Acceptance Test-Driven Development (ATDD) ensures software meets business requirements by involving collaboration between developers, testers, and users to define acceptance criteria before development begins. This approach reduces misunderstandings and defects by focusing on clear, testable user stories that guide coding and validation processes. Discover how integrating ATDD into your workflow can improve product quality and stakeholder satisfaction throughout the full article.
Table of Comparison
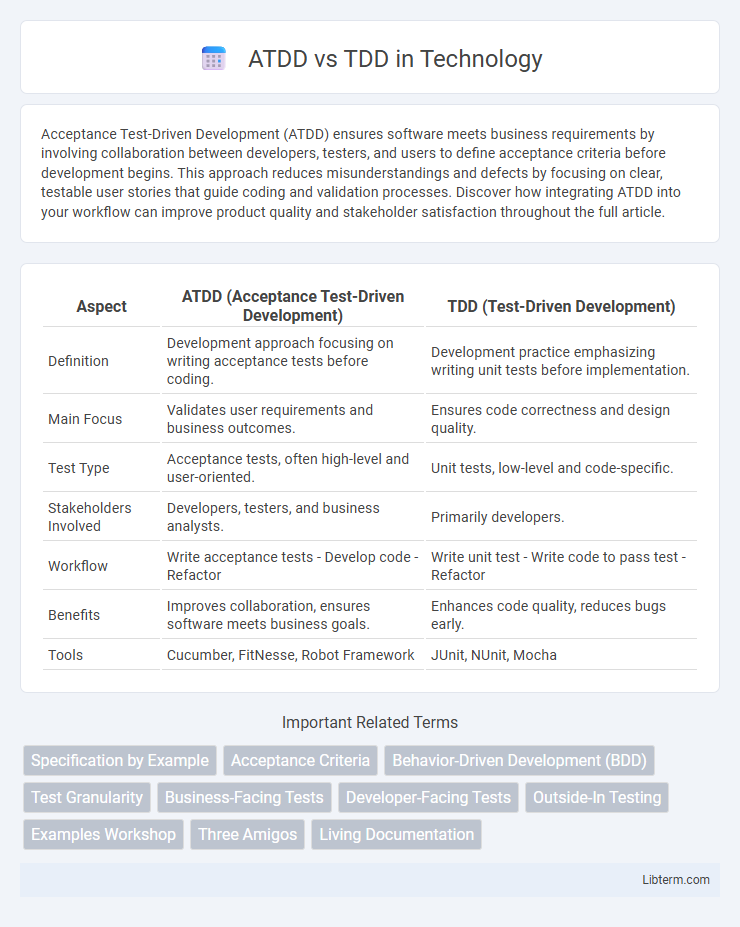
| Aspect | ATDD (Acceptance Test-Driven Development) | TDD (Test-Driven Development) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Development approach focusing on writing acceptance tests before coding. | Development practice emphasizing writing unit tests before implementation. |
| Main Focus | Validates user requirements and business outcomes. | Ensures code correctness and design quality. |
| Test Type | Acceptance tests, often high-level and user-oriented. | Unit tests, low-level and code-specific. |
| Stakeholders Involved | Developers, testers, and business analysts. | Primarily developers. |
| Workflow | Write acceptance tests - Develop code - Refactor | Write unit test - Write code to pass test - Refactor |
| Benefits | Improves collaboration, ensures software meets business goals. | Enhances code quality, reduces bugs early. |
| Tools | Cucumber, FitNesse, Robot Framework | JUnit, NUnit, Mocha |
Understanding ATDD: A Brief Overview
Acceptance Test-Driven Development (ATDD) centers on collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders to create acceptance criteria before coding begins. This approach ensures the software meets user requirements by defining tests from a user perspective, promoting early feedback and reducing misunderstandings. ATDD complements Test-Driven Development (TDD) by focusing on functional behavior rather than low-level unit tests, enhancing alignment with business goals.
What is Test-Driven Development (TDD)?
Test-Driven Development (TDD) is a software development process where developers write automated test cases before writing the actual code. This approach ensures that code is designed to pass specific tests, improving code quality and reducing bugs. TDD follows a strict cycle of writing a failing test, implementing the minimal code to pass the test, and refactoring while keeping tests green.
Key Principles of ATDD and TDD
ATDD (Acceptance Test-Driven Development) centers on collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders to define acceptance criteria before coding, ensuring that software meets user requirements through executable acceptance tests. TDD (Test-Driven Development) emphasizes writing unit tests prior to code implementation, driving design and functionality with a cycle of red-green-refactor to produce reliable and maintainable code. Both methodologies promote early testing and feedback but differ in scope, with ATDD focusing on acceptance-level validation and TDD on low-level code correctness.
Major Differences Between ATDD and TDD
Acceptance Test-Driven Development (ATDD) emphasizes collaboration among developers, testers, and business stakeholders by defining acceptance criteria before coding begins, ensuring the software meets business requirements. Test-Driven Development (TDD) centers on developers writing unit tests prior to implementation, focusing on code correctness and design quality at a granular level. While ATDD bridges communication gaps and drives acceptance-level tests, TDD is primarily about improving code reliability and facilitating refactoring through developer-written unit tests.
Benefits of Adopting ATDD
Adopting Acceptance Test-Driven Development (ATDD) ensures enhanced collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders by defining clear acceptance criteria before coding begins. This approach reduces misunderstandings and misaligned expectations, leading to higher-quality software that meets user requirements. ATDD also accelerates feedback loops with automated acceptance tests, minimizing defects and improving project visibility throughout the development lifecycle.
Advantages of Implementing TDD
Test-Driven Development (TDD) enhances code quality by enforcing the creation of tests before writing functional code, leading to fewer bugs and more reliable software. It promotes better design decisions through incremental development and continuous refactoring, resulting in maintainable and modular codebases. Developers gain immediate feedback on code correctness, accelerating debugging and improving overall development efficiency.
ATDD vs TDD: Use Cases and Scenarios
ATDD (Acceptance Test-Driven Development) is ideal for projects requiring close collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders to define clear acceptance criteria before coding begins, ensuring alignment on functionality and requirements. TDD (Test-Driven Development) suits scenarios emphasizing developer-centric unit testing to drive code design and improve code quality with fast feedback loops during development. For complex systems with evolving requirements, ATDD enhances communication and clarifies expectations, while TDD excels in iterative coding environments focused on robustness and refactoring safety.
Challenges and Pitfalls in ATDD and TDD
ATDD and TDD both face challenges such as unclear or ambiguous requirements that hinder effective test creation and automation. ATDD often struggles with collaboration barriers between developers, testers, and business stakeholders, leading to misaligned acceptance criteria. TDD pitfalls include excessive focus on unit tests that miss broader integration issues and the risk of writing brittle tests that require frequent maintenance.
Best Practices for Choosing ATDD or TDD
Selecting between ATDD (Acceptance Test-Driven Development) and TDD (Test-Driven Development) depends on project goals and team collaboration dynamics. ATDD is best suited for projects prioritizing clear communication among developers, testers, and stakeholders through shared acceptance criteria, ensuring the software meets business requirements. TDD excels in improving code quality and design by focusing on unit testing and developer-driven tests, making it ideal for technically complex systems requiring robust, maintainable code.
Conclusion: Deciding Between ATDD and TDD
Choosing between ATDD and TDD depends on project scope and team collaboration dynamics. ATDD enhances communication among stakeholders by defining acceptance criteria before development, ideal for aligning requirements in complex projects. TDD focuses on code quality and design through iterative unit testing, suitable for developers aiming to improve functionality with precise, test-driven code.
ATDD Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com