OAuth is an open-standard authorization protocol enabling secure third-party access to your web resources without sharing passwords. It allows users to grant limited access to their accounts on one site to another, enhancing security and user convenience. Discover how OAuth can protect your online identity and simplify authentication in the full article.
Table of Comparison
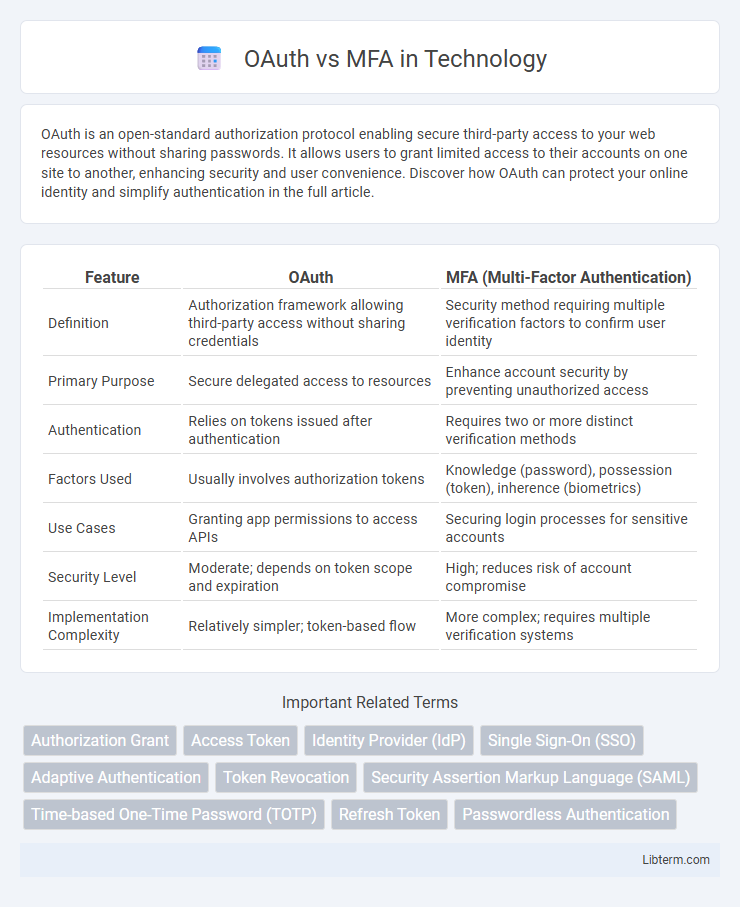
| Feature | OAuth | MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Authorization framework allowing third-party access without sharing credentials | Security method requiring multiple verification factors to confirm user identity |
| Primary Purpose | Secure delegated access to resources | Enhance account security by preventing unauthorized access |
| Authentication | Relies on tokens issued after authentication | Requires two or more distinct verification methods |
| Factors Used | Usually involves authorization tokens | Knowledge (password), possession (token), inherence (biometrics) |
| Use Cases | Granting app permissions to access APIs | Securing login processes for sensitive accounts |
| Security Level | Moderate; depends on token scope and expiration | High; reduces risk of account compromise |
| Implementation Complexity | Relatively simpler; token-based flow | More complex; requires multiple verification systems |
Introduction to OAuth and MFA
OAuth is an open standard for secure authorization that allows third-party applications to access user resources without sharing passwords, using access tokens for limited permissions. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) enhances security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors from categories like knowledge, possession, or inherence before granting access. Implementing OAuth alongside MFA strengthens identity verification and protects sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Defining OAuth: What Is It?
OAuth is an open standard for access delegation commonly used to grant websites or applications limited access to user information without exposing passwords. It enables third-party services to securely access resources on behalf of a user through token-based authentication. Unlike Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), which enhances security by requiring multiple verification methods, OAuth primarily facilitates authorization with streamlined user consent.
Understanding Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) enhances security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors, such as something they know (password), something they have (a smartphone or hardware token), or something they are (biometric data). Unlike OAuth, which is an authorization protocol allowing third-party applications limited access to user data without sharing credentials, MFA protects user accounts by preventing unauthorized access even if one factor is compromised. Implementing MFA significantly reduces the risk of breaches caused by stolen or weak passwords, strengthening overall identity verification processes.
Key Differences Between OAuth and MFA
OAuth is an authorization protocol that enables third-party applications to access user resources without sharing passwords, primarily focusing on delegated access. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) enhances security by requiring users to verify identity using two or more authentication factors, such as passwords, biometrics, or one-time codes. OAuth manages access permissions between services, while MFA strengthens the login process by adding layers of user verification.
OAuth Use Cases and Applications
OAuth enables secure delegated access by allowing users to grant third-party applications limited permissions without sharing authentication credentials. Common use cases include social login integration, where users authenticate through platforms like Google or Facebook, and API authorization for applications requiring controlled access to user data. OAuth is essential in mobile and web applications for seamless, secure access to resources across services while maintaining user privacy and security.
MFA Use Cases and Applications
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) enhances security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple independent credentials, such as passwords, biometrics, or hardware tokens, making it essential for sensitive environments like online banking, healthcare systems, and corporate networks. MFA is widely applied in preventing unauthorized access in cloud services, VPNs, and identity management platforms, significantly reducing risks of phishing and credential theft. Unlike OAuth, which delegates access authorization between applications, MFA focuses on strengthening user authentication to ensure secure login processes across diverse applications and devices.
Security Strengths: OAuth vs MFA
OAuth provides secure delegated access by allowing third-party applications to access user resources without sharing credentials, reducing risks related to password exposure. MFA enhances security strength by requiring multiple verification factors, significantly decreasing the likelihood of unauthorized access even if one factor is compromised. Combining OAuth with MFA creates a robust security framework by protecting both authentication and authorization processes against various cyber threats.
Combining OAuth and MFA for Enhanced Security
Combining OAuth and MFA significantly enhances cybersecurity by integrating secure authorization with multi-factor authentication's robust identity verification. OAuth facilitates delegated access to resources through access tokens while MFA adds an additional verification layer, reducing the risk of unauthorized access even if OAuth tokens are compromised. Implementing OAuth with MFA ensures both secure resource authorization and strong user authentication, strengthening protection against credential theft and phishing attacks.
Common Misconceptions About OAuth and MFA
OAuth is often mistakenly confused with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), but OAuth is actually an authorization framework that enables third-party applications to access user data without sharing passwords. MFA enhances security by requiring multiple verification methods, such as passwords and biometric factors, which is separate from OAuth's role in delegated access. Understanding that OAuth controls access permissions while MFA focuses on authentication layers is crucial for effective cybersecurity implementation.
Choosing the Right Authentication Method for Your Needs
OAuth provides secure delegated access by allowing users to authorize third-party applications without sharing passwords, ideal for service integration and API access. MFA enhances security by requiring multiple forms of verification such as passwords, biometrics, or tokens, offering stronger protection against unauthorized access. Choosing between OAuth and MFA depends on specific needs: OAuth excels in user convenience and delegated permissions, while MFA is preferred for high-security environments requiring robust identity verification.
OAuth Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com