gRPC is a high-performance, open-source RPC framework developed by Google, designed to enable efficient communication between distributed systems. It leverages HTTP/2 for multiplexed connections, supports multiple programming languages, and uses Protocol Buffers for compact serialization. Explore the rest of the article to discover how gRPC can enhance Your application's scalability and interoperability.
Table of Comparison
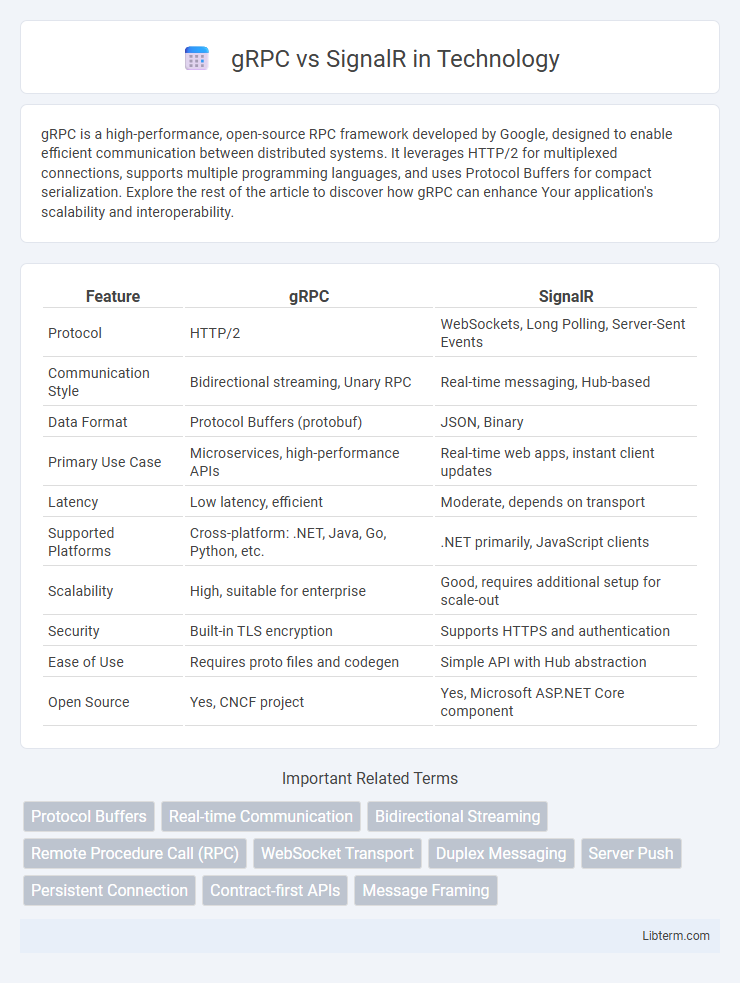
| Feature | gRPC | SignalR |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol | HTTP/2 | WebSockets, Long Polling, Server-Sent Events |
| Communication Style | Bidirectional streaming, Unary RPC | Real-time messaging, Hub-based |
| Data Format | Protocol Buffers (protobuf) | JSON, Binary |
| Primary Use Case | Microservices, high-performance APIs | Real-time web apps, instant client updates |
| Latency | Low latency, efficient | Moderate, depends on transport |
| Supported Platforms | Cross-platform: .NET, Java, Go, Python, etc. | .NET primarily, JavaScript clients |
| Scalability | High, suitable for enterprise | Good, requires additional setup for scale-out |
| Security | Built-in TLS encryption | Supports HTTPS and authentication |
| Ease of Use | Requires proto files and codegen | Simple API with Hub abstraction |
| Open Source | Yes, CNCF project | Yes, Microsoft ASP.NET Core component |
Introduction to gRPC and SignalR
gRPC is a high-performance, open-source remote procedure call (RPC) framework that enables efficient communication between distributed systems using HTTP/2 and Protocol Buffers for serialization. SignalR is a real-time web communication library for ASP.NET that simplifies the process of adding real-time functionality to web applications by enabling bi-directional communication between client and server over WebSockets or fallback transports. Both gRPC and SignalR are designed to improve communication scenarios, with gRPC excelling in low-latency, cross-platform services and SignalR specializing in real-time web updates and push notifications.
Core Features Overview
gRPC offers high-performance, cross-platform RPC with strong support for contract-first API design using Protocol Buffers, enabling efficient binary serialization and HTTP/2-based multiplexing. SignalR provides real-time web functionality with automatic connection management, supporting WebSockets, Server-Sent Events, and Long Polling for dynamic client-server communication. gRPC excels in low-latency microservices and inter-process communication, while SignalR is optimized for real-time web applications requiring instant client updates.
Communication Patterns and Protocols
gRPC utilizes HTTP/2 protocol and supports bidirectional streaming, enabling efficient, low-latency communication suited for microservices and real-time applications. SignalR relies on WebSockets and automatically falls back to other techniques like Server-Sent Events or long polling, providing seamless real-time messaging in web apps. gRPC is designed for high-performance RPC calls with strong typing, while SignalR excels in handling real-time client-server communication with dynamic connection management.
Performance and Scalability Comparison
gRPC offers superior performance with low latency and high throughput due to its use of HTTP/2 and binary serialization, making it ideal for microservices and real-time communication in distributed systems. SignalR, while supporting real-time web functionality with automatic fallback transports, generally incurs higher overhead and latency, impacting scalability in large-scale scenarios. For applications requiring massive concurrent connections and efficient resource utilization, gRPC provides better scalability compared to SignalR's easier integration with web-based client platforms.
Language and Platform Support
gRPC offers extensive language and platform support including C#, Java, Go, Python, and Node.js, making it ideal for cross-platform microservices and API communication. SignalR is primarily designed for the .NET ecosystem, with strong support in C# for real-time web applications on Windows and Azure environments. Developers seeking broad interoperability often prefer gRPC, while SignalR excels in building real-time features within Microsoft-centric platforms.
Use Cases and Suitability
gRPC excels in building high-performance, low-latency communication for microservices, real-time data streaming, and inter-service APIs, making it ideal for backend connectivity in distributed systems. SignalR is suited for real-time web applications requiring bidirectional communication, such as chat applications, live dashboards, and online gaming, due to its seamless integration with ASP.NET and automatic fallback to compatible protocols. Choosing between gRPC and SignalR depends on the need for optimized binary communication and strong contract enforcement versus ease of use in browser-based real-time scenarios.
Security and Authentication
gRPC supports robust security features through SSL/TLS encryption and integrates with various authentication mechanisms such as OAuth2, JWT, and mTLS for mutual authentication. SignalR uses ASP.NET Core's authentication and authorization frameworks, enabling seamless integration with identity systems like Azure AD, cookies, and bearer tokens for securing connections. Both technologies offer strong protections, but gRPC's low-level protocol design provides finer-grained control over security policies, ideal for high-performance, secure microservices communication.
Development and Integration Complexity
gRPC offers a more streamlined development experience for applications requiring high-performance communication, leveraging HTTP/2 and Protocol Buffers for efficient data serialization, which reduces message size and enhances speed. SignalR simplifies real-time web functionality integration using WebSockets and automatic fallback protocols, but its abstraction can introduce complexity when handling custom protocols or non-web clients. Both technologies require specific knowledge: gRPC demands familiarity with protobuf schema design, while SignalR necessitates understanding of ASP.NET Core infrastructure for seamless integration.
Real-Time Capabilities
gRPC delivers high-performance, low-latency communication ideal for real-time applications requiring efficient binary serialization and full-duplex streaming over HTTP/2. SignalR excels in real-time web functionality by abstracting WebSockets, Server-Sent Events, and Long Polling, automatically selecting the best transport mechanism for scalable, interactive web applications. For scenarios demanding rapid bidirectional messaging with minimal overhead, gRPC is optimal, while SignalR provides flexibility and ease of integration within ASP.NET environments for real-time user interaction.
Choosing the Right Technology
Selecting between gRPC and SignalR depends on the specific application requirements such as communication patterns, latency, and scalability. gRPC excels in high-performance, low-latency, bidirectional streaming scenarios ideal for microservices and real-time backend communication, while SignalR is tailored for web applications needing real-time client-server messaging with automatic fallback and connection management. Evaluating factors like protocol support, platform compatibility, and message complexity ensures the right choice for efficient real-time communication architecture.
gRPC Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com