Accounting plays a crucial role in tracking financial transactions, ensuring regulatory compliance, and supporting informed business decisions through accurate financial reporting. Effective accounting practices help you manage budgets, analyze profitability, and plan for future growth. Explore the rest of this article to understand key accounting principles and how they can benefit your business.
Table of Comparison
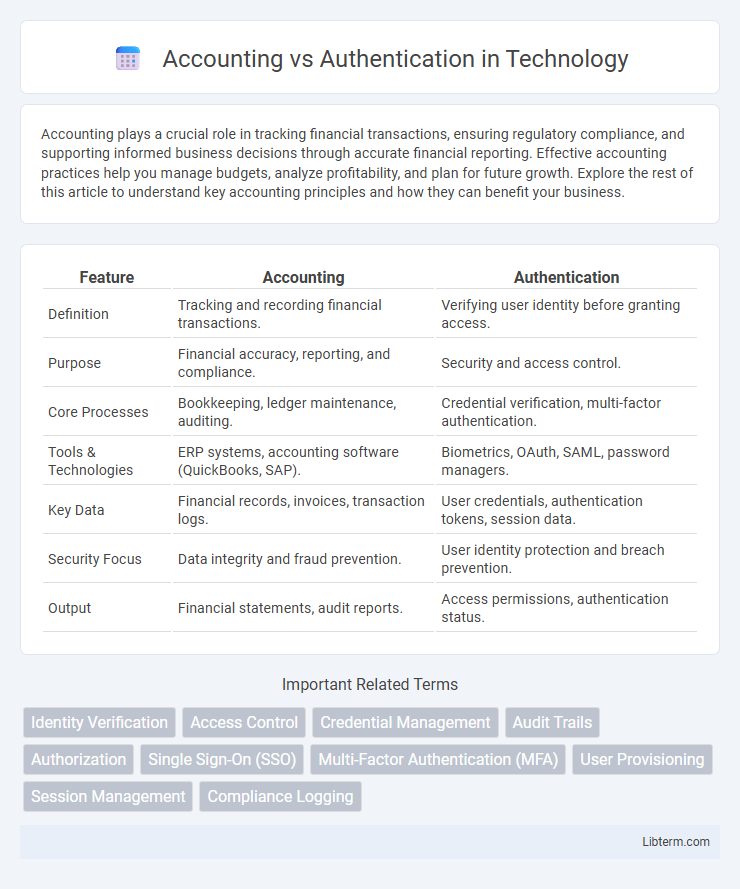
| Feature | Accounting | Authentication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tracking and recording financial transactions. | Verifying user identity before granting access. |
| Purpose | Financial accuracy, reporting, and compliance. | Security and access control. |
| Core Processes | Bookkeeping, ledger maintenance, auditing. | Credential verification, multi-factor authentication. |
| Tools & Technologies | ERP systems, accounting software (QuickBooks, SAP). | Biometrics, OAuth, SAML, password managers. |
| Key Data | Financial records, invoices, transaction logs. | User credentials, authentication tokens, session data. |
| Security Focus | Data integrity and fraud prevention. | User identity protection and breach prevention. |
| Output | Financial statements, audit reports. | Access permissions, authentication status. |
Introduction to Accounting vs Authentication
Accounting involves the systematic recording, reporting, and analysis of financial transactions to ensure accuracy and compliance with regulatory standards. Authentication verifies the identity of users or systems to protect data integrity and prevent unauthorized access in digital environments. Understanding the differences between accounting and authentication is crucial for managing secure and transparent information systems.
Defining Accounting in Information Systems
Accounting in information systems involves tracking and recording user activities, resource consumption, and system usage for auditing, billing, and performance analysis. It enables organizations to monitor access patterns, allocate costs accurately, and ensure compliance with security policies. Unlike authentication, which verifies user identities, accounting focuses on documenting detailed transaction data within network and computing environments.
Understanding Authentication Mechanisms
Authentication mechanisms verify user identities through methods such as passwords, biometrics, or multi-factor authentication to ensure secure access control. These processes establish trust by validating credentials before granting permissions, which is critical in distinguishing legitimate users from unauthorized entities. Unlike accounting, which tracks user activities for audit and billing purposes, authentication solely focuses on identity verification at the access point.
Key Differences Between Accounting and Authentication
Accounting tracks user activities and resource usage within a system, generating logs and reports for monitoring and billing purposes. Authentication verifies the identity of users or devices before granting access to network services or systems, often using credentials like passwords or biometrics. While authentication ensures only authorized users gain entry, accounting records what those users do after access is granted.
Roles of Accounting in Cybersecurity
Accounting in cybersecurity involves tracking user activities, resource usage, and system access to ensure accountability and detect anomalies. It provides detailed logs and reports that support auditing, compliance, and forensic analysis, helping organizations identify unauthorized actions and policy violations. This role complements authentication by validating user identity, while accounting monitors ongoing behavior to maintain security and operational integrity.
Importance of Authentication in Data Protection
Authentication serves as the cornerstone of data protection by verifying user identities to prevent unauthorized access and safeguard sensitive information. Strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), reduce the risk of data breaches and ensure compliance with data security regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Effective authentication enhances overall security frameworks, making it indispensable for maintaining data integrity and confidentiality in any digital environment.
Common Methods Used in Accounting Processes
Common methods used in accounting processes include double-entry bookkeeping, which ensures accuracy by recording transactions in debit and credit accounts, and the use of accounting software like QuickBooks and SAP for automating financial data management. Periodic financial reporting, internal audits, and reconciliations are essential for maintaining compliance and detecting discrepancies. These methods collectively support precise financial record-keeping and decision-making within organizations.
Popular Authentication Techniques and Protocols
Popular authentication techniques include multi-factor authentication (MFA), biometrics, password-based methods, and token-based authentication, which provide secure verification of user identities. Common authentication protocols such as OAuth 2.0, OpenID Connect, SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language), and Kerberos enable seamless and secure access control across diverse platforms. Unlike accounting, which tracks user activities and resource usage, authentication primarily ensures that only authorized users gain access to systems and data.
Challenges in Implementing Accounting and Authentication
Implementing accounting and authentication poses significant challenges due to the complexity of integrating diverse systems and ensuring accurate, real-time data capture without performance degradation. Ensuring secure, scalable authentication methods while maintaining user privacy and compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA adds layers of difficulty. Additionally, balancing the need for detailed accounting logs with minimal impact on network resources often requires sophisticated infrastructure and continuous monitoring.
Best Practices for Balancing Accounting and Authentication
Implementing robust accounting and authentication best practices ensures secure access control while providing precise resource usage tracking. Leveraging multi-factor authentication (MFA) enhances identity verification, whereas real-time accounting systems offer granular monitoring of user activities. Balancing these elements requires integrating adaptive authentication with continuous accounting audits to detect anomalies and maintain compliance effectively.
Accounting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com