Rate limiting controls the number of requests a user or system can make to an API or service within a specified timeframe, protecting servers from overload and abuse. Effective rate limiting ensures optimal performance and enhances security by preventing denial-of-service attacks and resource exhaustion. Explore the rest of the article to learn how implementing rate limiting can safeguard your applications and improve user experience.
Table of Comparison
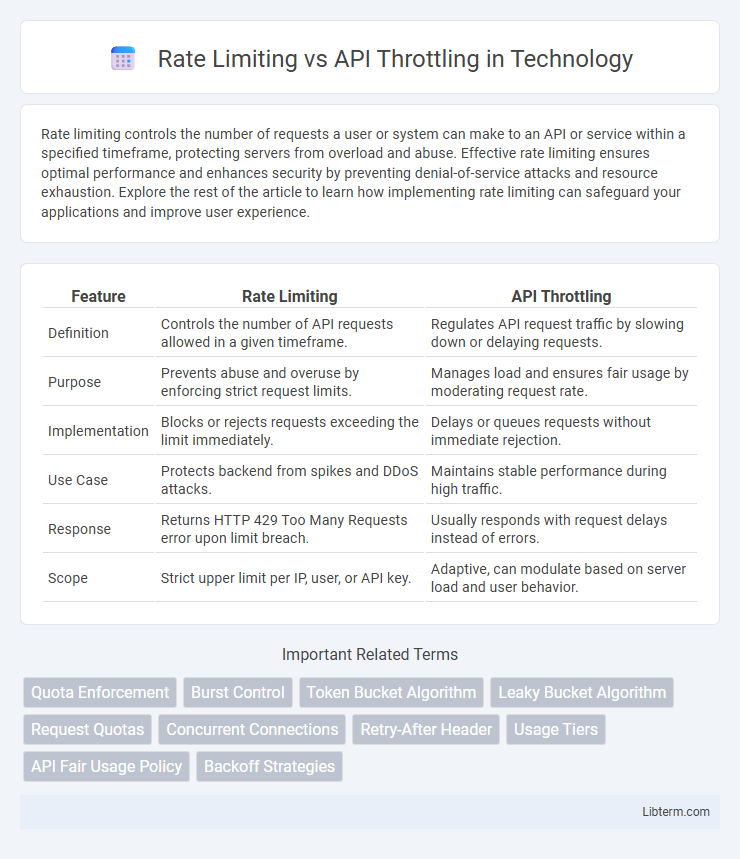
| Feature | Rate Limiting | API Throttling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Controls the number of API requests allowed in a given timeframe. | Regulates API request traffic by slowing down or delaying requests. |
| Purpose | Prevents abuse and overuse by enforcing strict request limits. | Manages load and ensures fair usage by moderating request rate. |
| Implementation | Blocks or rejects requests exceeding the limit immediately. | Delays or queues requests without immediate rejection. |
| Use Case | Protects backend from spikes and DDoS attacks. | Maintains stable performance during high traffic. |
| Response | Returns HTTP 429 Too Many Requests error upon limit breach. | Usually responds with request delays instead of errors. |
| Scope | Strict upper limit per IP, user, or API key. | Adaptive, can modulate based on server load and user behavior. |
Understanding Rate Limiting and API Throttling
Rate limiting controls the number of API requests a user or client can make within a specified time window to prevent abuse and ensure fair resource distribution. API throttling dynamically adjusts the request processing rate based on current system load, often slowing down or queuing excess requests to maintain performance stability. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for designing scalable APIs that protect backend services while optimizing user experience.
Key Differences Between Rate Limiting and Throttling
Rate limiting controls the number of API requests a user can make within a defined time window to prevent abuse and ensure fair usage, while API throttling dynamically adjusts the request processing rate based on server load or predefined thresholds to maintain system stability. Rate limiting enforces strict quotas by rejecting requests that exceed the limit, whereas throttling slows down request processing or queues requests to manage traffic spikes without immediate rejection. Rate limiting is typically static and policy-driven, whereas throttling is adaptive and responsive to real-time conditions, optimizing resource allocation and user experience.
Why Rate Limiting Matters in APIs
Rate limiting ensures APIs maintain performance and reliability by capping the number of requests a client can make within a specified timeframe, preventing server overload and potential downtime. It protects backend resources from abuse and helps manage traffic spikes, ensuring fair usage among all users. Implementing rate limiting is critical for maintaining API availability, reducing latency, and safeguarding against denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
How API Throttling Protects Services
API throttling protects services by controlling the number of requests a user can make within a specified time frame, effectively preventing server overload and ensuring consistent performance. By capping request rates, throttling helps maintain service availability during traffic spikes and mitigates the impact of abusive behaviors like DDoS attacks. This mechanism preserves backend resources, ensuring fair usage and enhancing overall reliability of the API infrastructure.
Common Techniques for Implementing Rate Limiting
Common techniques for implementing rate limiting include token bucket, leaky bucket, fixed window, and sliding window algorithms. Token bucket allows a set number of tokens to be consumed per time frame, providing smooth request handling, while leaky bucket enforces a constant output rate by queuing incoming requests. Fixed window counts requests within discrete time intervals, and sliding window improves accuracy by tracking request timestamps within a rolling timeframe.
Throttling Algorithms Explained
API throttling manages traffic by controlling the number of requests a client can make over a specific period, preventing system overload. Common throttling algorithms include Token Bucket, which allows bursts of traffic by accumulating tokens, and Leaky Bucket, which processes requests at a steady rate to smooth traffic spikes. Rate limiting sets fixed request caps per time window, while throttling algorithms dynamically adjust request flow based on system capacity and usage patterns.
Benefits of Rate Limiting for Developers
Rate limiting protects APIs from excessive requests, ensuring system stability and consistent performance for developers by preventing server overload. It enhances security by mitigating denial-of-service attacks and reducing abuse, allowing developers to maintain reliable service availability. Implementing rate limiting helps manage resource consumption efficiently, facilitating scalable and predictable API usage patterns.
Real-World Use Cases for API Throttling
API throttling controls the rate of API requests by dynamically limiting bandwidth or access during peak times to maintain system stability and ensure fair resource distribution among users. Real-world use cases include social media platforms preventing abuse from automated bots, e-commerce sites managing flash sale traffic spikes, and financial services enforcing transaction limits for compliance and security. Effective throttling enhances user experience by reducing downtime and maintaining consistent performance under varying load conditions.
Best Practices for Managing API Traffic
Rate limiting enforces fixed thresholds on API requests within a specific timeframe to prevent overload, ensuring stable performance and fair resource allocation. API throttling dynamically adjusts request rates based on system capacity, allowing for adaptability during traffic spikes while maintaining service availability. Implementing a combination of both, along with monitoring tools and clear client communication, optimizes API traffic management and enhances overall user experience.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Rate Limiting vs API Throttling
Choosing the right strategy between rate limiting and API throttling depends on the specific requirements for controlling API traffic and maintaining service stability. Rate limiting enforces a fixed cap on the number of requests a client can make within a defined time window, preventing abuse and ensuring fair usage across all users. API throttling dynamically adjusts request handling based on current server load or client behavior, optimizing performance while minimizing latency during peak usage.
Rate Limiting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com