Log correlation enhances your ability to analyze and interpret complex data sets by linking related events across multiple sources. This process improves troubleshooting efficiency, security incident detection, and system performance monitoring. Discover effective log correlation techniques and tools to optimize your data analysis in the full article.
Table of Comparison
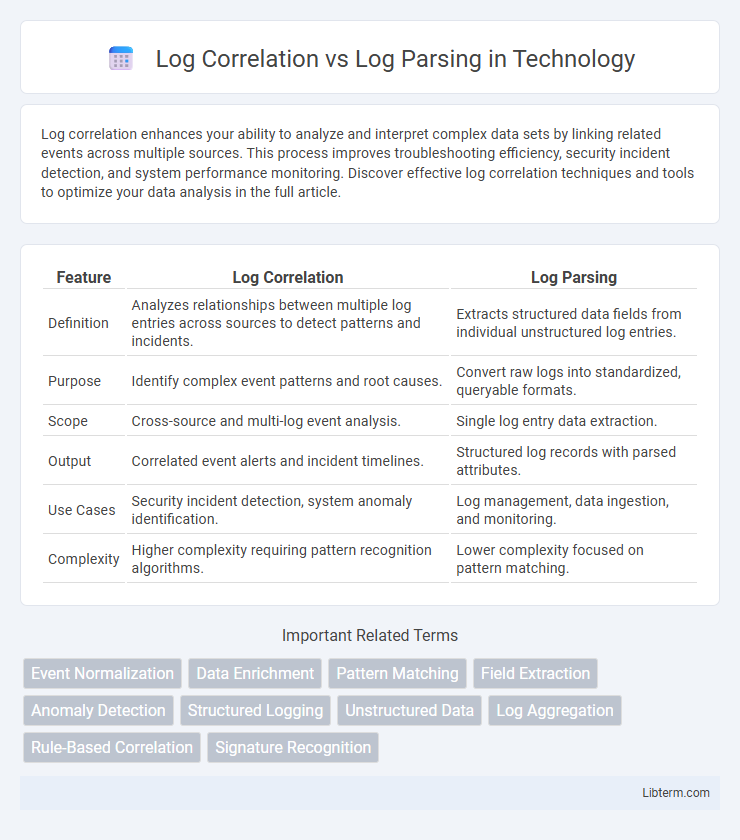
| Feature | Log Correlation | Log Parsing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzes relationships between multiple log entries across sources to detect patterns and incidents. | Extracts structured data fields from individual unstructured log entries. |
| Purpose | Identify complex event patterns and root causes. | Convert raw logs into standardized, queryable formats. |
| Scope | Cross-source and multi-log event analysis. | Single log entry data extraction. |
| Output | Correlated event alerts and incident timelines. | Structured log records with parsed attributes. |
| Use Cases | Security incident detection, system anomaly identification. | Log management, data ingestion, and monitoring. |
| Complexity | Higher complexity requiring pattern recognition algorithms. | Lower complexity focused on pattern matching. |
Introduction to Log Correlation and Log Parsing
Log correlation aggregates and analyzes log data from multiple sources to identify patterns and relationships, enhancing incident detection and troubleshooting. Log parsing extracts structured information from raw log entries by identifying and categorizing key components such as timestamps, error codes, and event types. Both techniques are essential in log management, with log parsing providing the foundation for effective log correlation and comprehensive data analysis.
Defining Log Parsing: Key Concepts
Log parsing involves extracting structured data from unstructured log messages by identifying patterns, keywords, and fields to convert raw logs into a readable format. Key concepts include tokens, delimiters, and pattern matching algorithms such as regular expressions that help categorize and index log data efficiently. Accurate log parsing is essential for enabling advanced log correlation, which aggregates parsed logs to identify complex events and system behaviors.
Understanding Log Correlation Techniques
Log correlation techniques analyze multiple log entries from diverse sources to identify related events and uncover patterns indicating system behavior or security incidents. These methods utilize timestamp alignment, unique identifiers, and event sequencing to link dispersed logs, enabling comprehensive monitoring and root cause analysis. Effective log correlation enhances anomaly detection and incident response by providing a unified view of complex, distributed system activities.
Differences Between Log Parsing and Log Correlation
Log parsing involves extracting structured data from unstructured log files by identifying patterns and converting raw logs into standardized formats. Log correlation connects events across multiple logs or sources to identify relationships and detect incidents or anomalies over time. The primary difference lies in log parsing focusing on data extraction and organization, while log correlation emphasizes linking and analyzing events to provide broader insights.
Importance of Log Parsing for Data Structure
Log parsing is essential for converting unstructured log data into organized, structured formats that enable efficient analysis and correlation. By extracting key fields such as timestamps, error codes, and user IDs, log parsing facilitates accurate log correlation across diverse systems and applications. This structured data foundation significantly improves the speed and reliability of identifying patterns, anomalies, and root causes in complex IT environments.
Role of Log Correlation in Security and Monitoring
Log correlation plays a critical role in security and monitoring by aggregating and analyzing data from diverse log sources to identify patterns and detect anomalies that individual logs might miss. It enables real-time threat detection and incident response by linking seemingly unrelated events across networks, applications, and systems. Unlike log parsing, which primarily focuses on extracting structured data from raw logs, log correlation provides contextual insights essential for comprehensive security analytics and proactive monitoring.
Use Cases for Log Parsing in IT Environments
Log parsing in IT environments is essential for extracting structured data from unstructured log files, enabling efficient monitoring, troubleshooting, and alert generation. It supports use cases such as identifying security threats by parsing log entries for suspicious activities, automating compliance reporting through the extraction of relevant audit data, and optimizing system performance by analyzing parsed logs for error patterns or resource bottlenecks. This process facilitates faster root cause analysis and improves data accuracy compared to log correlation, which primarily focuses on linking related log events across multiple sources.
Common Applications of Log Correlation
Log correlation is widely used in security information and event management (SIEM) systems to detect complex threats by linking related events across multiple sources, enhancing incident response and forensic analysis. Unlike log parsing, which extracts structured data from raw logs, log correlation identifies patterns and relationships between disparate log entries to provide a comprehensive view of system behavior. Common applications include fraud detection, network security monitoring, and compliance auditing, where correlating events reveals hidden anomalies and potential breaches.
Challenges in Implementing Log Parsing and Correlation
Implementing log parsing faces challenges such as handling diverse log formats and extracting meaningful data from unstructured entries, which complicates automated analysis. Log correlation struggles with linking related events across multiple sources due to inconsistent timestamps and varying log granularities, impacting accurate incident detection. Both processes require robust algorithms and scalable infrastructure to manage high-volume data streams in real time for effective monitoring and troubleshooting.
Choosing the Right Approach: Parsing vs Correlation
Log parsing extracts structured fields from raw log data, enabling detailed analysis and filtering of specific events, while log correlation links related logs from multiple sources to identify patterns and diagnose complex issues. Choosing the right approach depends on the goal: parsing is essential for ingesting and normalizing data for further processing, whereas correlation provides contextual insights by connecting log events across systems to detect anomalies or root causes. Effective log management often combines both techniques to enhance visibility, streamline troubleshooting, and improve operational intelligence.
Log Correlation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com