Ruby, JavaScript |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; strict type rules. | More flexible; focuses on capabilities. |
| Error Detection | Errors caught early during compilation. | Errors detected during execution. |
| Use Cases | Large scalable systems requiring strong type safety. | Rapid prototyping and dynamic applications. |
| Advantages | Enhanced type safety, clear intent. | Increased flexibility, ease of use. |
| Disadvantages | Less adaptable, verbose code. | Potential runtime errors, less type clarity. |
Understanding Type Systems in Programming
Nominal typing enforces type compatibility based on explicit declarations and named types, ensuring strict conformity during compile-time, commonly used in languages like Java and C#. Duck typing determines type compatibility by object behavior and available methods rather than explicit type definitions, prevalent in dynamically typed languages like Python and Ruby. Understanding these paradigms is crucial for choosing the right type system that balances code safety, flexibility, and development speed.
What is Nominal Typing?
Nominal typing is a type system where compatibility and equivalence of types are determined by explicit declarations and type names rather than their structure or behavior. In nominal typing, two types are considered identical only if they share the same name or a declared subtype relationship, ensuring strict type safety and clear inheritance hierarchies. This approach contrasts with structural type systems, emphasizing explicit relationships over mere compatibility of properties or methods.
What is Duck Typing?
Duck typing is a programming concept where an object's suitability is determined by the presence of certain methods and properties rather than its explicit type or class. It emphasizes interface compliance and behavior over inheritance, allowing more flexible and dynamic coding practices in languages like Python and JavaScript. This approach supports polymorphism by enabling objects to be used interchangeably if they implement the required operations, regardless of their class hierarchy.
Key Differences Between Nominal and Duck Typing
Nominal typing enforces type compatibility based on explicit declarations and named types, requiring that types have a specific, recognized identity to be considered compatible. Duck typing relies on the presence of certain methods or properties, allowing an object to be typed based on its behavior rather than its explicit type name, emphasizing structural compatibility over nominal identity. The core difference lies in nominal typing's strict type equivalence versus duck typing's flexible, behavior-oriented approach to type compatibility.
Advantages of Nominal Typing
Nominal typing enforces strict type compatibility based on explicit declarations, enhancing code safety and reducing runtime errors by ensuring objects conform to predefined interfaces or classes. This approach simplifies maintenance and refactoring by providing clearer type hierarchies, which improve readability and tooling support such as autocompletion and static analysis. Developers benefit from stronger guarantees of correctness, particularly in large codebases or systems requiring rigorous type checking and formal validation.
Benefits of Duck Typing
Duck typing enhances flexibility in programming by allowing objects to be used based on their behavior rather than strict type hierarchies, promoting code reusability across diverse classes. It enables more dynamic and concise code, reducing the need for explicit interfaces or class inheritance and facilitating rapid prototyping and iterative development. By focusing on method availability rather than formal type definitions, duck typing improves interoperability and simplifies integration within loosely coupled systems.
Common Use Cases for Nominal Typing
Nominal typing is commonly used in statically typed languages like Java, C#, and C++ where type safety and explicit type declarations are critical for large-scale software development and maintainability. It enforces strict type compatibility based on explicit declarations, making it ideal for APIs, libraries, and systems requiring rigorous type checks and clear interfaces. This approach minimizes runtime errors by ensuring that only objects of the declared types or their subclasses can be assigned, which is crucial in enterprise applications and systems with complex hierarchies.
Duck Typing in Dynamic Languages
Duck typing in dynamic languages such as Python, Ruby, and JavaScript prioritizes an object's behavior over its explicit type, enabling flexible and faster development. This approach checks for the presence of methods and properties at runtime, allowing objects that "quack like a duck" to be used interchangeably without inheritance constraints. The flexibility of duck typing enhances code reusability and polymorphism but requires careful runtime checks to avoid type-related errors.
Potential Drawbacks and Limitations
Nominal typing enforces strict type equivalence based on explicit declarations, which can limit flexibility and increase boilerplate code in large-scale applications. Duck typing, relying on an object's behavior rather than its class, may lead to runtime errors due to the absence of compile-time type checks and can complicate debugging processes. Both typing systems present trade-offs in maintainability and error detection, impacting software robustness and developer productivity.
Choosing the Right Typing System for Your Project
Choosing the right typing system depends on your project's requirements for type safety and flexibility; nominal typing enforces strict type compatibility through explicit declarations, enhancing reliability in large, complex codebases. Duck typing emphasizes object behavior over explicit type definitions, promoting agility and rapid development in dynamic languages like Python and JavaScript. Evaluating factors such as code maintainability, error detection needs, and team expertise guides the selection between nominal and duck typing to optimize software robustness and developer productivity.
Nominal Typing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com