The Authorization Code Grant is a secure OAuth 2.0 flow designed for server-side applications to obtain access tokens without exposing user credentials. It involves redirecting the user to an authorization server to obtain an authorization code, which your backend exchanges for an access token. Discover how this flow enhances security and improves your app's authentication process by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
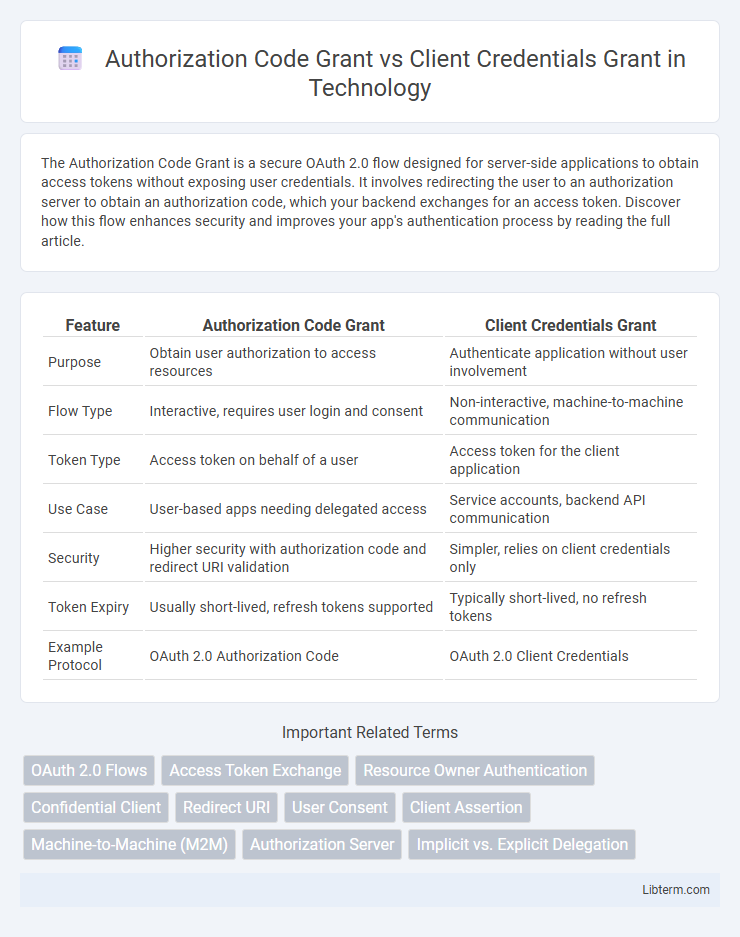
| Feature | Authorization Code Grant | Client Credentials Grant |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Obtain user authorization to access resources | Authenticate application without user involvement |
| Flow Type | Interactive, requires user login and consent | Non-interactive, machine-to-machine communication |
| Token Type | Access token on behalf of a user | Access token for the client application |
| Use Case | User-based apps needing delegated access | Service accounts, backend API communication |
| Security | Higher security with authorization code and redirect URI validation | Simpler, relies on client credentials only |
| Token Expiry | Usually short-lived, refresh tokens supported | Typically short-lived, no refresh tokens |
| Example Protocol | OAuth 2.0 Authorization Code | OAuth 2.0 Client Credentials |
Introduction to OAuth 2.0 Grant Types
OAuth 2.0 grant types define different methods for obtaining access tokens, each tailored to specific use cases and security requirements. The Authorization Code Grant is designed for user-centric applications where authorization involves user interaction and consent, typically used in web and mobile apps. The Client Credentials Grant suits machine-to-machine authentication, enabling server-to-server communication without user involvement, prioritizing secure client authentication.
What is Authorization Code Grant?
Authorization Code Grant is an OAuth 2.0 authorization flow designed for applications that can securely store client secrets, enabling users to grant access without sharing credentials. It involves redirecting the user to an authorization server to obtain an authorization code, which the client exchanges for an access token, ensuring enhanced security and user consent. This grant type is ideal for web and mobile applications requesting access to user-protected resources.
What is Client Credentials Grant?
Client Credentials Grant is an OAuth 2.0 flow used for server-to-server authentication, where the client application directly requests an access token by presenting its own credentials, without involving a user. This grant type is ideal for machine-to-machine communication, enabling secure access to resources or APIs under the application's control. Unlike Authorization Code Grant, which requires user authorization and involves an authorization code exchange, Client Credentials Grant operates solely on client authentication.
Key Differences Between the Two Flows
The Authorization Code Grant involves user interaction, requiring the resource owner's consent through a browser-based authorization step, making it ideal for applications needing delegated access. The Client Credentials Grant operates without user involvement, using only the client's credentials to obtain an access token, suitable for server-to-server communication or machine-to-machine authentication. Key differences include the presence of user authorization in Authorization Code Grant versus direct client authentication in Client Credentials Grant, and the typical usage scenarios reflecting these access requirements.
When to Use Authorization Code Grant
Use Authorization Code Grant when a client application needs to access resources on behalf of a user, ensuring secure user authentication and consent. This flow is ideal for web and mobile apps requiring user interaction to grant permissions, leveraging redirect-based exchange of authorization codes for access tokens. It provides enhanced security by involving user credentials indirectly, preventing exposure in client-side code.
When to Use Client Credentials Grant
Client Credentials Grant is ideal for server-to-server interactions where no user context is required, such as backend services accessing APIs securely. This grant type is used when applications need to authenticate themselves to access resources or perform automated tasks without user involvement. It provides a straightforward, secure method for machine-to-machine authentication, minimizing the complexity of user authorization flows inherent in Authorization Code Grant.
Security Considerations
Authorization Code Grant enhances security through user authentication and explicit consent, reducing risks of token interception by exchanging tokens server-side. Client Credentials Grant is suited for server-to-server communication without user context, relying heavily on secure storage of client secrets to prevent unauthorized access. Implementing secure transport (TLS) and proper token management practices is critical for both grants to mitigate token theft and replay attacks.
Common Use Cases in Real-world Applications
Authorization Code Grant is commonly used in web applications where users need to authenticate themselves and grant access to third-party apps, such as social media logins or payment processing platforms. Client Credentials Grant is preferred for server-to-server interactions without user context, including microservices communication and backend API integrations in enterprise environments. Both flows leverage OAuth 2.0 standards but serve distinct roles: user-centric access for Authorization Code vs. machine-to-machine authentication for Client Credentials.
Implementation Challenges and Best Practices
Authorization Code Grant implementation challenges include managing secure redirect URIs and handling authorization codes securely to prevent interception attacks. Best practices involve using Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE) to enhance security, validating redirect URIs strictly, and securely storing tokens. Client Credentials Grant challenges center on securely handling client secrets and limiting token scopes, with best practices emphasizing minimal privilege access, rotating client credentials regularly, and using secure environments for token storage.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right OAuth Grant Type
Authorization Code Grant suits applications needing user authentication, offering secure token exchange with user consent, while Client Credentials Grant best fits machine-to-machine communication without user involvement, providing direct access using client credentials. Selecting the appropriate OAuth grant depends on whether the flow requires user interaction or is purely backend service authorization. Enterprise developers prioritize Authorization Code for user data privacy and Client Credentials for service-to-service efficiency and security.
Authorization Code Grant Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com