Private cloud offers dedicated computing resources that enhance security and control for your organization, ensuring sensitive data remains protected. This approach provides customizable infrastructure tailored to specific business needs, improving performance and compliance. Discover how implementing a private cloud can transform your operations in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
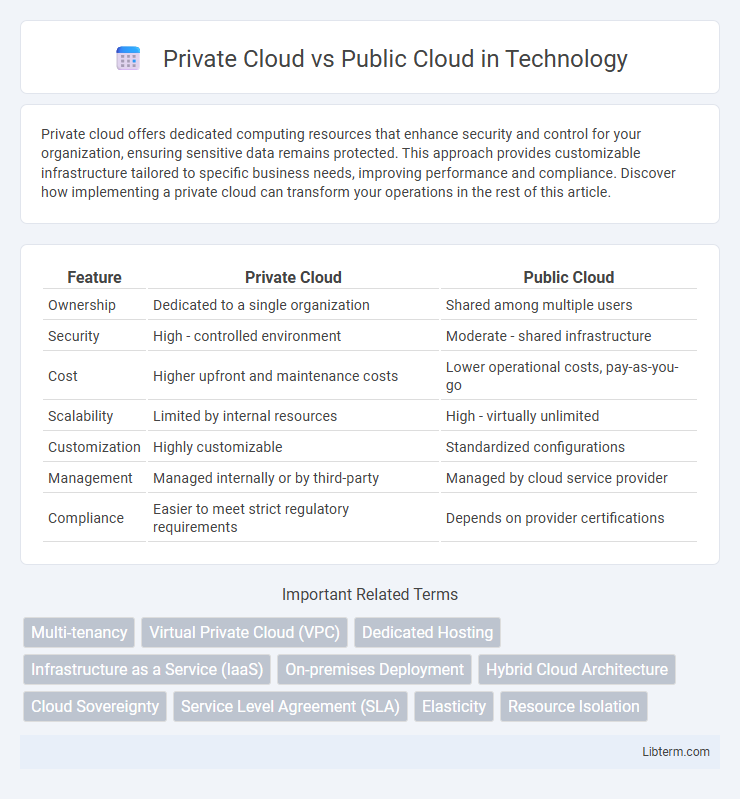
| Feature | Private Cloud | Public Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Dedicated to a single organization | Shared among multiple users |
| Security | High - controlled environment | Moderate - shared infrastructure |
| Cost | Higher upfront and maintenance costs | Lower operational costs, pay-as-you-go |
| Scalability | Limited by internal resources | High - virtually unlimited |
| Customization | Highly customizable | Standardized configurations |
| Management | Managed internally or by third-party | Managed by cloud service provider |
| Compliance | Easier to meet strict regulatory requirements | Depends on provider certifications |
Introduction to Cloud Computing Models
Private cloud offers dedicated infrastructure and enhanced security tailored for a single organization, ensuring compliance and control over data and applications. Public cloud provides scalable, cost-effective resources shared across multiple users, leveraging services from providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. Understanding these cloud computing models helps businesses choose the right balance between flexibility, control, and cost efficiency.
Defining Private Cloud: Key Features and Benefits
Private cloud refers to a cloud computing environment dedicated exclusively to a single organization, providing enhanced security, control, and customization compared to public cloud services. Key features include isolated infrastructure, on-premises or hosted data centers, and strict access controls that ensure compliance with regulatory and privacy requirements. Benefits of private cloud encompass improved data protection, tailored resource allocation, and greater flexibility to meet specific business needs and performance standards.
Defining Public Cloud: Key Features and Benefits
Public cloud environments provide scalable and cost-effective computing resources managed by third-party providers like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. Key features include on-demand self-service, broad network access, and resource pooling, enabling businesses to quickly deploy applications without owning physical infrastructure. Benefits of public cloud adoption include reduced capital expenditures, enhanced flexibility, automatic updates, and access to advanced technologies such as AI and machine learning services.
Security and Compliance Considerations
Private cloud environments offer enhanced security controls and customized compliance measures tailored to specific organizational needs, making them ideal for industries with strict regulatory requirements such as healthcare and finance. Public clouds provide scalable security features managed by cloud service providers, leveraging advanced threat detection and continuous monitoring but may present challenges with data sovereignty and compliance certification across multiple jurisdictions. Companies must evaluate their risk tolerance, data sensitivity, and regulatory obligations to determine the best fit between private cloud isolation and public cloud flexibility for secure, compliant operations.
Cost Analysis: Private Cloud vs Public Cloud
Private cloud deployments typically involve higher upfront capital expenses due to dedicated infrastructure and maintenance costs, whereas public clouds offer a pay-as-you-go pricing model with reduced initial investment. Operational expenses for private clouds include ongoing hardware upgrades and IT personnel, while public cloud costs fluctuate based on resource consumption, enabling scalability and cost efficiency. Total cost of ownership analysis reveals public clouds often provide lower costs for dynamic workloads, but private clouds may offer financial advantages for predictable, high-utilization environments.
Performance and Scalability Differences
Private cloud environments deliver dedicated resources that offer higher performance consistency and lower latency compared to public clouds, making them ideal for workloads requiring stringent performance guarantees. Public cloud platforms provide virtually unlimited scalability by leveraging massive multi-tenant infrastructure, enabling organizations to rapidly scale resources up or down based on demand without upfront capital investment. Performance in public clouds can vary due to shared resources and multi-tenancy, whereas private clouds ensure predictable, dedicated resource allocation tailored to specific business needs.
Customization and Control: A Comparative Overview
Private clouds offer superior customization and control, enabling organizations to tailor infrastructure, security settings, and compliance measures to specific business needs. Public clouds provide standardized environments with limited customization options, optimized for scalability and cost-efficiency but less granular control. Companies requiring stringent data governance and specialized workloads typically prefer private clouds for their enhanced configurability and management capabilities.
Use Case Scenarios: When to Choose Each Model
Private cloud is ideal for organizations requiring enhanced security, compliance, and control over sensitive data, such as financial institutions and healthcare providers. Public cloud suits businesses seeking scalability, cost efficiency, and access to a broad range of services, common in startups and e-commerce platforms. Hybrid cloud models combine these benefits, supporting diverse workloads with varying regulatory and performance needs.
Management and Maintenance Requirements
Private cloud environments demand dedicated IT teams to manage infrastructure, perform regular maintenance, and ensure security compliance, resulting in higher operational overhead. Public cloud providers handle most maintenance tasks, including hardware updates, patch management, and network security, reducing the management burden for users. Organizations must weigh the trade-off between control in private clouds and the streamlined maintenance offered by public cloud services.
Future Trends in Cloud Deployment Choices
Future trends in cloud deployment indicate a growing shift towards hybrid and multi-cloud strategies that combine private and public cloud environments to optimize scalability, security, and cost-efficiency. Artificial intelligence and edge computing integration will drive more organizations to adopt private clouds for sensitive workloads while leveraging public clouds for burst capacity and global reach. Enhanced automation and advanced security frameworks in cloud platforms will further influence enterprises to balance private cloud control with public cloud flexibility in their infrastructure choices.
Private Cloud Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com