A firewall is a critical network security device that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules. It acts as a barrier between trusted internal networks and untrusted external networks, protecting your data from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Explore the rest of this article to understand how firewalls work and why they're essential for safeguarding your digital environment.
Table of Comparison
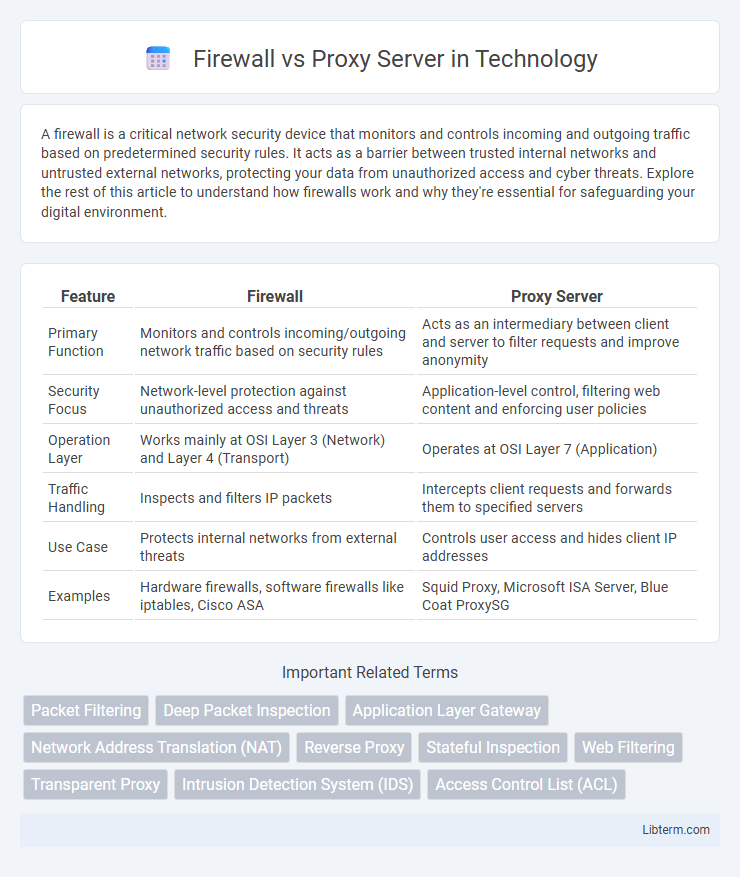
| Feature | Firewall | Proxy Server |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Monitors and controls incoming/outgoing network traffic based on security rules | Acts as an intermediary between client and server to filter requests and improve anonymity |
| Security Focus | Network-level protection against unauthorized access and threats | Application-level control, filtering web content and enforcing user policies |
| Operation Layer | Works mainly at OSI Layer 3 (Network) and Layer 4 (Transport) | Operates at OSI Layer 7 (Application) |
| Traffic Handling | Inspects and filters IP packets | Intercepts client requests and forwards them to specified servers |
| Use Case | Protects internal networks from external threats | Controls user access and hides client IP addresses |
| Examples | Hardware firewalls, software firewalls like iptables, Cisco ASA | Squid Proxy, Microsoft ISA Server, Blue Coat ProxySG |
Introduction to Firewalls and Proxy Servers
Firewalls act as security barriers that monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules, providing essential protection against unauthorized access and cyber threats. Proxy servers function as intermediaries between client devices and the internet, masking IP addresses to enhance privacy, filter content, and improve access speed. Both firewalls and proxy servers are integral to network security infrastructure, serving complementary roles in safeguarding data and controlling network communications.
Understanding How Firewalls Work
Firewalls monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules, acting as a barrier between trusted internal networks and untrusted external networks. They analyze packet headers and payloads to detect unauthorized access attempts, blocking threats such as malware, intrusion attempts, and data breaches. Unlike proxy servers that act as intermediaries for client requests, firewalls enforce strict security policies at the network perimeter to prevent cyber attacks and protect sensitive information.
How Proxy Servers Function
Proxy servers function as intermediaries between a client and the internet, forwarding requests from users to the web while masking their IP addresses to enhance privacy and security. They filter incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined policies, cache content to improve load times, and can block access to malicious or unwanted websites. By anonymizing user activities and controlling data flow, proxy servers help organizations enforce internet usage policies and protect internal networks from external threats.
Key Differences Between Firewalls and Proxy Servers
Firewalls filter network traffic based on security rules to prevent unauthorized access, while proxy servers act as intermediaries between clients and servers to manage requests and enhance privacy. Firewalls operate primarily at the network and transport layers, blocking or allowing traffic, whereas proxy servers function at the application layer, handling specific protocols such as HTTP or FTP. Firewalls protect entire networks, and proxy servers provide anonymity and caching for individual user requests.
Security Benefits of Firewalls
Firewalls provide robust security benefits by actively monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on an established set of security rules, effectively blocking unauthorized access and potential cyber threats. Unlike proxy servers that primarily serve as intermediaries for requests, firewalls offer advanced capabilities such as intrusion prevention, stateful packet inspection, and real-time threat analysis to protect sensitive data and network integrity. With customizable policies and deep packet inspection, firewalls fortify perimeter defenses, reduce attack surfaces, and ensure compliance with security standards across enterprise networks.
Security Advantages of Proxy Servers
Proxy servers enhance security by masking user IP addresses, preventing direct exposure to external threats and reducing the risk of targeted attacks. They filter and control web traffic, blocking access to malicious websites and enforcing organizational policies to minimize data breaches and malware infections. Unlike traditional firewalls, proxy servers enable detailed content inspection and logging, improving threat detection and incident response capabilities.
Use Cases: When to Use a Firewall
Firewalls are essential for protecting internal networks from unauthorized access by filtering incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules, making them ideal for securing enterprise environments and preventing cyberattacks. They are crucial in scenarios requiring network segmentation, perimeter defense, and monitoring of suspicious activity to safeguard sensitive data and critical systems. Use firewalls when enforcing strict access controls, blocking malicious traffic, and ensuring compliance with organizational security policies.
Use Cases: When to Use a Proxy Server
A proxy server is ideal for improving browsing privacy, controlling employee internet access, and caching web content to enhance loading speeds in corporate networks. It serves as an intermediary between users and the internet, making it useful for content filtering, bypassing geo-restrictions, and monitoring user activity. Organizations leverage proxy servers to secure sensitive data by masking IP addresses while enabling web analytics and bandwidth management.
Combining Firewalls and Proxy Servers for Maximum Security
Combining firewalls and proxy servers enhances network security by leveraging the firewall's ability to filter incoming and outgoing traffic at the packet level with the proxy server's capacity to intercept and inspect application-layer requests. Firewalls control access based on IP addresses and ports, while proxy servers improve privacy by masking user IPs and caching content, reducing exposure to external threats. This integrated approach enables comprehensive protection against unauthorized access, malware, and data breaches, optimizing security protocols for enterprise networks.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Network Needs
Firewall focuses on controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on security rules, providing robust protection against unauthorized access and cyber threats. Proxy servers act as intermediaries between users and the internet, enhancing privacy, content filtering, and caching to improve network performance and user anonymity. Evaluate your network's security requirements, traffic control needs, and privacy goals to decide between a firewall's comprehensive defense or a proxy server's traffic management and anonymity features.
Firewall Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com