User space refers to the memory area where application software and user processes run, isolated from the kernel space to maintain system stability and security. Understanding user space is crucial for optimizing program performance and managing system resources efficiently. Explore the rest of the article to learn how user space impacts your computing experience and application development.
Table of Comparison
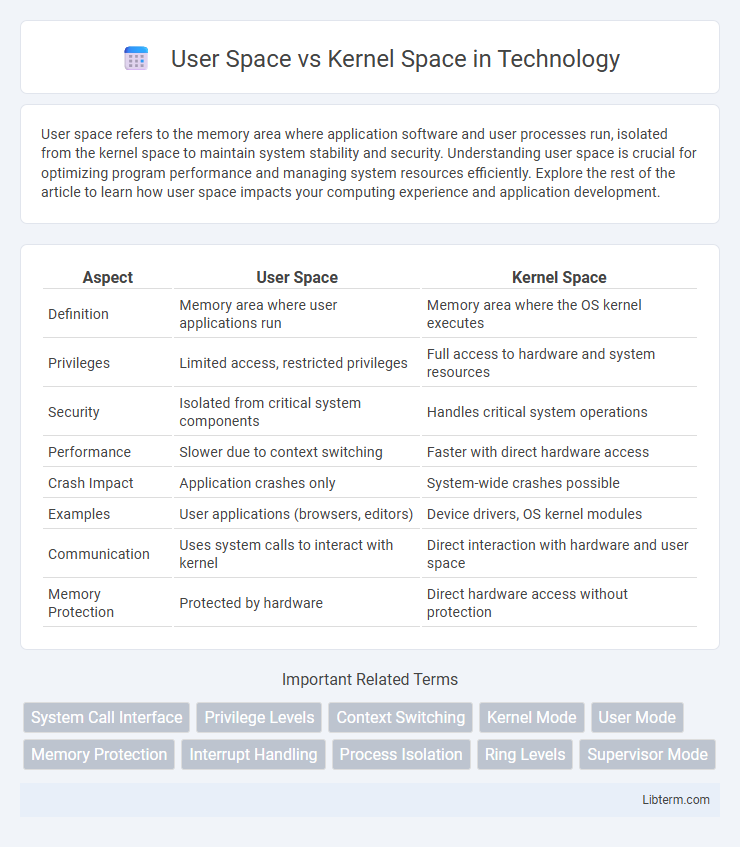
| Aspect | User Space | Kernel Space |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Memory area where user applications run | Memory area where the OS kernel executes |
| Privileges | Limited access, restricted privileges | Full access to hardware and system resources |
| Security | Isolated from critical system components | Handles critical system operations |
| Performance | Slower due to context switching | Faster with direct hardware access |
| Crash Impact | Application crashes only | System-wide crashes possible |
| Examples | User applications (browsers, editors) | Device drivers, OS kernel modules |
| Communication | Uses system calls to interact with kernel | Direct interaction with hardware and user space |
| Memory Protection | Protected by hardware | Direct hardware access without protection |
Introduction to User Space and Kernel Space
User space and kernel space are two distinct memory areas in an operating system that separate regular application processes from core system functions. User space is where all user applications run with restricted access, ensuring system protection and process isolation. Kernel space operates with full system privileges, managing hardware interaction, memory management, and process control to maintain system stability and security.
Defining User Space
User space refers to the memory area where application software and user-level processes execute, isolated from the operating system kernel to ensure system stability and security. It enables programs to run with restricted privileges, preventing direct hardware access, which minimizes the risk of system crashes or unauthorized operations. This separation between user space and kernel space is fundamental to modern operating systems' design, facilitating controlled interaction through system calls.
Defining Kernel Space
Kernel space is a protected memory area where the operating system kernel executes and provides essential services like process management, memory management, and hardware control. This privileged mode allows direct access to system resources, ensuring security and stability by isolating kernel operations from user applications. By preventing user space programs from executing kernel code directly, kernel space enforces strict boundaries that safeguard against accidental or malicious system interference.
Key Differences Between User Space and Kernel Space
User space operates with limited privileges, isolating applications from direct hardware access, while kernel space has full control over the system hardware and manages critical processes. Memory protection distinguishes them, as user space processes cannot directly access kernel memory, preventing unauthorized operations and system crashes. The boundary between them ensures stability and security by handling system calls as controlled gateways for communication between user applications and hardware.
How User Space Interacts with Kernel Space
User space interacts with kernel space primarily through system calls, which act as controlled gateways allowing user applications to request services like file operations, memory management, and device communication from the kernel. When a system call is invoked, the CPU switches from user mode to kernel mode, enabling the kernel to execute privileged instructions and securely manage hardware resources. This separation ensures stability and security by preventing direct access to critical system components while facilitating essential interactions between applications and the operating system.
Importance of Separation: Security and Stability
Separation between user space and kernel space is crucial for maintaining system security by preventing user applications from directly accessing critical kernel resources and compromising the entire operating system. This division ensures stability by isolating user-run processes from the core system operations, reducing the risk of crashes caused by faulty or malicious software. Kernel space handles privileged tasks such as hardware management and system calls, while user space operates applications with restricted access, creating a controlled environment that enhances overall system integrity.
System Calls: Bridging User and Kernel Space
System calls serve as the critical interface bridging user space and kernel space, enabling user applications to request essential services from the operating system kernel. When a system call is invoked, the processor transitions from user mode to kernel mode, granting the kernel access to protected resources and hardware. This controlled mechanism ensures secure communication while maintaining system stability and isolating user processes from direct kernel manipulation.
Examples of User Space and Kernel Space Processes
User space processes include web browsers like Chrome, text editors such as Microsoft Word, and media players like VLC, all operating with limited privileges to ensure system stability. Kernel space processes involve critical system functions like the Linux kernel scheduler, device drivers managing hardware communication, and memory management modules controlling virtual memory. These kernel components have unrestricted access to system resources, providing essential services for user space applications.
Performance Considerations in User vs Kernel Space
User space operations involve less privilege and reduced risk, but they cause performance overhead due to context switches between user and kernel modes. Kernel space executes with higher privileges and direct hardware access, enabling faster operations but increasing complexity and risk. Minimizing user-kernel transitions optimizes system performance by reducing latency and CPU utilization.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Space for Applications
Selecting between user space and kernel space depends on security, stability, and performance requirements of applications. User space offers better protection and easier debugging by isolating processes, ideal for most application-level tasks. Kernel space provides direct hardware access and higher efficiency but risks system stability if mismanaged, making it suitable for critical system components and device drivers.
User Space Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com