Unstructured data refers to information that lacks a predefined format or organization, making it challenging to analyze using traditional databases. It includes sources like emails, social media posts, videos, and images, which require advanced techniques such as natural language processing and machine learning for meaningful insights. Explore the rest of this article to discover how you can effectively manage and leverage unstructured data for your business.
Table of Comparison
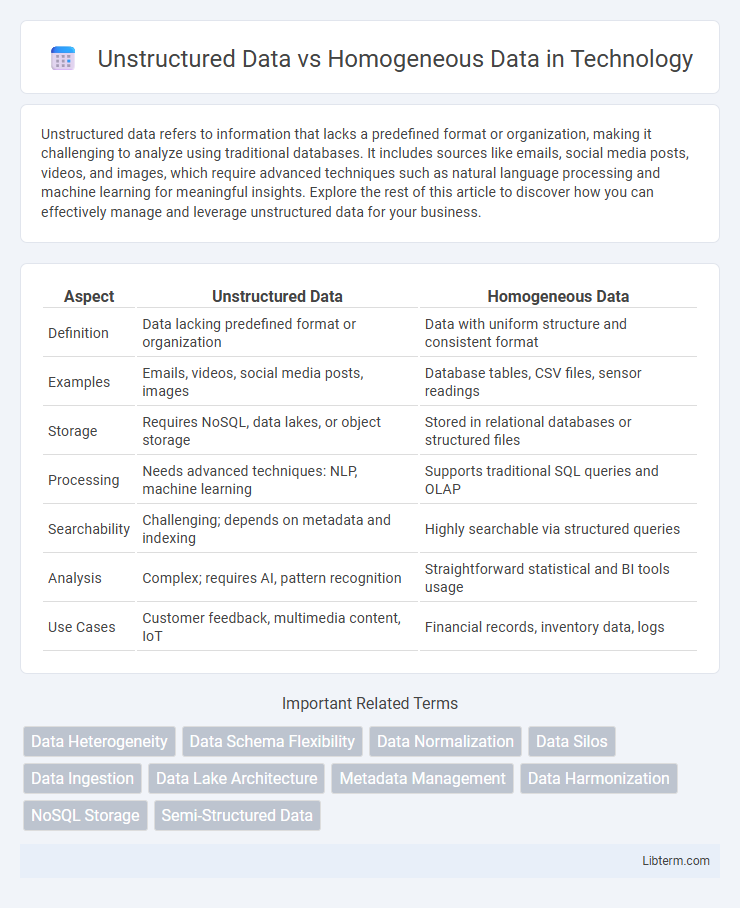
| Aspect | Unstructured Data | Homogeneous Data |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data lacking predefined format or organization | Data with uniform structure and consistent format |
| Examples | Emails, videos, social media posts, images | Database tables, CSV files, sensor readings |
| Storage | Requires NoSQL, data lakes, or object storage | Stored in relational databases or structured files |
| Processing | Needs advanced techniques: NLP, machine learning | Supports traditional SQL queries and OLAP |
| Searchability | Challenging; depends on metadata and indexing | Highly searchable via structured queries |
| Analysis | Complex; requires AI, pattern recognition | Straightforward statistical and BI tools usage |
| Use Cases | Customer feedback, multimedia content, IoT | Financial records, inventory data, logs |
Introduction to Unstructured and Homogeneous Data
Unstructured data refers to information that lacks a predefined format or organization, including text documents, images, videos, and social media content, making it challenging to analyze using traditional databases. Homogeneous data consists of uniform, consistently structured information, such as numerical datasets or standardized records, enabling straightforward processing and analysis. Understanding the distinction between unstructured and homogeneous data is crucial for selecting appropriate storage, management, and analytical techniques in data science and machine learning applications.
Defining Unstructured Data
Unstructured data comprises information that lacks a predefined data model or organization, including text documents, images, videos, and social media posts. Unlike homogeneous data, which is uniform and organized in consistent formats like databases or spreadsheets, unstructured data requires advanced processing techniques such as natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning for analysis. The vast volume and variety of unstructured data present challenges in storage, management, and extraction of meaningful insights compared to the structured nature of homogeneous data.
Understanding Homogeneous Data
Homogeneous data consists of uniform and consistent data types or formats, allowing for easier storage, processing, and analysis compared to unstructured data. This type of data is typically found in structured databases where entries follow a predefined schema, such as numerical values, dates, or standardized text fields. Understanding homogeneous data is crucial for optimizing data management systems and improving the accuracy of statistical modeling and machine learning algorithms.
Key Characteristics of Unstructured Data
Unstructured data lacks a predefined format or organization, making it highly diverse and complex, often including text files, images, videos, and social media content. It does not fit neatly into traditional relational databases, requiring advanced processing techniques such as natural language processing and machine learning for analysis. Contrastingly, homogeneous data is uniform and structured, enabling easier storage, querying, and management within standardized database systems.
Main Features of Homogeneous Data
Homogeneous data consists of uniform data types or formats, allowing for consistent processing and analysis. It facilitates easier data integration, querying, and statistical operations due to its structured nature and predictable schema. This uniformity enhances data quality, reduces complexity, and improves the efficiency of data management systems compared to unstructured data.
Differences Between Unstructured and Homogeneous Data
Unstructured data consists of diverse formats like text, images, and videos that lack a predefined data model, making it complex to analyze and organize. Homogeneous data, in contrast, refers to uniform data types with consistent structure and format, allowing for straightforward processing and integration. The primary difference lies in data variability and structure, where unstructured data demands advanced techniques for extraction and understanding, while homogeneous data supports efficient querying and standard analytical methods.
Use Cases for Unstructured Data
Unstructured data, such as emails, videos, social media posts, and sensor data, is pivotal in use cases like customer sentiment analysis, fraud detection, and predictive maintenance, where insights emerge from complex, varied inputs. Unlike homogeneous data, which is organized and consistent for straightforward analysis, unstructured data requires advanced technologies like natural language processing and machine learning to extract meaningful information. Industries including healthcare, finance, and retail leverage unstructured data to enhance decision-making, personalize customer experiences, and optimize operational efficiency.
Applications of Homogeneous Data
Homogeneous data, characterized by uniform format and consistent structure, is extensively applied in financial analytics, where predictable data types such as transaction records enable efficient modeling and forecasting. In healthcare, homogeneous data facilitates streamlined patient record management and supports machine learning algorithms for diagnosis by providing standardized input. Manufacturing industries rely on homogeneous data to monitor production processes and optimize supply chain operations through consistent sensor readings and inventory logs.
Challenges in Managing Unstructured vs Homogeneous Data
Unstructured data, such as emails, videos, and social media posts, presents significant challenges in storage, organization, and analysis due to its lack of predefined format and diverse sources. Homogeneous data, characterized by uniform format and structure like relational databases, allows for easier integration, querying, and management but may limit insights when handling complex or varied information. The complexity of managing unstructured data demands advanced processing techniques like natural language processing and machine learning to extract meaningful patterns, whereas homogeneous data benefits from established data management tools and standardized query languages like SQL.
Future Trends in Data Management
Future trends in data management highlight the growing importance of unstructured data, which now constitutes over 80% of enterprise data, driven by the rise of multimedia, social media, and IoT-generated content. Advanced AI and machine learning technologies are evolving to efficiently analyze and extract insights from unstructured data, offering richer, more actionable intelligence compared to traditional homogeneous data sets. Data management platforms are increasingly integrating automated classification and semantic analysis tools to handle the complexity and scale of heterogeneous data environments, fostering enhanced decision-making and innovation.
Unstructured Data Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com