Cloud storage offers a scalable and secure solution for storing and accessing your data from any device with an internet connection. By leveraging cloud storage, businesses and individuals can ensure data backup, collaboration, and seamless sharing without the need for physical hardware. Discover how cloud storage can revolutionize your data management by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
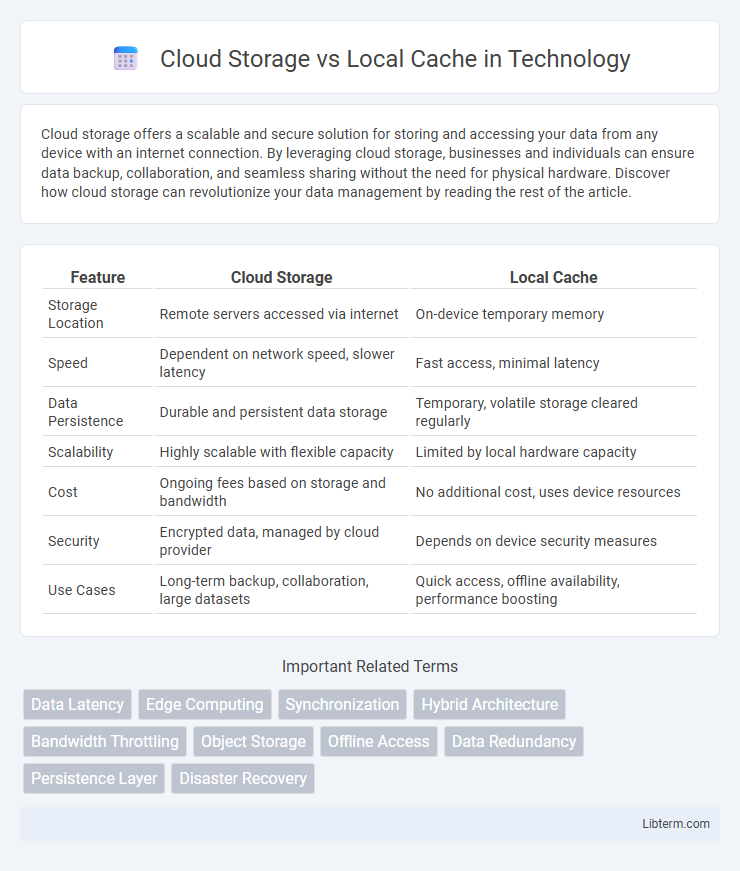
| Feature | Cloud Storage | Local Cache |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Location | Remote servers accessed via internet | On-device temporary memory |
| Speed | Dependent on network speed, slower latency | Fast access, minimal latency |
| Data Persistence | Durable and persistent data storage | Temporary, volatile storage cleared regularly |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with flexible capacity | Limited by local hardware capacity |
| Cost | Ongoing fees based on storage and bandwidth | No additional cost, uses device resources |
| Security | Encrypted data, managed by cloud provider | Depends on device security measures |
| Use Cases | Long-term backup, collaboration, large datasets | Quick access, offline availability, performance boosting |
Introduction to Cloud Storage and Local Cache
Cloud storage enables data to be stored on remote servers accessed via the internet, providing scalable capacity and seamless data synchronization across multiple devices. Local cache temporarily stores frequently accessed data on a user's device or local server, enhancing retrieval speed and reducing latency by minimizing the need to fetch information from remote cloud servers. This balance between cloud storage's vast accessibility and local cache's performance optimization is critical for efficient data management in modern computing.
Key Differences Between Cloud Storage and Local Cache
Cloud storage offers scalable, remotely accessible data storage managed by third-party providers, ensuring data durability and backup, while local cache provides temporary, high-speed data storage on nearby devices to reduce latency and improve performance. Cloud storage is ideal for long-term storage with access from multiple locations, whereas local cache enhances application responsiveness by storing frequently accessed data locally. Security for cloud storage depends on provider policies and network protection, contrasting with local cache's reliance on device security and susceptibility to data loss if the device fails.
Performance Comparison: Speed and Latency
Cloud storage typically experiences higher latency and slower data retrieval speeds compared to local cache due to network dependencies and distance from data centers. Local cache offers faster access by storing frequently used data closer to the processor, significantly reducing read/write latency and improving application responsiveness. Performance gains with local cache are most noticeable in real-time applications and scenarios requiring rapid data processing, while cloud storage prioritizes scalability and accessibility over speed.
Data Security and Privacy Considerations
Cloud storage offers robust encryption protocols and multi-factor authentication to protect data from unauthorized access, while allowing remote accessibility and centralized management. Local cache stores data temporarily on a device, reducing latency and dependency on internet connectivity but may be more vulnerable to physical device theft or malware attacks without proper encryption. Organizations must balance the cloud's continuous security updates and regulatory compliance with the local cache's risk of data exposure and limited control over security measures.
Cost Implications of Cloud Storage vs Local Cache
Cloud storage costs include ongoing fees for data transfer, storage capacity, and retrieval, which can escalate with increased usage and long-term retention. Local cache requires upfront investment in hardware and maintenance but offers predictable costs without recurring fees, potentially reducing expenses for frequently accessed data. Evaluating usage patterns and scalability needs is crucial to determine the most cost-effective solution.
Scalability and Flexibility in Data Management
Cloud storage offers superior scalability by enabling on-demand resource allocation and virtually unlimited capacity, making it ideal for dynamic data growth. Local cache provides rapid data access and low latency but is constrained by physical storage limits, reducing flexibility as data scales. Combining cloud storage with local cache optimizes data management by balancing scalable capacity and high-speed accessibility.
Reliability and Accessibility: Uptime and Availability
Cloud storage ensures high reliability with 99.9% uptime SLAs backed by redundant data centers, providing consistent availability across geographic regions. Local cache offers instant accessibility with low latency but can suffer from limited reliability due to hardware failures or local power outages. Combining cloud storage with local caching optimizes data availability by balancing the cloud's persistent uptime with the cache's fast, offline access.
Use Cases: When to Choose Cloud Storage or Local Cache
Cloud storage is ideal for scalable, remote access to large datasets, especially when collaboration, backup, and disaster recovery are priorities. Local cache excels in scenarios requiring low latency and high-speed access to frequently used data, such as real-time applications or offline functionality. Choosing between cloud storage and local cache depends on factors like data size, access speed, network reliability, and security requirements.
Integration with Existing Systems and Applications
Cloud storage seamlessly integrates with existing systems through APIs and standardized protocols, enabling real-time data access and synchronization across multiple platforms. Local cache enhances application performance by storing frequently accessed data near the user, reducing latency and load on the central system. Combining cloud storage with local cache optimizes data availability and system responsiveness, ensuring compatibility with legacy applications and modern infrastructures alike.
Future Trends in Data Storage Solutions
Cloud storage is increasingly integrated with edge computing, enabling faster data access and reduced latency by storing frequently accessed data locally through intelligent local caches. Advances in AI-driven cache management optimize data retrieval, balancing between cloud scalability and local speed. Future data storage solutions emphasize hybrid architectures combining cloud robustness with strategic local caching to support real-time applications and IoT device proliferation.
Cloud Storage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com