A network segment refers to a portion of a computer network separated by devices like switches or routers to improve performance and reduce traffic congestion. Segmenting a network enhances security by isolating sensitive data and limits broadcast traffic, thereby optimizing overall network efficiency. Explore the rest of the article to understand how network segmentation can benefit your IT infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
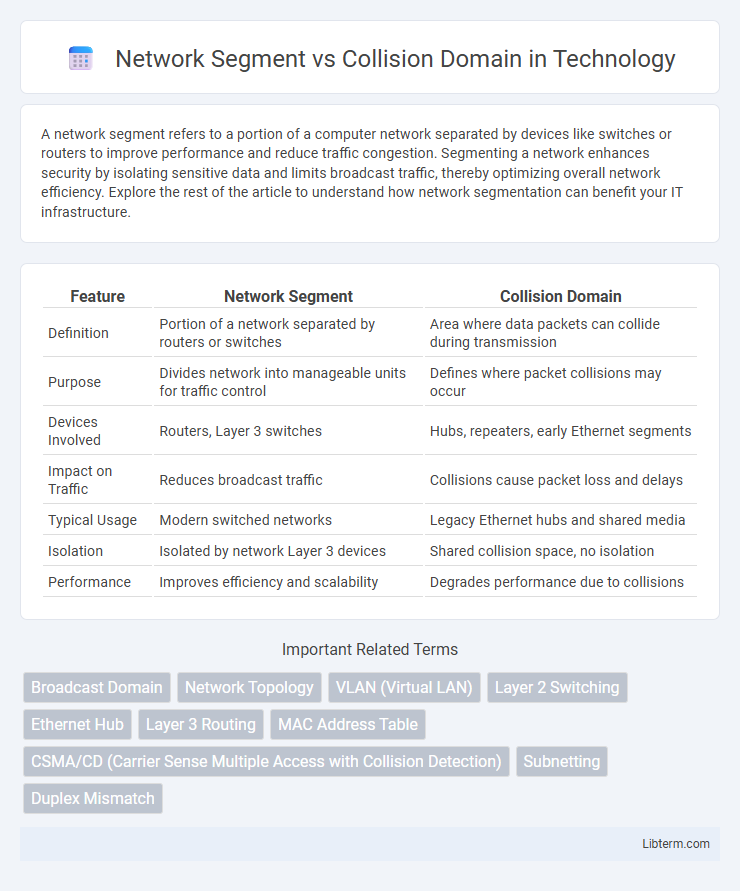
| Feature | Network Segment | Collision Domain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Portion of a network separated by routers or switches | Area where data packets can collide during transmission |
| Purpose | Divides network into manageable units for traffic control | Defines where packet collisions may occur |
| Devices Involved | Routers, Layer 3 switches | Hubs, repeaters, early Ethernet segments |
| Impact on Traffic | Reduces broadcast traffic | Collisions cause packet loss and delays |
| Typical Usage | Modern switched networks | Legacy Ethernet hubs and shared media |
| Isolation | Isolated by network Layer 3 devices | Shared collision space, no isolation |
| Performance | Improves efficiency and scalability | Degrades performance due to collisions |
Introduction: Understanding Network Segments and Collision Domains
Network segments are distinct sections of a computer network separated by devices like switches or routers, designed to manage traffic efficiently. Collision domains refer to parts of a network where data packets can collide during transmission, primarily occurring in hubs or shared media environments. Understanding the difference enhances network performance by minimizing collisions and optimizing data flow across segments.
Defining Network Segments
Network segments are distinct physical or logical divisions within a network that separate traffic to improve performance and security by isolating communication paths. Each network segment represents a defined broadcast domain that can limit data packet propagation and reduce congestion. Unlike collision domains, which are areas where data packets can collide, segments use devices like switches or routers to manage and control traffic flow efficiently.
What is a Collision Domain?
A collision domain is a network segment where data packets can collide with one another when being sent on a shared medium, typically in Ethernet networks using hubs or repeaters. It is defined by all devices whose data transmissions can interfere, causing collisions that result in network retransmissions and reduced performance. Network segments separated by switches or routers reduce the size of collision domains, improving overall network efficiency and minimizing packet collisions.
Key Differences Between Network Segment and Collision Domain
A network segment is a portion of a computer network separated by devices like routers or switches, designed to reduce traffic and improve performance, while a collision domain is an area where data packets can collide during transmission. Network segments increase network efficiency by partitioning traffic, whereas collision domains relate specifically to potential data packet collisions within shared mediums such as hubs or coaxial cables. Understanding the distinction is crucial for optimizing network design, as segments manage overall traffic flow, and collision domains determine the likelihood of data transmission conflicts.
How Network Devices Impact Segments and Collision Domains
Network switches create multiple collision domains by isolating each connected device, thereby reducing collisions and increasing network efficiency, while hubs extend a single collision domain across all ports, causing increased collisions. Routers segment broadcast domains rather than collision domains, directing traffic between different network segments and improving overall performance. Network bridges divide collision domains by forwarding traffic only to the intended segment, minimizing packet collisions and optimizing data flow.
Role of Switches and Hubs in Collision Domains
Switches segment a network into multiple collision domains by providing dedicated bandwidth to each connected device, effectively isolating traffic and reducing collisions. Hubs, however, operate within a single collision domain by broadcasting incoming signals to all ports, causing devices to compete for bandwidth and increasing collision likelihood. The use of switches significantly improves network efficiency by minimizing collisions, whereas hubs create a shared collision domain that limits performance.
Designing Efficient Network Segmentation
Designing efficient network segmentation requires understanding the distinctions between network segments and collision domains to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion. Network segments divide a LAN into multiple sections using devices like switches or routers, enhancing performance by isolating traffic and limiting broadcast domains. Collision domains are subnetworks where packet collisions can occur; minimizing their size with switches instead of hubs reduces collisions, increases throughput, and improves overall network efficiency.
Collision Domain Reduction Strategies
Collision domain reduction strategies primarily involve network segmentation using switches and bridges to isolate traffic and minimize data collisions. Implementing VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) further divides the network into separate collision domains, enhancing performance and reducing broadcast traffic. Employing full-duplex communication in switches eliminates collisions by allowing simultaneous data transmission and reception on separate channels.
Network Performance: Segmenting and Collision Domain Considerations
Network segmentation reduces collision domains by dividing a large network into smaller, manageable segments, thereby minimizing data packet collisions and improving overall network performance. Each collision domain represents a network segment where devices compete for bandwidth, leading to potential delays and decreased efficiency. Implementing switches or routers to create multiple collision domains enhances data throughput and reduces latency by isolating traffic within smaller network segments.
Conclusion: Optimizing Networks with Proper Segmentation
Proper network segmentation reduces collision domains, enhancing overall network performance and minimizing data packet collisions. By dividing a large network into smaller segments using switches or routers, devices communicate more efficiently within each segment, reducing congestion and improving bandwidth utilization. Optimizing networks with clear segmentation strategies ensures faster data transmission, increased scalability, and improved security by containing broadcast traffic and isolating faults.
Network Segment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com