Disk storage plays a crucial role in managing and preserving your digital data efficiently. Understanding the different types of disks, such as HDDs and SSDs, helps optimize your system's speed and reliability. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to choose the best disk for your needs and maximize your computer's performance.
Table of Comparison
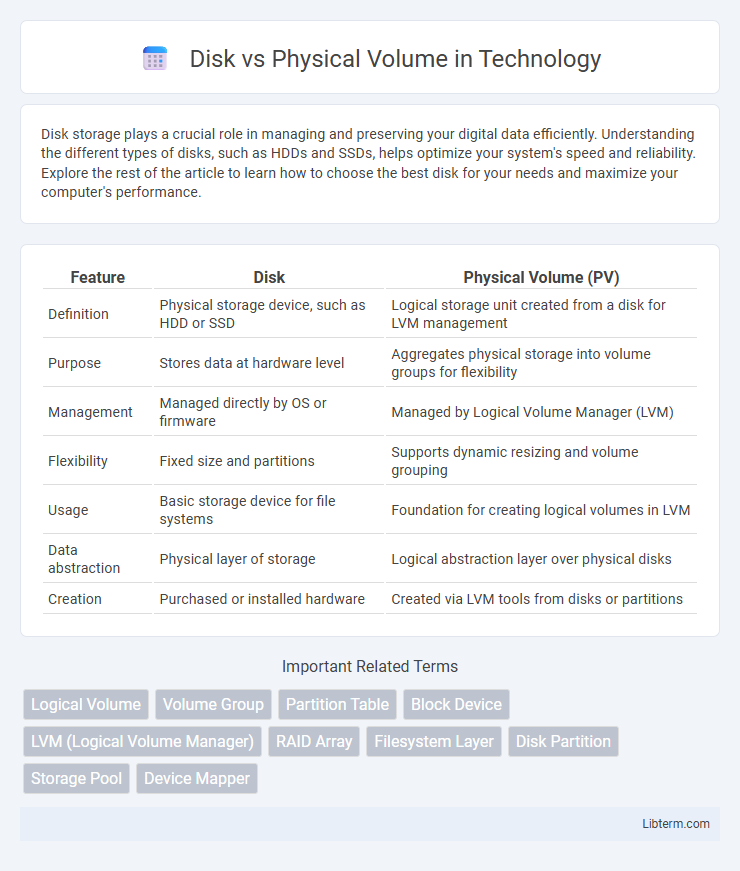
| Feature | Disk | Physical Volume (PV) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical storage device, such as HDD or SSD | Logical storage unit created from a disk for LVM management |
| Purpose | Stores data at hardware level | Aggregates physical storage into volume groups for flexibility |
| Management | Managed directly by OS or firmware | Managed by Logical Volume Manager (LVM) |
| Flexibility | Fixed size and partitions | Supports dynamic resizing and volume grouping |
| Usage | Basic storage device for file systems | Foundation for creating logical volumes in LVM |
| Data abstraction | Physical layer of storage | Logical abstraction layer over physical disks |
| Creation | Purchased or installed hardware | Created via LVM tools from disks or partitions |
Overview: Disk vs Physical Volume
A disk refers to a physical storage device that holds data, such as a hard disk drive (HDD) or solid-state drive (SSD), while a physical volume (PV) is a storage unit within the Logical Volume Manager (LVM) framework that abstracts the disk for flexible management. Physical volumes are created by initializing disks or disk partitions, enabling them to be grouped into volume groups (VGs) for dynamic allocation. This separation allows better storage management, as PVs serve as building blocks for logical volumes without being tied directly to raw disk constraints.
Defining Disks in Modern Computing
Disks in modern computing refer to physical storage devices such as HDDs or SSDs that provide non-volatile data retention and are fundamental for system operations. Physical volumes, often created from these disks, represent partitioned segments or entire disks used in logical volume management systems to enable flexible storage allocation. Understanding disks as tangible hardware components is crucial before delving into logical abstractions like physical volumes that optimize storage management and scalability.
What is a Physical Volume?
A Physical Volume (PV) is a storage device or partition used in Logical Volume Management (LVM) to create flexible and manageable storage pools. Unlike a traditional disk that represents the entire hardware storage unit, a PV can be a part of a disk, multiple disks, or RAID arrays, allowing the creation of Volume Groups (VGs) for advanced storage management. PVs provide abstraction over physical disks, enabling features like resizing, snapshots, and dynamic volume allocation in Linux environments.
Key Differences Between Disk and Physical Volume
A disk is a physical storage device, such as a hard drive or SSD, that stores digital data, while a physical volume (PV) refers to a partition or segment of a disk that is used in Logical Volume Management (LVM) systems. Disks serve as the hardware foundation, whereas physical volumes act as abstraction layers allowing flexible allocation and management of storage space. Key differences include the physical hardware nature of disks compared to the logical, managed structure of physical volumes in LVM environments.
Disk Usage in Traditional Storage Systems
Disk usage in traditional storage systems is managed by dividing physical disks into physical volumes, which serve as the fundamental units for data allocation and storage management. Physical volumes enable efficient space utilization by grouping contiguous disk sectors, simplifying volume management and enhancing read/write performance. This hierarchical structure allows administrators to optimize storage capacity while maintaining data integrity and facilitating easier backups.
Role of Physical Volumes in LVM
In Logical Volume Management (LVM), Physical Volumes (PVs) serve as the basic storage units, representing physical disks or disk partitions that are initialized and used to create Volume Groups (VGs). Unlike standalone disks, PVs abstract the underlying hardware, allowing for flexible allocation and management of storage space across multiple devices. By aggregating PVs into VGs, LVM facilitates dynamic resizing, snapshot creation, and efficient space utilization within Logical Volumes (LVs).
Advantages of Using Physical Volumes Over Disks
Physical volumes offer enhanced flexibility and efficient storage management by enabling dynamic resizing and aggregation of multiple disks into a single logical unit. They support advanced features such as snapshots and volume mirroring, improving data protection and disaster recovery capabilities. Utilizing physical volumes enhances performance through optimized block management and reduces downtime during storage upgrades or maintenance.
Scenarios Where Disks Are Preferred
Disks are preferred in scenarios requiring high capacity storage with cost efficiency, such as bulk data archiving and backup solutions where scalability is critical. They offer straightforward management and compatibility with most operating systems, making them ideal for environments needing rapid deployment and minimal configuration. Physical volumes are less advantageous here due to their complexity and limited flexibility compared to conventional disk storage.
File System Management: Disk vs Physical Volume
Disk refers to the entire storage device that can contain multiple physical volumes, while a physical volume is a partition or segment of the disk designated for specific use within a volume management system. File system management on a disk involves organizing data across partitions, managing metadata, and handling read/write operations to maximize space utilization and performance. Physical volumes enable flexible management by allowing dynamic resizing, pooling, and allocation of storage resources that enhance efficiency in file system operations.
Choosing the Right Storage Approach for Your Needs
Choosing between Disk and Physical Volume for storage depends on factors like flexibility, scalability, and management complexity. Physical Volumes, as part of Logical Volume Management (LVM), offer dynamic resizing, snapshot capabilities, and easier storage pooling compared to traditional disk partitions. Selecting Physical Volumes can optimize resource use and simplify storage administration in environments requiring frequent adjustments and high availability.
Disk Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com