Verification ensures the accuracy and authenticity of data, protecting your information from errors and fraud. It plays a crucial role in maintaining security across digital platforms and financial transactions. Dive into the article to discover how effective verification methods can safeguard your assets.
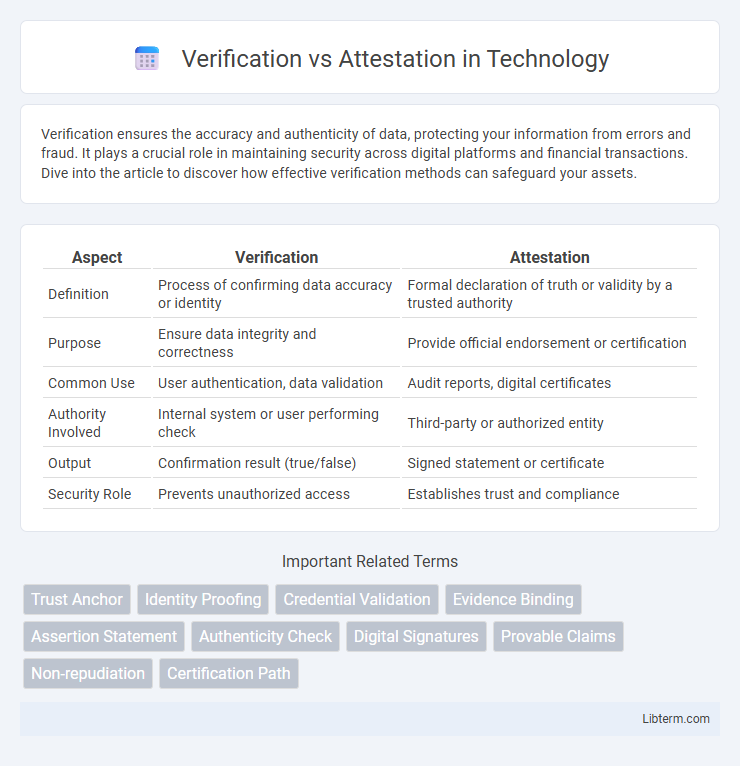
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Verification | Attestation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of confirming data accuracy or identity | Formal declaration of truth or validity by a trusted authority |
| Purpose | Ensure data integrity and correctness | Provide official endorsement or certification |
| Common Use | User authentication, data validation | Audit reports, digital certificates |
| Authority Involved | Internal system or user performing check | Third-party or authorized entity |
| Output | Confirmation result (true/false) | Signed statement or certificate |
| Security Role | Prevents unauthorized access | Establishes trust and compliance |
Understanding Verification and Attestation
Verification involves the process of confirming the accuracy and truthfulness of information through direct evidence, often by examining documents, records, or physical assets. Attestation refers to a formal declaration made by an independent third party, such as a certified auditor, affirming the reliability and validity of a specific statement or financial report. Understanding the distinction highlights verification as the factual inspection step, while attestation represents an official confirmation endorsing those verified facts.
Key Differences Between Verification and Attestation
Verification involves the process of examining evidence and validating facts to ensure accuracy and truthfulness, often through direct inspection or data analysis. Attestation, on the other hand, refers to a formal declaration or certification by a qualified individual, confirming that information or processes comply with established standards or criteria. The key difference lies in verification being focused on evidence assessment, while attestation provides an official endorsement of that evidence by an authoritative party.
The Purpose of Verification
Verification ensures the accuracy and validity of information by systematically checking facts, documents, or data against established standards or criteria. It serves to confirm compliance, identify discrepancies, and provide confidence in the integrity of the verified subject. This process is critical in various industries such as finance, software development, and quality control to prevent errors and maintain trust.
The Role of Attestation
Attestation plays a critical role in reinforcing trust by providing a formal statement from an independent party confirming the accuracy or authenticity of information. Unlike verification, which involves checking data directly against standards or evidence, attestation offers assurance through certification or endorsement by a qualified professional. This process is essential in fields like auditing, cybersecurity, and compliance, where validating claims through credible third-party confirmation enhances reliability and accountability.
Common Use Cases for Verification
Verification is commonly used in identity management systems, such as confirming user credentials during account creation or login to prevent fraud. It also plays a critical role in supply chain management by validating product authenticity and tracking provenance. Financial institutions rely on verification to ensure customer information matches records, supporting compliance with Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations.
Real-World Applications of Attestation
Attestation plays a critical role in supply chain management by providing third-party validation of product authenticity and compliance, thereby reducing fraud and enhancing trust among stakeholders. In cybersecurity, attestation verifies system integrity and software authenticity, ensuring devices operate securely within trusted environments. Financial auditing leverages attestation reports to confirm the accuracy and reliability of financial statements, supporting regulatory compliance and investor confidence.
Benefits of Verification Processes
Verification processes enhance data accuracy by systematically validating information against established criteria, reducing errors and inconsistencies. These processes increase trustworthiness and reliability of records, facilitating informed decision-making and regulatory compliance. Efficient verification also streamlines operations by identifying discrepancies early, minimizing risks and enhancing overall organizational efficiency.
Advantages of Attestation Methods
Attestation methods provide enhanced credibility by involving an independent third party to validate information, increasing trust and reliability for stakeholders. These methods often comply with regulatory standards, ensuring transparency and reducing legal risks for organizations. Attestation also supports improved decision-making by delivering verified data that stakeholders can confidently rely on for audits and financial reporting.
Challenges in Verification and Attestation
Challenges in verification include the complexity of accurately assessing identity or data against established standards, often hindered by incomplete or inconsistent information. Attestation faces difficulties in ensuring the credibility and reliability of declarations made by third parties without direct access to underlying evidence. Both processes must address concerns related to data privacy, fraud prevention, and maintaining trust in automated and manual validation systems.
Choosing Between Verification and Attestation
Choosing between verification and attestation depends on the level of assurance required and the scope of the information involved. Verification involves confirming the accuracy and truthfulness of facts or data, suitable for routine checks and internal control processes. Attestation provides a formal, third-party endorsement, typically necessary for compliance, financial reporting, or regulatory requirements demanding an independent assessment.
Verification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com