Staging transforms your space to highlight its best features and create an inviting atmosphere that appeals to potential buyers. Strategic furniture placement, lighting, and decor can help showcase the functionality and flow of each room, making it easier for buyers to envision themselves living there. Discover how professional staging can enhance your property's appeal and speed up the selling process in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
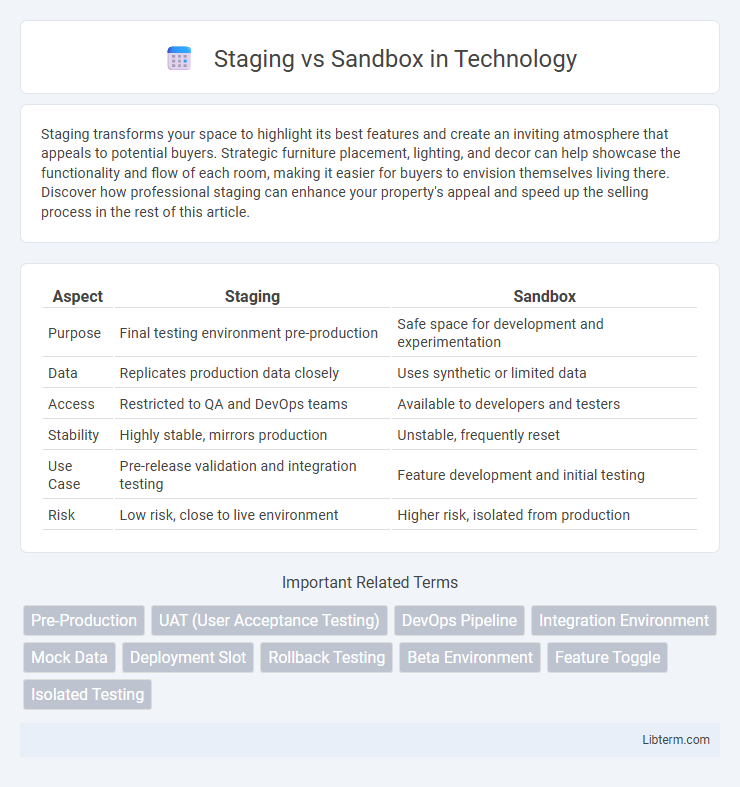
| Aspect | Staging | Sandbox |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Final testing environment pre-production | Safe space for development and experimentation |
| Data | Replicates production data closely | Uses synthetic or limited data |
| Access | Restricted to QA and DevOps teams | Available to developers and testers |
| Stability | Highly stable, mirrors production | Unstable, frequently reset |
| Use Case | Pre-release validation and integration testing | Feature development and initial testing |
| Risk | Low risk, close to live environment | Higher risk, isolated from production |
Introduction to Staging and Sandbox Environments
Staging environments replicate the production setup to test new features and updates under real-world conditions, ensuring reliability before deployment. Sandbox environments provide isolated spaces for developers to experiment, troubleshoot, and develop code without impacting live systems. Both environments are essential for maintaining software quality and stability throughout the development lifecycle.
What is a Staging Environment?
A staging environment is a pre-production environment that closely replicates the live production system, allowing teams to test new features, fixes, and updates in conditions that mirror the actual user experience. It is designed to identify bugs, performance issues, and integration problems before deployment, ensuring higher software quality and reducing risks of failures in production. This environment typically contains a duplicate of production data and configurations to simulate real-world scenarios accurately.
What is a Sandbox Environment?
A Sandbox environment is a secure, isolated testing space designed for developers to experiment with new code or features without affecting the live production system. It mimics the production setup but allows unrestricted testing, debugging, and integration activities, ensuring that errors or changes do not impact real users. This environment is essential for safe innovation, enabling thorough validation before deployment to staging or production environments.
Key Differences Between Staging and Sandbox
Staging environments replicate the production setup to enable final testing and quality assurance before deployment, ensuring data integrity and system performance mirror live conditions. Sandbox environments provide isolated spaces for developers to experiment, develop new features, and test code without affecting production or staging data. Key differences include the purpose--staging for validation and sandbox for experimentation--and data fidelity, with staging using production-like data and sandbox often using synthetic or partial datasets.
Use Cases for Staging Environments
Staging environments provide a critical platform for pre-production testing by replicating the exact conditions of a live system, enabling developers to validate new features, perform quality assurance, and identify bugs before deployment. Use cases include user acceptance testing (UAT), performance testing under production-like loads, and integration testing with third-party services to ensure seamless functionality. This environment minimizes risks by allowing comprehensive real-world simulations without affecting end users or live data.
Use Cases for Sandbox Environments
Sandbox environments are primarily used for testing new features, developing code, and experimenting with configurations without impacting live systems. They enable developers and testers to simulate real-world scenarios safely, ensuring issues are identified and resolved before deployment. Common use cases include validating software updates, performing security testing, and training users in a risk-free setting.
Benefits of Staging vs Sandbox
Staging environments provide a near-exact replica of the production system, enabling thorough testing of new features in conditions that closely mimic live usage, which reduces the risk of post-deployment issues. Sandboxes offer isolated spaces primarily for development and experimentation without impacting other systems but lack the comprehensive integration testing capability found in staging. The key benefit of staging over sandbox is its ability to validate end-to-end workflows and performance under realistic scenarios, ensuring higher confidence before release.
Best Practices for Staging and Sandbox Environments
Staging environments should mirror production setups precisely to ensure accurate testing of new features and configurations before deployment, minimizing risks of bugs in live systems. Sandbox environments are best used for isolated experimentation and development, allowing developers to test code without impacting shared resources or the integrity of staging and production environments. Both environments require strict access controls, regular data refreshes, and clear separation to maintain security and operational efficiency.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Confusing staging and sandbox environments often leads to improper testing, causing deployment failures in production. A common mistake is using sandbox data in staging, which lacks production-level realism and can result in overlooked bugs. Ignoring environment-specific configurations during testing in staging or sandbox risks inconsistent application behavior upon release.
Choosing the Right Environment for Your Project
Choosing the right environment for your project depends on the testing goals and risk tolerance. Staging environments replicate production settings, allowing final validation and user acceptance testing with realistic data, ideal for catching critical bugs before deployment. Sandbox environments offer isolated spaces for experimental development and early-stage testing without affecting production data, providing flexibility for developers to innovate safely.
Staging Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com