Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) offers scalable, secure, and durable cloud storage designed for data backup, archiving, and analytics. It provides seamless integration with various AWS services, ensuring high availability and easy access to your data from anywhere. Explore the full article to discover how S3 can optimize your data management and enhance your cloud infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
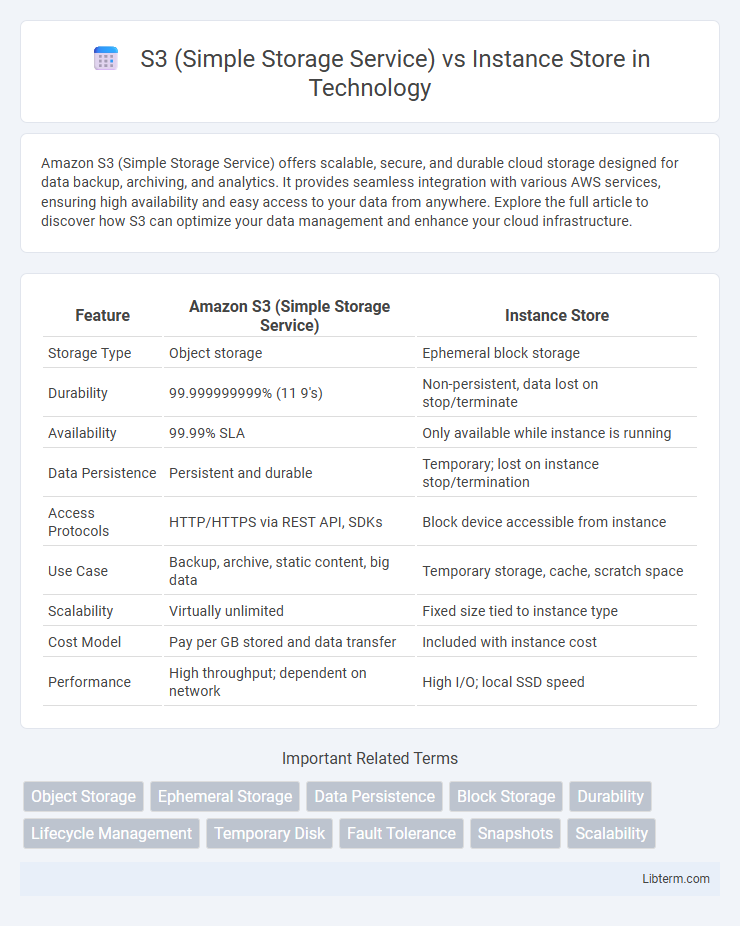
| Feature | Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) | Instance Store |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Type | Object storage | Ephemeral block storage |
| Durability | 99.999999999% (11 9's) | Non-persistent, data lost on stop/terminate |
| Availability | 99.99% SLA | Only available while instance is running |
| Data Persistence | Persistent and durable | Temporary; lost on instance stop/termination |
| Access Protocols | HTTP/HTTPS via REST API, SDKs | Block device accessible from instance |
| Use Case | Backup, archive, static content, big data | Temporary storage, cache, scratch space |
| Scalability | Virtually unlimited | Fixed size tied to instance type |
| Cost Model | Pay per GB stored and data transfer | Included with instance cost |
| Performance | High throughput; dependent on network | High I/O; local SSD speed |
Introduction to S3 and Instance Store
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) offers scalable, durable object storage designed for data backup, archiving, and big data analytics with a 99.999999999% durability guarantee. Instance Store provides temporary block-level storage physically attached to EC2 instances, delivering high I/O performance ideal for ephemeral data like caches or buffers. Unlike Instance Store, S3 is network-attached with unlimited storage capacity and persistent data availability independent of instance lifecycle.
Key Differences Between S3 and Instance Store
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) offers highly durable, scalable, and persistent object storage accessible over the internet, designed for long-term data storage and backup with 99.999999999% (11 nines) durability. In contrast, Instance Store provides ephemeral storage physically attached to the host server, offering high I/O performance but data loss upon instance termination or failure. S3 supports data accessibility across multiple regions with built-in replication and lifecycle management, while Instance Store is limited to the lifecycle of its associated EC2 instance and lacks data replication features.
Use Cases for S3
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) excels in use cases requiring durable, scalable, and highly available object storage for backup, archival, and big data analytics. It supports static website hosting, content distribution, and disaster recovery due to its global infrastructure and virtually unlimited storage capacity. Unlike Instance Store, which is ephemeral and tied to a specific EC2 instance, S3 provides persistent storage accessible from multiple instances and services concurrently.
Use Cases for Instance Store
Instance Store provides ephemeral storage physically attached to the host server, making it ideal for temporary data such as caches, buffers, and scratch data that require high I/O performance and low latency. Use cases include processing data that can be regenerated quickly, like log storage during instance runtime or intermediate files in scientific computations and big data analytics. Unlike S3, Instance Store does not offer durability or persistence, so it is not suitable for critical data requiring long-term storage or high availability.
Performance Comparison: S3 vs Instance Store
Instance Store provides high-performance local storage with low latency and high IOPS, ideal for temporary data requiring rapid access during instance runtime. Amazon S3 offers scalable object storage with slightly higher latency but excels in durability, availability, and data persistence across regions. For workloads demanding ultra-fast, ephemeral storage, Instance Store outperforms S3, whereas S3 supports long-term data storage and sharing with consistent throughput at cloud scale.
Durability and Availability
Amazon S3 offers 99.999999999% (11 nines) of durability by automatically replicating data across multiple geographically separated Availability Zones, ensuring persistent storage even in the event of hardware failures. Instance Store provides ephemeral storage tied directly to the life of an EC2 instance, meaning data is lost when the instance stops or terminates, resulting in zero durability and significantly lower availability. For critical data requiring long-term persistence and high availability, S3 is the preferred choice, while Instance Store suits transient data with high I/O requirements but no durability guarantees.
Cost Analysis: S3 vs Instance Store
Amazon S3 offers scalable, pay-as-you-go object storage with costs based on data volume, requests, and data transfer, making it cost-effective for long-term storage and infrequent access. Instance Store provides ephemeral storage directly attached to EC2 instances, incurring no additional cost but limited by instance lifespan and capacity, suitable for temporary data and high I/O demands. Cost analysis favors S3 for durability and availability at scale, while Instance Store minimizes expenses for transient workloads without persistent data requirements.
Data Security and Compliance
Amazon S3 offers robust data security features including encryption at rest using SSE-S3, SSE-KMS, or SSE-C, comprehensive access controls via IAM policies, bucket policies, and ACLs, and compliance certifications such as HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS. In contrast, Instance Store provides ephemeral storage physically attached to the host server, meaning data is lost upon instance termination and lacks intrinsic encryption or compliance features, making it unsuitable for sensitive or regulated data. For enterprises requiring stringent data security and regulatory compliance, Amazon S3 is the preferred storage solution due to its durability, encryption options, and compliance frameworks.
Scalability and Flexibility
Amazon S3 offers virtually unlimited scalability with automatic scaling to handle petabytes of data and millions of requests per second, making it ideal for dynamic workloads and large-scale storage needs. Instance Store provides temporary, high-performance block storage directly attached to EC2 instances but lacks persistence and scalability beyond the instance's lifecycle and capacity. S3's flexibility supports diverse data types and access patterns with integrated data management features, whereas Instance Store is constrained by instance type and is best suited for transient storage requiring low latency.
Choosing the Right Storage Solution
Choosing between S3 (Simple Storage Service) and Instance Store depends on your application's durability, persistence, and scalability requirements. S3 provides highly durable, scalable object storage ideal for data backup, archival, and content distribution, offering 99.999999999% (11 nines) durability and seamless integration with AWS services. Instance Store offers ephemeral block-level storage with low-latency access, suited for temporary data like caches or buffers but lacks data persistence after instance termination, making it less ideal for critical or long-term storage needs.
S3 (Simple Storage Service) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com