Modular repositories break down large codebases into smaller, manageable components, enhancing collaboration and scalability. This approach streamlines development workflows and simplifies dependency management across multiple projects. Explore the full article to learn how modular repositories can transform Your development process.
Table of Comparison
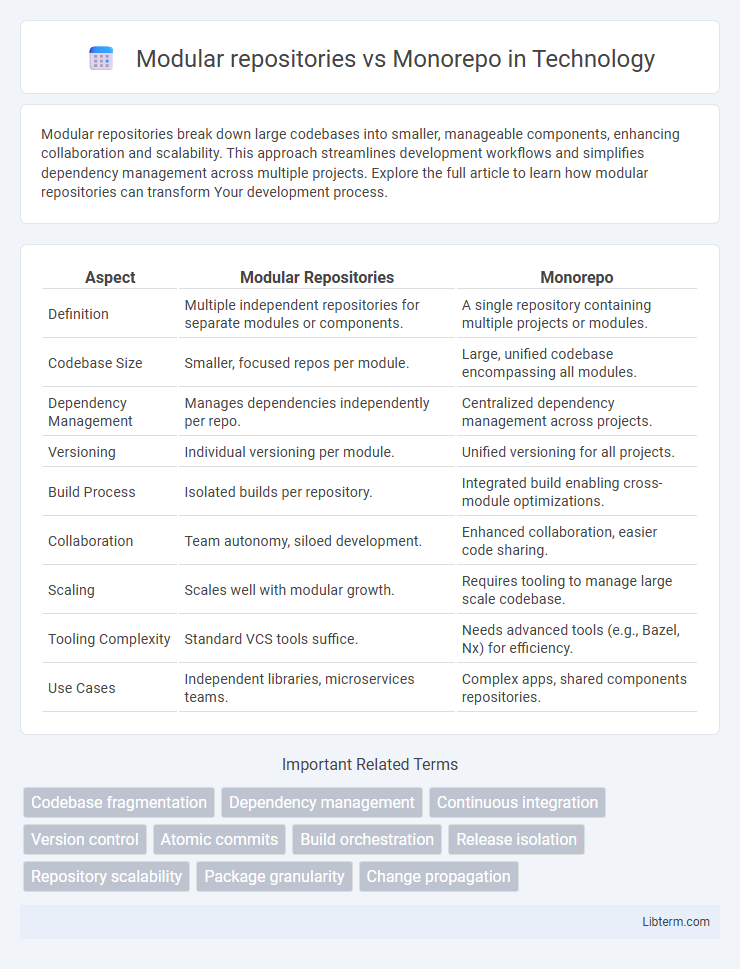
| Aspect | Modular Repositories | Monorepo |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple independent repositories for separate modules or components. | A single repository containing multiple projects or modules. |
| Codebase Size | Smaller, focused repos per module. | Large, unified codebase encompassing all modules. |
| Dependency Management | Manages dependencies independently per repo. | Centralized dependency management across projects. |
| Versioning | Individual versioning per module. | Unified versioning for all projects. |
| Build Process | Isolated builds per repository. | Integrated build enabling cross-module optimizations. |
| Collaboration | Team autonomy, siloed development. | Enhanced collaboration, easier code sharing. |
| Scaling | Scales well with modular growth. | Requires tooling to manage large scale codebase. |
| Tooling Complexity | Standard VCS tools suffice. | Needs advanced tools (e.g., Bazel, Nx) for efficiency. |
| Use Cases | Independent libraries, microservices teams. | Complex apps, shared components repositories. |
Introduction to Codebase Organization
Modular repositories break code into multiple smaller, independent repositories, allowing teams to manage projects with clear boundaries and separate versioning. Monorepo consolidates all codebases into a single repository, facilitating easier cross-project refactoring, unified dependency management, and streamlined CI/CD pipelines. Choosing between modular repositories and monorepos depends on factors like team size, project complexity, and integration needs.
Defining Modular Repositories
Modular repositories organize codebases into independent, self-contained modules stored in separate repositories, enabling isolated development, testing, and deployment cycles. This structure enhances code maintainability, reduces inter-team dependencies, and allows teams to adopt different technologies or versioning schemes per module. In contrast, monorepos consolidate all modules into a single repository, which simplifies integration but can create challenges in scalability and repository management.
Understanding the Monorepo Approach
The Monorepo approach consolidates multiple projects into a single repository, enabling streamlined dependency management and consistent version control across an organization. This approach facilitates atomic commits, easier code sharing, and improved collaboration among development teams by maintaining a unified codebase. Companies like Google and Facebook leverage monorepos to handle vast codebases efficiently, benefiting from integrated tooling and scalable build systems.
Pros and Cons of Modular Repositories
Modular repositories enable independent versioning and deployment, allowing teams to work on isolated components without affecting the entire codebase, which enhances scalability and reduces merge conflicts. However, managing dependencies across repositories can become complex and may lead to duplication or compatibility issues. The separation promotes clear ownership and faster builds but can hinder comprehensive cross-module refactoring and increase overhead in synchronizing changes.
Advantages and Challenges of Monorepos
Monorepos enhance code sharing and collaboration by consolidating multiple projects into a single repository, simplifying dependency management and versioning consistency. They support atomic changes across projects and improve developer productivity through unified tooling and comprehensive code visibility. However, challenges include scaling issues with large codebases, increased build times, and complex access controls, requiring robust infrastructure and sophisticated CI/CD pipelines to maintain efficiency.
Comparing Collaboration and Workflow
Modular repositories enhance collaboration by allowing teams to work independently on isolated codebases, reducing merge conflicts and simplifying version control. Monorepos centralize all projects in a single repository, fostering better visibility and shared code reuse, but require strict coordination to manage complex workflows. Choosing between them depends on the organization's size, project interdependencies, and preferred development practices.
Impact on CI/CD and Deployment
Modular repositories enable independent CI/CD pipelines, reducing build times and isolating deployment risks by targeting specific modules, while monorepos centralize code management, allowing unified testing but often leading to longer build and deployment cycles due to the entire codebase being processed. Monorepos facilitate atomic changes across multiple projects, simplifying dependency management during deployment, but can increase CI/CD complexity and resource consumption. Modular repos enhance scalability and parallel development, promoting faster iteration and more efficient rollback strategies in deployment workflows.
Version Control Strategies
Modular repositories isolate projects into separate version control histories, enabling independent versioning and targeted updates, which reduces conflicts and improves scalability. Monorepos consolidate multiple projects into a single repository, simplifying cross-project refactoring and consistent dependency management while requiring sophisticated tooling for branch management and conflict resolution. Effective version control strategies in monorepos often involve feature branching, commit zoning, and continuous integration to maintain codebase stability across numerous interdependent modules.
Scalability and Maintenance Considerations
Modular repositories enhance scalability by allowing independent development and deployment of components, reducing build times and easing version control complexity. Monorepos centralize code management, which simplifies dependency updates and enforces consistency but may suffer from slower build processes and larger codebase challenges. Maintenance in modular repositories benefits from isolated changes and targeted testing, while monorepos require robust tooling to manage scale yet provide unified workflow and integrated refactoring capabilities.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Project
Choosing between modular repositories and a monorepo depends on project scale, team size, and collaboration requirements. Modular repositories offer granular control, making them ideal for smaller teams or independent services with distinct lifecycles. Monorepos streamline dependency management and code sharing, benefiting large projects with tight integration and frequent cross-team collaboration.
Modular repositories Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com