Automation streamlines repetitive tasks, boosts efficiency, and reduces human error across various industries. Implementing automation technologies can lower operational costs while increasing productivity and allowing your workforce to focus on higher-value activities. Explore the rest of this article to discover how automation can transform your business and the latest trends shaping its future.
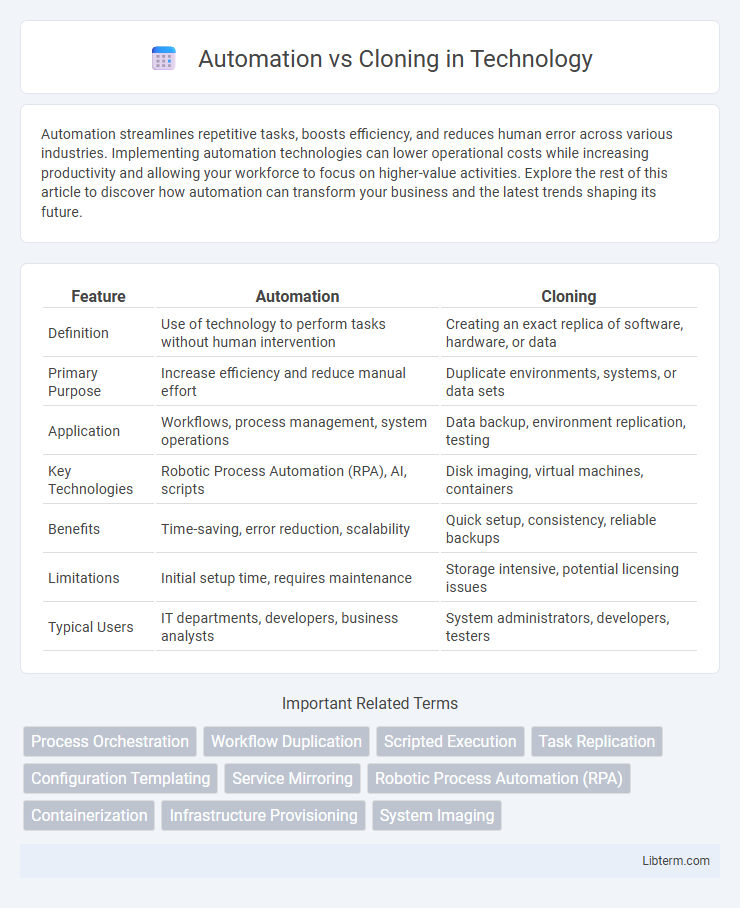
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Automation | Cloning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of technology to perform tasks without human intervention | Creating an exact replica of software, hardware, or data |
| Primary Purpose | Increase efficiency and reduce manual effort | Duplicate environments, systems, or data sets |
| Application | Workflows, process management, system operations | Data backup, environment replication, testing |
| Key Technologies | Robotic Process Automation (RPA), AI, scripts | Disk imaging, virtual machines, containers |
| Benefits | Time-saving, error reduction, scalability | Quick setup, consistency, reliable backups |
| Limitations | Initial setup time, requires maintenance | Storage intensive, potential licensing issues |
| Typical Users | IT departments, developers, business analysts | System administrators, developers, testers |
Understanding Automation: Definition and Scope
Automation involves using technology to perform tasks with minimal human intervention, increasing efficiency and consistency across processes. It encompasses software robots, machine learning algorithms, and control systems designed to execute repetitive or complex functions automatically. Unlike cloning, which replicates biological or digital entities, automation transforms workflows by integrating intelligent tools that optimize performance and reduce manual effort.
What is Cloning? Key Concepts Explained
Cloning refers to creating an exact genetic replica of an organism, cell, or DNA sequence, enabling the production of identical copies with the same genetic material. Key concepts in cloning include reproductive cloning, which produces a new organism, and therapeutic cloning, aimed at generating tissues or cells for medical treatments. Unlike automation, which involves using technology to perform tasks or processes, cloning specifically involves biological replication at the genetic level.
Automation vs Cloning: Core Differences
Automation involves using software or tools to execute repetitive tasks systematically, improving efficiency and reducing human error, while cloning replicates an entire system or environment to create an exact duplicate for testing or deployment purposes. Automation streamlines processes through scripts and predefined actions, whereas cloning copies the complete state of data, configurations, and system settings. The core difference lies in automation enhancing workflow productivity by executing tasks, whereas cloning focuses on duplication for consistency and backup.
Common Use Cases for Automation
Automation is widely used for repetitive tasks such as data entry, process monitoring, and customer support through chatbots, enabling increased efficiency and reduced human error. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines workflows in industries like finance and healthcare by automating invoice processing, claims management, and appointment scheduling. Automation also enhances software testing and deployment, accelerating development cycles and ensuring consistent quality across releases.
Real-World Applications of Cloning
Real-world applications of cloning include therapeutic cloning for regenerating damaged tissues and organs, agricultural cloning to reproduce genetically superior livestock, and conservation efforts to revive endangered species. Cloning enables precise genetic replication, offering solutions in medicine, biotechnology, and environmental management that automation alone cannot achieve. These applications demonstrate cloning's unique role in advancing health treatments, food production, and biodiversity preservation.
Advantages of Automation in Modern Workflows
Automation in modern workflows significantly enhances efficiency by reducing manual errors and accelerating task completion, leading to higher productivity and consistent output quality. It enables seamless integration with diverse software systems, facilitating real-time data processing and dynamic adaptability to changing business demands. Automation also improves scalability and resource allocation, allowing organizations to optimize operational costs while maintaining flexibility in complex environments.
Benefits and Risks of Cloning Technologies
Cloning technologies offer significant benefits such as preserving endangered species, advancing medical research through identical genetic models, and enabling the replication of genetically superior organisms. However, risks include ethical concerns regarding identity and individuality, potential loss of genetic diversity, and the possibility of unforeseen genetic defects or abnormalities. The balance between these benefits and risks necessitates careful regulation and ongoing scientific evaluation to ensure responsible application.
Automation vs Cloning: Ethical Considerations
Automation and cloning raise distinct ethical considerations rooted in their impact on individuality and societal values. Automation prompts concerns about job displacement, accountability in decision-making, and privacy implications, while cloning challenges the notions of identity, genetic integrity, and consent. Evaluating the ethical frameworks for both technologies is crucial to ensure responsible use that respects human dignity and social equity.
Future Trends: Automation and Cloning in Industry
Automation and cloning technologies are driving unprecedented efficiency and customization in industrial processes. Future trends indicate increased integration of AI-powered automation with advanced cloning techniques, enabling rapid replication of complex products and systems. This fusion will transform manufacturing scalability, reduce production costs, and enhance innovation cycles across sectors.
Choosing Between Automation and Cloning: Factors to Consider
Choosing between automation and cloning requires evaluating factors such as scalability, cost efficiency, and complexity of tasks. Automation excels in repetitive, rule-based processes with high scalability potential, while cloning is beneficial for replicating specific configurations or environments quickly. Consider the level of customization needed and the impact on maintenance before deciding the optimal approach for your project.
Automation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com